
Eating strawberries can reduce the risks of dementia, study finds
A recent study has found that eating strawberries daily could reduce the risk of developing dementia. Researchers at the University of Cincinnati claim that by eating the fruit every day, certain people of middle age could reduce their risk of dementia. The 12-week study published in Nutrients had 30 overweight patients - who had complained of mild cognitive impairment - abstain from eating berries, aside from a daily packet of supplement powder mixed with water and consumed with breakfast. Half of the participants, who were 50 to 65 years old, received a powder that contained the equivalent of one cup of whole strawberries (the standard serving size), whilst the other half received a placebo. Participants' long-term memory, mood, and metabolic health were measured by researchers. The team found that those who had taken the strawberry powder had performed better on a wordlist learning test, as well as having a significant reduction in depressive symptoms. "Both strawberries and blueberries contain antioxidants called anthocyanins, which have been implicated in a variety of berry health benefits such as metabolic and cognitive enhancements," said Robert Krikorian, professor emeritus in the UC College of Medicine's Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Neuroscience. "There is epidemiological data suggesting that people who consume strawberries or blueberries regularly have a slower rate of cognitive decline with ageing." Ellagitannins and ellagic acid are also found in strawberries, which are known to possess anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer properties. Krikorian went on to explain that strawberries may have improved cognitive function by reducing inflammation in the brain. "Executive abilities begin to decline in midlife and excess abdominal fat, as in insulin resistance and obesity, will tend to increase inflammation, including in the brain," he explained. The university did, however, acknowledge that Krikorian's research was partly funded by the California Strawberry Commission. Although said that the group had no role in the design of the study, data collection and analysis, or publication of the results. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel
2023-11-13 20:48

Scientists discover new truth about the Sun's structure
Our understanding of the Sun may have completely changed after astronomers calculated that it might not be quite as big as we thought it was. The Sun is so powerful that it can disrupt the Earth’s magnetic field giving us the Northern Lights. It also continually baffles scientists, as one recent discovery found that part of the Sun is broken. Now, experts have discovered that the Sun may be a bit smaller than everyone thought, which could alter how we think of the star at the centre of our universe. Two astronomers made the calculation that the radius of the Sun is smaller, by a few hundredths of a per cent, than originally believed. The results, which are being peer-reviewed, are based on evidence gathered from sound waves that are made and trapped inside the burning hot sun. These sound waves are known as p-modes and they make noise like a growling stomach, suggesting a pressure change in the Sun’s interior. Analysing p-mode oscillations offers a “dynamically more robust” understanding of the Sun’s insides, according to astrophysicists Masao Takata from the University of Tokyo and Douglas Gough from Cambridge University. According to their research using evidence from p-modes, the solar photospheric radius is fractionally smaller than calculations made using the traditional reference model for the Sun’s seismic radius that analyses waves called f-modes. The reason for this difference is not very well understood. Astrophysicist Emily Brunsden told New Scientist: “To understand the reason for their difference is tricky because there’s just a lot of things going on.” How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-09 19:48

Elon Musk wants a volunteer to have their head cut open for his brain implants
