
This is the reason why self-service checkouts are fitted with mirrors
With the increasing number of self-service checkout machines popping up in stores for convenience, there is one simple feature that is used to put off potential shoplifters - mirrors. There's a good chance that you've looked at your reflection in the screens fitted to these machines, and the purpose of it is for potential shoplifters to catch themselves in the mirror in the hopes of making them feel guilty. This pang of a guilty conscience is hoped to prevent them from committing any crime (it's not just there for vanity purposes like most of us use it for). Research also backs up the theory that people who see themselves in a mirror are less likely to do something bad. A 1976 study from Letters of Evolutionary Behavioural Science found that when people are around mirrors, they "behave in accordance with social desirability". "Mirrors influence impulsivity, a feature that is closely related to decision-making in both social and non-social situations." When participants in the experiment were looking at mirrors, their "private self-awareness was activated" by them and as a result influenced "decision-making as a non-social cues". Similarly, Psychology Today notes how a mirror allows "people to literally watch over themselves" and this "dramatically boosts our self-awareness". Meanwhile, the issue of self-service checkouts and shoplifting was highlighted in a report by Mashed last year which it appeared to confirm that Walmart's attempt at combatting this problem was a psychological method with the addition of mirrors (though Walmart, alongside other supermarkets, has never confirmed the purpose of their mirrors at their self-service checkout services). Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-09 18:15
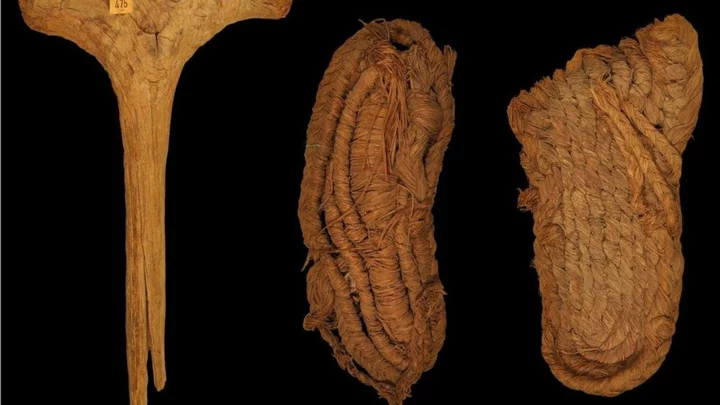

Prehistoric footwear dating back 6,200 years discovered in a Spanish cave
A pair of shoes thought to be the oldest ever found in Europe are now estimated to be even older than scientists had previously thought. About 20 pairs of sandals found in southern Spain are at least 6,200 years old, while other woven objects found in the cave date back 9,500 years, according to a new study. The scientists used carbon-dating on 76 objects found in the Cueva de los Murciélagos, Albuñol, near Granada, which were originally discovered by miners in the 19th century. The objects are particularly valuable to science because they represent the first direct evidence of certain hunter-gatherer skills, such as weaving, in southern Europe. They are made of wood, reed and esparto grass. The shoes measured about eight inches in length. The study was published in the journal Science Advances by a team from the Universidad de Alcalá (UAH) and the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB). Francisco Martínez Sevilla, a researcher at the Prehistory Department of UAH, said: “These are the earliest and widest-ranging assemblage of prehistoric footwear, both in the Iberian Peninsula and in Europe, unparalleled at other latitudes. “The new dating of the esparto baskets from the Cueva de los Murciélagos of Albuñol opens a window of opportunity to understanding the last hunter-gatherer societies of the early Holocene. “The quality and technological complexity of the basketry makes us question the simplistic assumptions we have about human communities prior to the arrival of agriculture in Southern Europe.” He said the project placed the cave as “a unique site in Europe to study the organic materials of prehistoric populations”. Cueva de los Murciélagos, or “Cave of the Bats,” is located on the coast of Granada, to the south of the Sierra Nevada. The finds are thought to have been so well-preserved because of low humidity levels in the area. Study co-author María Herrero Otal added: “The esparto grass objects from Cueva de los Murciélagos are the oldest and best-preserved set of plant fibre materials in Southern Europe so far known. “The technological diversity and the treatment of the raw material documented demonstrates the ability of prehistoric communities to master this type of craftsmanship, at least since 9,500 years ago, in the Mesolithic period. “Only one type of technique related to hunter-gatherers has been identified, while the typological, technological and treatment range of esparto grass was extended during the Neolithic from 7,200 to 6,200 years before the present.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-09 17:57

Archaeologists have just found a rare 18th-century cold bath
Archaeologists have found a rare cold bath below the 18th-century Bath Assembly Rooms. The rooms, completed in 1771, were fashionable places of entertainment, conversation, dancing and gambling and cold baths were seen as good for people's health. The cold bath is in the centre of a suite of three rooms beneath one end of the ballroom. It has dressing rooms on either side. The excavation involved removing a later floor that had been installed over the cold bath and removing tonnes of rubble to reveal steps down into it. Bruce Eaton, of Wessex Archaeology, which oversaw the excavation, told the Guardian: “Although historical records indicated that there was a cold bath buried beneath the Bath Assembly Rooms, we had no idea what preservation of the bath would be like. “The building suffered damage at the hands of the Luftwaffe and the rooms were remodelled in the late 20th century but, after carefully excavating tonnes of concrete and rubble, we saw the original structure emerge in its entirety. “It’s tremendous to be able to piece together this rare archaeological evidence of an 18th-century cold bath with social historical accounts from the time.” Tatjana LeBoff, a project curator at the National Trust, said: “The cold bath at the assembly rooms is highly unusual. It is a rare, if not unique, surviving example, and possibly it was the only one ever built in an assembly room.” The trust was researching records, letters, diaries and other documents to discover more about the cold bath, she said. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-09 16:47
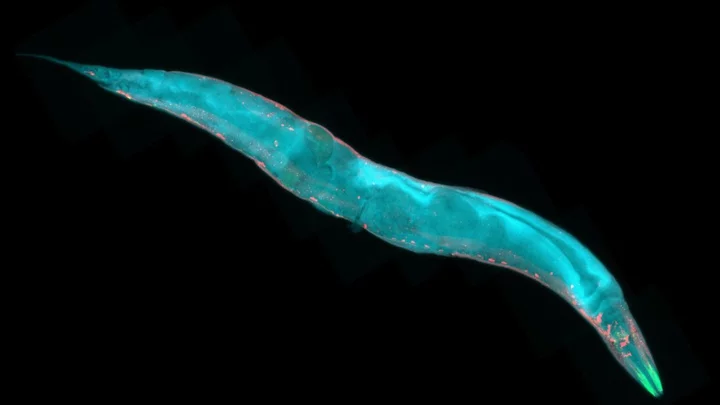
Study suggests even basic worms can experience human-like emotions
Everybody hurts sometimes – even the most basic worms in the animal kingdom which have no eyes, spine or brain. That’s what scientists have found out about nematode species Caenorhabditis elegans, which possesses basic emotions such as fear. Researchers zapped the worms to see if they would display negative reactions, and the worms continued to “flee” at high speeds for minutes after. The scientists at Nagoya City University in Japan and Northeastern University in the US said the response shows a brain state which is comparable to fear in humans. "These properties have been recently regarded as essential features of emotion, suggesting that C. elegans response to electric shock may reflect a form of emotion, akin to fear," the researchers wrote. The findings are the most recent in a debate over which animals can experience primitive versions of our own emotions. Crayfish and bumblebees have all shown animals can have lasting positive and negative mental states. C. elegans is one of the most basic worms in the animal kingdom. At about 1mm in length it is also tiny and transparent, with no brain, sight or smell. Nonetheless, worms which sensed an electric current for 45 seconds “ran away” for more than two minutes. During this state, they ignored food which was placed nearby, instead scurrying at high speeds. This suggests that the emotional response could be triggered by different stimuli and that one stimulus could inhibit responses to others. When the shock was just five seconds long, the worms fled for a minute and a half before calming down. And when the researchers repeated the experiments with worms that were not to produce neuropeptides – which are the equivalent to human hormones – the worms stayed in a state of fear for longer. "Because the requirement of neuropeptide signaling [in worms] is reminiscent of neuropeptide regulation of fear in mammals including humans, the fear-like brain state may be regulated by evolutionarily conserved molecular mechanisms," the authors of the study wrote. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-08 18:17