Elon Musk's chip implant company Neuralink is looking for its first volunteer since the company got approved to perform tests on humans by the FDA. Prior to its approval for human clinical trials, Reuters reported that the company had killed roughly 1,500 animals during testing. The volunteer would have to be willing to have a piece of their skull removed so a robotic surgeon can insert thin wires and electrodes into their brain. The company told Bloomberg News, the ideal candidate will be a quadriplegic under the age of 40. Neuralink hopes to eventually make a device that will allow people to send messages or play games using only their thoughts. Ashlee Vance, the author of the 2015 biography 'Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic Future', said in his Bloomberg report that despite "an outpouring of interest from thousands of prospective patients," the company is still seeking its first volunteer. The chip would enable computer functions to be performed using only thoughts via a "think-and-click" mechanism. If the ideal volunteer is chosen, a surgeon will remove part of the person's skull, before a robot dubbed "R1", equipped with cameras, sensors and a needle will push 64 threads into the brain whilst doing its best to avoid blood vessels. Reassuring. Each thread has roughly the diameter of 1/14th of a strand of human hair, and is lined with 16 electrodes that are programmed to gather data about the brain. The electrodes record neural activity related to movement intention, which is then decoded by Neuralink computers. Neuralink did not reveal how many participants would be enrolled in the trial or how many patients the FDA ultimately approved, after a negotiation between the company and agency which raised safety concerns, according to current and former employees. DJ Seo, co-founder and vice president for engineering of Neuralink told Bloomberg: "The short-term goal of the company is to build a generalised brain interface and restore autonomy to those with debilitating neurological conditions and unmet medical needs." "Then, really, the long-term goal is to have this available for billions of people and unlock human potential and go beyond our biological capabilities." Indy100 has reached out to Neuralink for comment. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel
2023-11-09 02:19
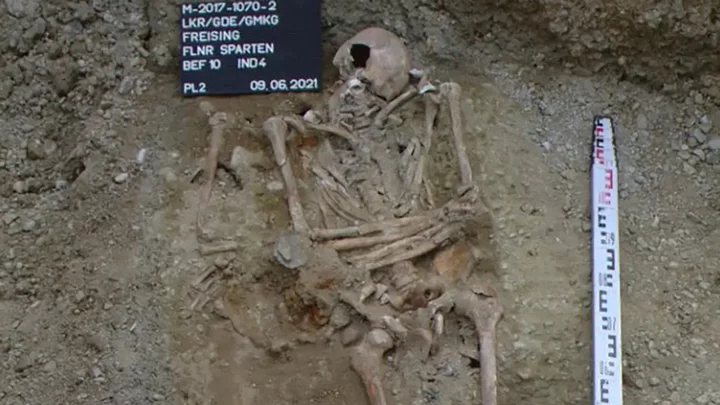

'Sophisticated' prosthetic hand found on medieval skeleton
If you thought prosthetic hands were too advanced for people living hundreds of years ago, think again. Archaeologists have found the remains of a man who died in Medieval Germany, who had prosthetics in place of several fingers. The grave was found by pipeline workers in Freising, a town near Munich. The Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation said: “Even for experienced archaeologists, this was a particularly special find: a skeleton in which parts of the fingers of its left hand are missing.” The archaeologists removed the metal from the man’s skeleton to restore and analyse it. They came to the conclusion that he had lost his fingers at some point in his life. Walter Irlinger, deputy of the general conservator at BSOMP, said: “The hollow prosthetic on the left hand replaced four fingers. The index, middle, ring and pinky fingers are individually formed out of sheet metal and are immobile. The prosthetic fingers lie slightly curved, parallel to one another.” The prosthetic also had scraps of fabric and leather, suggesting that the fingers had a leather cover, and were tied to the hand using straps. There was also a gauze-like material inside the fingers, which may have acted as a cushion for the man’s skin from contact with the metal. That period of German history included the Thirty Years’ War, which ended in 1648, which would have increased the need for amputations and prosthetics. One of the most famous amputees from the time was Götz von Berlichingen – or “Götz of the Iron Hand”. He was a German knight who lost his right hand from a cannon injury at the siege of Landshut in 1504. “In the past, prosthetics looked very much like what they were replacing,” said Jacky Finch, a researcher in the KNH Center for Biomedical Egyptology at the University of Manchester. “Nowadays, implants are placed in the sensory system to control nerve action, rather than devices attached to the body by straps or artificially powered.” The BSOMP statement continued: “Doctors at that time were already thinking about how they could make life easier for amputees. “In central Europe, there are currently around 50 similar prostheses from the late middle ages to early modern age that are known.” How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-08 01:49