5 times celebrities have spoken out against AI deepfakes
Deepfakes are becoming an increasing concern online with many celebrities and influencers' faces fronting fake scams – and in more sinister cases, NSFW material. For the blissfully unaware, a deepfake is a digitally altered piece of content, often without concern. They're often used with malicious intent for financial gain or to spread false information. The surge in deepfakes has prompted many high profilers to come forward and speak out including MrBeast and Tom Hanks: Martin Lewis The nation's favourite money-saving expert issued a warning over a "disgraceful" scam that could lead vulnerable people to lose money. Lewis said people are using the technology to "pervert and destroy" his reputation to scam people. An advert, which circulated online earlier this year, appeared to show Lewis endorsing an Elon Musk-backed investment scheme. "Musk’s new project opens up new opportunities for British citizens. No project has ever given such opportunities to residents of the country," the AI version of Lewis says in the footage. The real Lewis later told the BBC "it's pretty frightening." He continued: "These people are trying to pervert and destroy my reputation in order to steal money off vulnerable people, and frankly, it is disgraceful, and people are going to lose money and people’s mental health are going to be affected." MrBeast The popular YouTuber took to X/Twitter to address a deepfake video that went viral online. "Lots of people are getting this deepfake scam ad of me… are social media platforms ready to handle the rise of AI deepfakes? This is a serious problem," he posted to the platform. MrBeast included a clip that has been circulating online, that shows an AI version of him saying he's giving away iPhones. "You’re one of the 10,000 lucky people who will get an iPhone 15 pro for just $2," the deceiving clip said. "I’m MrBeast and I am doing the world’s largest iPhone 15 giveaway." Tom Hanks Hanks was forced to issue a warning over a deepfake advert promoting a dental plan using his presence. In a post to Instagram, Hank shared a screenshot of the ad, with overlaid text reading: "BEWARE!! There’s a video out there promoting some dental plan with an AI version of me. I have nothing to do with it." Nicki Minaj In a much lighter incident, the rapper was featured in ITV's Deep Fake Neighbour Wars. The programme showed an AI version of Minaj and her 'husband,' Tom Holland. Upon arriving home from their honeymoon, they found an intruder in their living room, Mark Zuckerberg. It plays on an internet rumour that joked Minaj and Holland were dating and expecting a baby in 2019. At the time, the actor joked to Esquire: "This actually really stressed me out... and then I realised I've never met Nicki Minaj. So that was a big relief for me because I'm not ready to have kids." She wrote: "HELP!!! What in the AI shapeshifting cloning conspiracy theory is this?!?!! I hope the whole internet get deleted!!!" Streamer Sweet Anita Meanwhile, popular streamer Sweet Anita was horrified to learn she was targeted by deepfake porn without her consent. "It has all the same consequences of revenge porn, and so now I will be living those consequences for a choice I never made," Sweet Anita told ITV. The streamer said the situation has made her "tired" and heightened her security fears. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-08 17:28

Scholar dedicated his career to arguing that Jesus was a hallucinogenic mushroom
Since the 1960s, one scholar has dedicated his career to arguing that Jesus was not a living man, but in fact a mushroom. John Marco Allegro was one of the first scholars permitted to decipher the ancient documents now known as the Dead Sea Scrolls, that were discovered in 1947 in the Judean Desert. They contained the oldest surviving versions of books that would later be incorporated into the biblical canon. Allegro and his colleagues were the first to go about making sense of the documents, as they were obviously discovered untranslated, eventually publishing the texts after hard work and disagreements. Allegro then went on to write two more books on the subject in 1958, The Dead Sea Scrolls and The People of the Dead Sea Scrolls, which remain extremely influential. Then in 1970 and again in 1979, Allegro published two more books. These expanded on his idea that Christianity was a cover for a secret cryptic sex cult generated by people under the influence of Amanita muscaria, more commonly known as Fly agaric. And that Jesus was a metaphor for the fungus and its influences. Using etymology, Allegro argued that early Christianity was created by an Essene cult that recorded their practices through the texts of the New Testament. And that evangelists misunderstood the text's true meaning when they transcribed it. There was never a man called Jesus, only a cult that used mushrooms to have hallucinations. He also argued that the God of the Old Testament was "a mighty penis in the heavens who in a thunderous climax of the storm ejaculated semen upon the furrows of Mother Earth." Allegro's views were not well received, with some believing he created the argument as revenge against Christian critics who dismissed his earlier translations of the Dead Sea Scrolls, whilst some believed he just ran away with the wrong idea. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-08 00:22
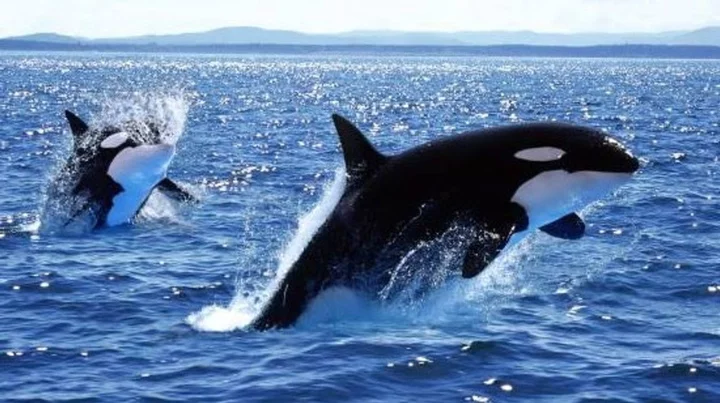

Orcas have been bullying porpoises for years – and scientists are baffled
An orcas diet consists of Chinook salmon and can eat up to two dozen fish a day - so why is it that the killer whales like to bully porpoises despite them not being part of their diet? That's the question which has left scientists scratching their heads, as the study published in Marine Mammal Science seeks to add further understanding to this subject. Around 78 cases of orcas targeting porpoises were noted by researchers from the UK, USA and Canada. It was said to be happening in the Salish Sea (located in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington). Some of the orcas' bullying tactics include pushing the porpoise along with their nose, holding the porpoise in their mouth, balancing the porpoise above water, slapping the porpoise with their tail, and raking the porpoise with their teeth, according to Science Alert. Killer whales also use porpoises as playthings as they catch them before letting them and proceeding to chase them once more - and they even play toss them around in a 'pass the porpoise' game, say whale watchers. That's some textbook tormenting. Out of these sightings, 28 of them have ended in the harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) or a Dall's porpoise being suspected to have been killed, though there's no record of the porpoises being eaten by the orcas. In terms of size, the porpoise is said to be fairly small being a similar size to a Chinook salmon - a large fish species that can grow up to 1.5 meters (5 feet). There are three theories that have been considered by the experts. Firstly, the bullying is all about creating coordination, and cohesion within the group of orcas, or alternatively that the orcas do this as a form of hunting practice. The final theory is that orcas could be trying to look after weak porpoises as if they were their own aka 'displaced epimeletic behaviour.' This mismothering behaviour – also known as 'displaced epimeletic behaviour' to scientists – might be due to their limited opportunities to look after youngsters as the stat shows. "Our research has shown that due to malnutrition, nearly 70 per cent of Southern Resident killer whale pregnancies have resulted in miscarriages or calves that died right away after birth." It seems that orcas are not the only bullies of the seas, as smaller dolphins e.g. bottlenose have similarly been seen harassing and killing for no clear reason. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-07 15:51