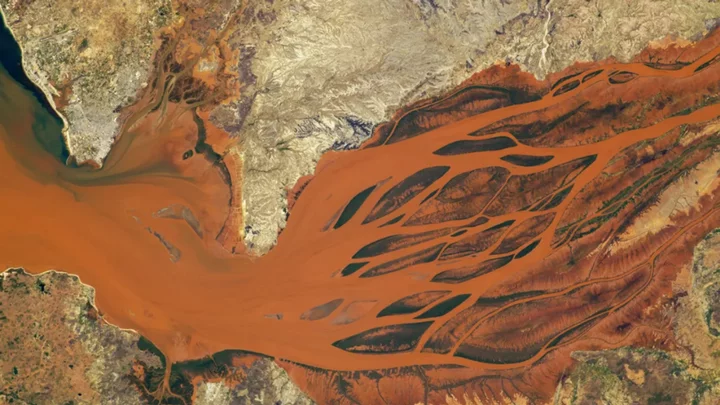

Astronauts capture the 'blood of Earth' in stunning photo
The Earth is home to truly stunning natural features, but sometimes you need a new perspective to appreciate it all over again. Thankfully, the experts at NASA are on hand to remind us just how incredible our planet is with the release of new photos showing the “blood of Earth”. The incredible images seem to show it bleeding, with dramatic red liquid appearing to cascade over the surface. However, it’s nothing at all to do with blood – which is probably just as well. Instead, the first picture shows the Laguna Colorada in the Bolivian Andes in South America from space. Remarkably, the image was taken by an astronaut onboard the International Space Station (ISS) using just a Nikon digital camera. The fact that it was taken more than 400 kilometres away from Earth on a handheld device is pretty staggering, and it offers a look at a natural phenomenon which we’d never otherwise get to see. The first picture shows the impact of red algae flourishing in the shallow water of the laguna, while the second shows the Betsiboka River Delta in Madagascar. This time, the red colour comes as a result of the iron-rich sediment. It’s pretty awe-inspiring stuff, and it’s not the first time that red “blood” has been seen running from our planet, either. Antarctica’s Blood Falls is a bizarre geographical feature in the McMurdo Dry Valleys region of the continent, and it’s one of the strangest natural phenomena you're likely to see. It features a flow of water the colour of blood that can be seen seeping out from a glacier into the ocean. The mystery behind it has fascinated members of the scientific community for decades, but a solution has now been found. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-11-07 20:25

Scientists think they’ve finally solved the mystery of how the dinosaurs went extinct
It’s one of the questions which has fascinated scientists for hundreds of years, but how did the dinosaurs really go extinct? Well, new research might have just solved the mystery once and for all. Of course, most people are familiar with the fact that an asteroid struck the Earth around 66 million years ago, but fewer people might know that the object measured a whopping 10 to 15 kilometres wide and landed in Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula. Fewer people still might know that while it sparked all sorts of devastation, including earthquakes and megatsunamis, and now experts have revealed that what might have really proved fatal for the dinosaurs was the dust that it caused. We’re not talking a little bit of dust, either. Trillions of tons of the stuff was released into the atmosphere when then asteroid struck. The damage done by this dust is explored in the new report published by Nature Geoscience. So much was released, in fact, that it caused a “global winter”, with huge clouds of silicate dust and sulphur causing temperatures to drop by 15C. The lack of light would have caused entire ecosystems to collapse, causing 75 per cent of species to be rendered extinct. The effects of the dust could have blocked out sunlight for as long as two years, which according to the Belgium researchers who led the study is what would have killed off dinosaurs gradually – rather than being killed off straight away by the asteroid. It is, however, what eventually led to other life forms emerging and ultimately the development of the human race. "Dinos dominated Earth and were doing just fine when the meteorite hit," co-author of the study and planetary scientist Philippe Claeys said. "Without the impact, my guess is that mammals - including us - had little chance to become the dominant organisms on this planet." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-11-07 19:24
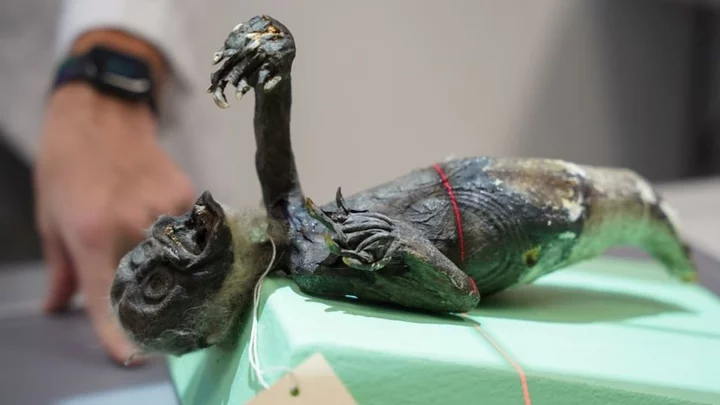
‘Mermaid mummy’ from Japan found to be a Frankenstein's mix of body parts