Scientists are using AI to develop simple test to search planets for alien life
Scientists are using AI to search planets for alien life. Researchers writing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences say artificial intelligence can determine with 90 per cent accuracy whether a sample from another planet is biological or not. Scientists hope that their test could be used on samples already collected by the Mars Curiosity rover’s Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument. The findings could also help tell us more about our own planet, revealing the history of mysterious and ancient rocks found on Earth. “The search for extraterrestrial life remains one of the most tantalizing endeavors in modern science,” said lead author Jim Cleaves of the Earth and Planets Laboratory, Carnegie Institution for Science, Washington, DC. “The implications of this new research are many, but there are three big takeaways: First, at some deep level, biochemistry differs from abiotic organic chemistry; second, we can look at Mars and ancient Earth samples to tell if they were once alive; and third, it is likely this new method could distinguish alternative biospheres from those of Earth, with significant implications for future astrobiology missions.” The technique was built by giving an artificial intelligent system data about 134 known samples, with information about whether they are biotic or abiotic. To test it, it was then given new samples – including those from living things, remnants of ancient life and other abiotic samples that did not point to life, such as pure chemicals. The system also started predicting another kind of sample type, dividing the biotic ones into “living” and “fossils”. That means it could tell the difference between a freshly harvested leaf and something else that died long ago, for instance. In the future, the technology could become even more advanced and detect other aspects of life. “This routine analytical method has the potential to revolutionize the search for extraterrestrial life and deepen our understanding of both the origin and chemistry of the earliest life on Earth,” said Robert Hazen, of the Carnegie Institution for Science, one of the leaders of the research. “It opens the way to using smart sensors on robotic spacecraft, landers and rovers to search for signs of life before the samples return to Earth.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-06 20:46
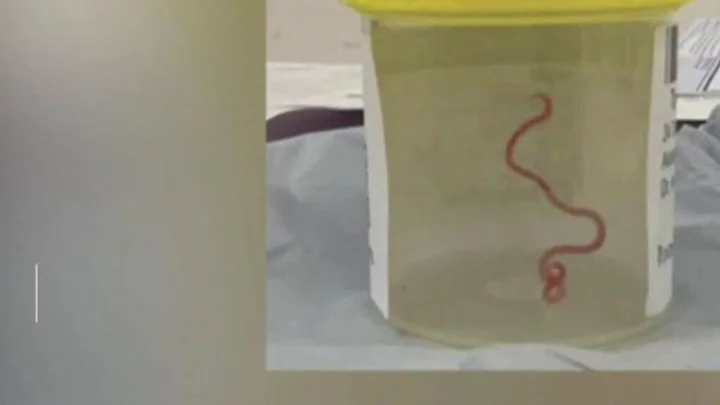

Scientists solve 5-year mystery of tiny unidentified 'sea creature'
Scientists have got to the bottom of a 5-year mystery after finally identifying a tiny sea creature captured on camera in 2018. It is the latest in a series of oceanic discoveries and experts recently observed “zombie worms” devour an alligator in an incredible experiment. For the tiny creature, the baffling question of its identity took a team of zoologists and parasitic worm specialists to solve after the small creature was pictured by an underwater photographer in 2018 off the coast of Okinawa in Japan. After photographer Ryo Minemizu captured the image, he shared it on social media asking the hive mind if they knew what the creature was, but everyone was left stumped. Minemizu was determined not to give up and instead went back to the area and was able to capture another ladybird-sized creature that was the same, or very similar, to the original one he had come across. The research team that was interested in identifying the sea creature approached him and Minemizu sent them the sample to research. Your browser does not support the video tag. Current Biology (2023) The team’s results were published in the Current Biology journal putting an end to the 5-year long mystery baffling experts. In a fascinating