Frankenstein’s monsters aren’t just for Halloween, as a team of US scientists have recently discovered. The experts at Northern Kentucky University (NKU) were tasked with analysing the remains of a supposed mummified “mermaid”, and what they found was pretty gruesome. The mummy was brought to America from Japan more than 100 years ago after being donated it to the Clark County Historical Society in Springfield, Ohio. It arrived at the society in 1906 but documents supplied alongside the strange specimen suggest it dates back to the mid-1800s. This means that for some 170 years, the true identity of the wisened, 29-cm-long creature remained a mystery. However, thanks to modern technology, the team at NKU has finally worked out that the sinister-looking “siren” is, in fact, a ghoulish hybrid of monkey, fish and lizard. Joseph Cress, who led the project, told Live Science that he and his colleagues used X-ray and CT scans to investigate the creepy cadaver. "This allowed us to see [the mummy] in almost every dimension in the hopes to see what was inside it," he explained. They determined that that the “mermaid” consists of the head and torso of a monkey sewed onto the body of a fish, and its “hands” are the clawed legs of a lizard – most likely a Komodo dragon. The scans also revealed a pair of wooden stakes hidden inside the chimeric corpse – one running from head to tail and another across the shoulder blades — which were presumably inserted to keep the monster in one piece. Cress and his colleagues are currently trying to reconstruct a more detailed model of the mermaid and its individual components, according to Live Science. Once these models are complete, they plan to send them to zoos and aquariums to help confirm the different parts on a species level. However, jaw-dropping this specimen may be, it's not the only “mermaid” to be debunked in recent times. In March 2022, researchers analysed a similar example that was found in a hidden box in a Japanese temple. They also expected the creature, which was 30.5 cm long and dated back to the mid-1700s, to be a monkey-fish hybrid. However, tests conducted in February this year revealed that it was, in fact, predominantly made of cloth, paper and cotton. It had been painted with sand and charcoal and held together by metal pins, while various animal parts, including fish skin and mammal hair, had been stuck to it. Experts believe that the two “mermaids” were made to resemble "ningyo" — hideous fish-like creatures with human heads and sharp claws from Japanese mythology. According to legend, a nun named Yaobikuni lived for 800 years and retained the youthful appearance of a young woman, after eating a ningyo. Her immortality made the creatures a symbol of longevity, so it’s likely that fraudsters tried to recreate the mermaids to sell them to wealthy seekers of immortality. Still, at least the owners of these two examples didn’t make the mistake of trying to eat them. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-11-01 19:18

Scientist claims that humans have ‘no free will’ after decades of research
Human beings are fascinating creatures and one of the oldest philosophical debates is over whether people truly have free will or not. For millennia, scientists have debated over whether free will is simply an illusion of the mind and is a concept that doesn’t even exist, or, if our species naturally possess it. Some experts, such as the philosopher Bernardo Kastrup, argue that we do have free will. He defined it as existing “if our choices are determined by that which we experientially identify with”. Kastrup claimed that his “tastes and preferences” are “consciously felt by” him, thus the choices he makes are “determined by these felt tastes and preferences”. Essentially, Kastrup argues, we are able to choose what action to perform and this gives humans a level of free will. On the other hand, neurobiologist Robert Sapolsky from Stanford University believes humans don’t have any free will, after studying the subject for “decades”. In his book Determined: A Science of Life Without Free Will, Sapolsky argues that almost all of our behaviour as humans is beyond our own conscious control. He argued: “The world is really screwed up and made much, much more unfair by the fact that we reward people and punish people for things they have no control over. “We’ve got no free will. Stop attributing stuff to us that isn’t there.” Sapolsky believes that behaviour that we believe originates from free will is actually related to your environment, body, upbringing and genes. Speaking on the CultureLab podcast by New Scientist, Sapolsky explained: “In terms of my orientation, my basic approach is you look at a behaviour and someone has just done something that’s wonderful or awful or ambiguously in-between or in the eyes of the beholder, but some behaviour has happened, and you ask, 'Why did that occur?' and you’re asking a whole hierarchy of questions.” He continued explaining that the prompts to our behaviour could include, “which neurons did what, 10 milliseconds before” and may even originate from “this morning’s hormone levels” and the impact this has on your sensitivity levels in the brain. Additionally, behaviour, he argues can determined by prior trauma and even go back to the “childhood and foetal environment” and our individual genes. To summarise, he argued: “If you’re talking about genes, by definition, genes and behaviour, by definition, you’re talking about evolution and you’re talking about neurobiology and genetic variance and neuronal function. “If you’re talking about, you know, early trauma in life, you’re talking about epigenetics and you’re talking about adult propensity. “So, they’re all one continuous seam of influences, and when you look at it that way, there’s not a damn crack anywhere in there to shoehorn in a notion of free will.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-31 23:29

Mysterious holes discovered on the outside of the International Space Station
If there’s one thing astronauts don’t want to face when out in the endless expanse of space, it’s signs that their station is being sabotaged. And yet, cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Nikolai Chubwere forced to face a strange phenomenon during a spacewalk last week. The pair exited the International Space Station (ISS) on Wednesday to fix a radiator which had sprung a leak. And while they were out, they were met by a close encounter of a very strange kind. Inspecting the source of the leak during their outing, Kononenko reported seeing a number of holes on the radiator panel. "The holes have very even edges, like they've been drilled through," he told Moscow Mission Control, according to Space.com. "There are lots of them. They are spread in a chaotic manner." The cosmonauts were given tissues and cloths to soak up any fluid that had seeped out of the radiator, with the pool of liquid coolant described as a growing “blob”. However, Kononenko got so close to the “blob” that one of his tethers became contaminated. This meant that it had to be bagged up and discarded outside the ISS before the cosmonauts could go back inside. The external radiator was mounted on the outside of Russia’s Nauka module – home to a multipurpose laboratory – which was launched in 2021. It was used as a backup to another radiator which regulates the temperature inside the lab. Kononenko and Chub closed a number of valves to cut off the external radiator from its ammonia supply, and it’s believed that the “blob” formed from residual ammonia that was disturbed when the valves were being shut. The toxic liquid certainly wouldn’t have been welcome on board the space station, hence why the two colleagues embarked upon their spacewalk armed with cloths to wipe down their spacesuits and tools. Russian engineers on the ground will use the data they collected to further investigate the cause of the leak and figure out how to fix the radiator. The question now is will they be able to work out where those mysterious little holes came from? Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-10-29 23:57
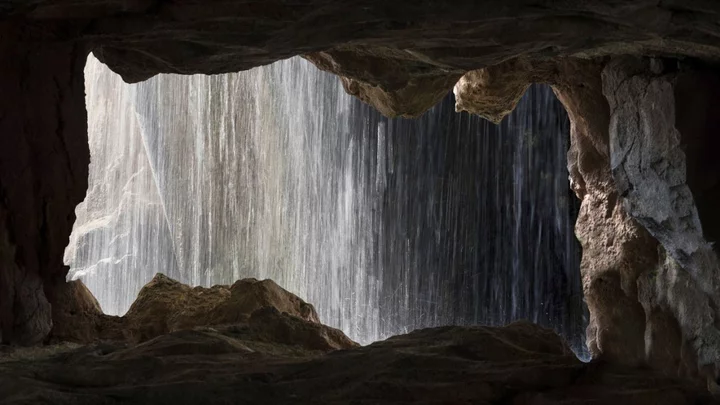

Scientist discovers oldest water on Earth and drinks it
A scientist who found the oldest water ever discovered on Earth decided the best course of action was, of course, to drink it. Professor Barbara Sherwood Lollar was leading a team of geologists studying a Canadian mine in 2016 when she made the remarkable discovery. The flowing water about three kilometres below the surface was between 1.5bn and 2.6bn years old, according to tests, making it the oldest water found on Earth. “When people think about this water they assume it must be some tiny amount of water trapped within the rock,” said Prof Sherwood Lollar. “But in fact it’s very much bubbling right up out at you. These things are flowing at rates of litres per minute – the volume of the water is much larger than anyone anticipated.” Upon tasting the ancient water, she found that it was “very salty and bitter” and “much saltier than seawater”. That was an encouraging sign, because saltier water tends to be older. In this case, where the