twist, the team found that the sample was not one, but two creatures that were clinging tightly to one another. Both were identified as types of cercariae parasitic larvae worms, with experts dubbing one as the “sailor” and the other as a “passenger” thanks to how they behave when they are connected. Passengers were much smaller than the sailors and when they were bonded together, they formed a flat-topped hemisphere shape. They squeeze their bodies together with heads facing the inside of the sphere, meanwhile, their tails latch onto one another. Experts believe the two individual creatures have created a colonial organism that suits both of their needs and according to the study's authors, “represents the first case of labor division in digenean larvae”. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-05 23:26
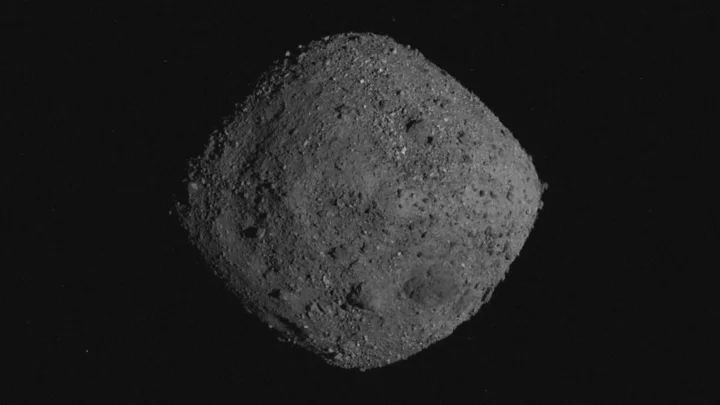

Scientists weren't expecting what they found when they opened up the Bennu asteroid capsule
In late September, scientists at NASA and around the world eagerly awaited the arrival of the OSIRIS-REx capsule containing a sample of the asteroid Bennu. The capsule safely landed on Earth on Sunday 24 September in a Utah desert containing a sample of the asteroid Bennu – categorised as one of the two “most hazardous known asteroids”. When the capsule was first opened, it sparked audible gasps from scientists. Since its arrival, NASA has kept its cards fairly close to its chest but a new blog post from the space agency suggests that progress is going slowly for the “best reason” as there is more sample material than they had anticipated. They explained: “The abundance of material found when the science canister lid was removed earlier this week has meant that the process of disassembling the TAGSAM (Touch-and-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism) head – which holds the bulk of material from the asteroid – is off to a methodical start.” The OSIRIS-REx’s mission took 7 years to complete, with the sample currently being analysed by NASA taken three years ago before making its way down to Earth. Imagery from the moment the sample was taken confirmed to scientists that there would be asteroid material where they found it, but the quantity of dark particles were far more than they had anticipated. “The very best ‘problem’ to have is that there is so much material, it’s taking longer than we expected to collect it,” said deputy OSIRIS-REx curation lead Christopher Snead of NASA’s Johnson Space Center. “There’s a lot of abundant material outside the TAGSAM head that’s interesting in its own right. It’s really spectacular to have all that material there.” In the coming weeks, experts will continue to work through the particles and begin the complex process of carefully disassembling the TAGSAM to reach the bulk of the Bennu sample inside. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-05 22:59
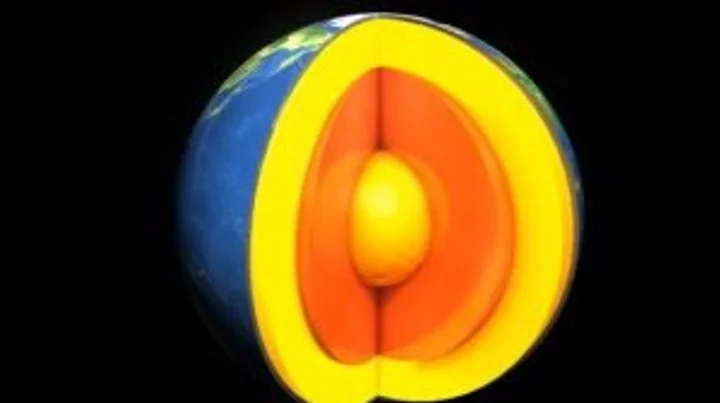

Scientists shed surprising new light on the Earth's 'butter-like' inner core
For centuries we’ve been told that the Moon is made of cheese but now, it turns out, the Earth is more like butter. Or, at least, its inner core is. A new study led by experts at the University of Texas (UT) and collaborators in China found that iron atoms at the very centre of our world move around much more than previously thought, and the implications could be huge. Scientists have long sought to dissect the insides of our planet but it isn’t easy, given that we have no way of directly exploring its core. The deepest hole humans have ever dug – branded the "entrance to hell" – extended an impressive 12,263m (40,230ft) down, but even that doesn’t come close to breaking through the crust to the layers beneath. Still, thanks to techniques like seismic tomography – which analyses how waves of energy travel through different materials during earthquakes – we’ve been able to map out the world’s interior. Now, researchers have used lab experiments and AI algorithms to shed a striking new light on the heart of the planet. "Seismologists have found that the centre of the Earth, called the inner core, is surprisingly soft, kind of like how butter is soft in your kitchen," Youjun Zhang, a Sichuan University professor who co-led the investigation, said in a statement shared with Phys.org. "The big discovery that we've found is that solid iron becomes surprisingly soft deep inside the Earth because its atoms can move much more than we ever imagined. This increased movement makes the inner core less rigid, weaker against shear forces." The findings are significant because they could help explain the role that the inner core plays in generating the world’s magnetic field. They could also help us understand a number of the inner core’s key properties, which have long flummoxed experts. "Now, we know about the fundamental mechanism that will help us with understanding the dynamic processes and evolution of the Earth's inner core," Jung-Fu Lin, one of the study's lead authors, explained. Given that it is impossible for scientists to directly extract specimens from the inner core, Lin and his colleagues recreated it in miniature. They took a small iron plate, shot it with a fast-moving projectile, and collected the resulting temperature, pressure and velocity data, which they then fed into an AI computer model. Using this machine learning system, they were able to scale up the sample iron atoms configuration to mimic the atomic environment within the inner core. At this beefed-up scale, the researchers observed groups of atoms moving about while still maintaining their overall structure. Inner Core iron atom motion model University of Texas This movement could explain why seismic measurements of the inner core reveal an environment that's softer and more malleable than would be expected at such pressures, Prof Zhang explained. Around half of the energy that goes into generating the Earth's magnetic field can be attributed to the inner core, with the rest coming from the outer core, according to the UT team. Thanks to Zhang, Lin and their colleagues, we now have a clearer understanding of the inner core’s machinations at an atomic level, which could help inform how energy and heat are generated at the heart of the planet. This could also shed light on how the inner and outer core work together to generate the Earth’s magnetic field – a key ingredient in making a planet habitable. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-05 19:17

Scientists believe vegetarianism could be in your DNA
Vegetarianism may be written in your DNA, a study has found. According to new research which analysed 5000 vegetarians and 300,000 meat eaters, there are genes associated with how well someone is able to adhere to a vegetarian lifestyle. Researchers identified three genes that are strongly identified and another 31 that are potentially identified with vegetarianism. In a genetic analysis, the researchers saw that vegetarians are more likely than non-vegetarians to have different variations of these genes. This might be because of how different people process lipids, or fats. Several of the genes that the study found to be associated with vegetarianism had to do with metabolising lipids and given plants and meat differ in the complexity of their lipids, it may be that some people genetically need some lipids offered by meat. “At this time we can say is that genetics plays a significant role in vegetarianism and that some people may be genetically better suited for a vegetarian diet than others,” said lead study author Dr. Nabeel Yaseen, professor emeritus of pathology at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine. “A large proportion of self-described vegetarians actually report consuming meat products when responding to detailed questionnaires,” he said. “This suggests that many people who would like to be vegetarian are not able to do so, and our data suggest that genetics is at least part of the reason.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-05 16:22