water has been ageing for billions of years, it is hardly surprising. “If you’re a geologist who works with rocks, you’ve probably licked a lot of rocks,” said Sherwood Lollar. Her team also found that life had once been present in the water, by looking at the sulphate – the composition of salts – in it. “We were able to indicate that the signal we are seeing in the fluids has to have been produced by microbiology – and most importantly has to have been produced over a very long time scale. “The microbes that produced this signature couldn’t have done it overnight. “This has to be an indication that organisms have been present in these fluids on a geological timescale.” Fortunately, the scientist had no terrifying sci-fi movie-esq reaction to drinking the ancient water, and lived to tell the tale. The paper was published in Nature in 2016. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-27 00:29
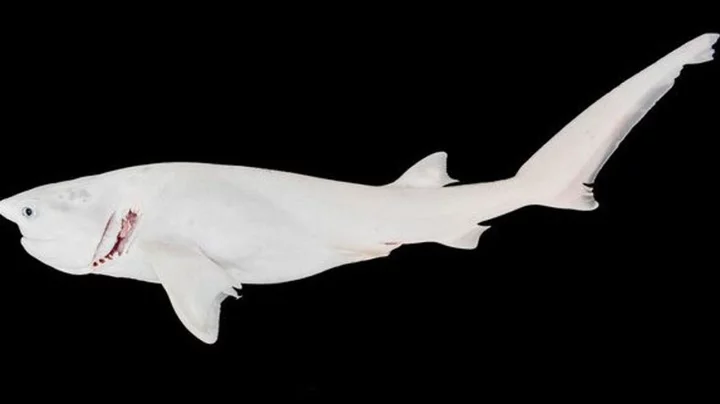

Scientists have discovered a ghost-white shark with a rare condition
Scientists have discovered a ghost-white shark with a rare condition. The predator was accidentally hooked by fishermen dedicated to catching sole. They were working from the coastal area of Los Chimus in Peru and informed authorities of the find. At the time of its capture, the shark had injuries to its gill slits as a result of being caught up in the net last month. The marine animal was transferred to the Peruvian Institute of the Sea (IMARPE) in Chimbote to undergo tests. Scientists discovered that the shark had leucism, which causes partial loss of pigmentation. The condition differs to albinism, which is a complete lack of melanin - a substance in the body that produces hair, eye and skin pigmentation. Albinos often have pink or red eyes but while leucism often makes an animal’s skin white, it does not affect their eye colour. IMARPE said this is the first known case of a shark in Peruvian waters having this condition. The fish was a young female that measured 89cm in length. Sexual maturity in females takes place when they are around 220cm in length. The predatory species sits high on the trophic food chain and mostly feeds on other sharks, rays, cetaceans and sea lions. Broadnose sevengill sharks are known to hunt in packs to bring down large prey. They are recognisable by their seven gill slits as most shark species have five. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-10-26 21:21

Meta is being sued by 41 states over ‘addictive’ content allegedly harmful to children
Mark Zuckerberg's Meta is facing lawsuits from 41 states alleging there are addictive features aimed at hooking young users. The filings allege that Meta knowingly uses features on their platforms Instagram and Facebook to pull in and addict children. States are also claiming that Meta's algorithms were designed to coerce children into harmful content with features like "infinite scroll" and persistent notifications hoooking young users to continue using the app. Meta has been accused of violating federal privacy laws for children and consumer protection laws. The 233-page joint complaint obtained by Deadline, states: "Research has shown that young people's use of Meta's Social Media Platforms is associated with depression, anxiety, insomnia, interference with education and daily life, and many other negative outcomes. "Nonetheless, Meta has continued to deny and downplay these harmful effects to the pubic and to promote its Platforms as safe for young users." The complaint also said that the company's "motive is profit, and in seeking to maximise its financial gains, Meta has repeatedly misled the pubic about the substantial dangers of its Social Media Platforms." Weighing in on the lawsuit, a Meta spokesperson said: "We share the attorney general's commitment to providing teens with safe, positive experiences online, and have already introduced over 30 tools to support teens and their families. We're disappointed that instead of working productively with companies across the industry to create clear, age-appropriate standards for the many apps teens use, the attorneys general have chosen this path." In May, U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy called social media a "profound risk" for youth and encouraged parents to restrict their children's access to it. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-10-25 17:25
