
Global regulators seek to crack down on decentralised finance
By Huw Jones LONDON Global securities regulators set out on Thursday their first blueprint to make participants in
2023-09-07 20:16
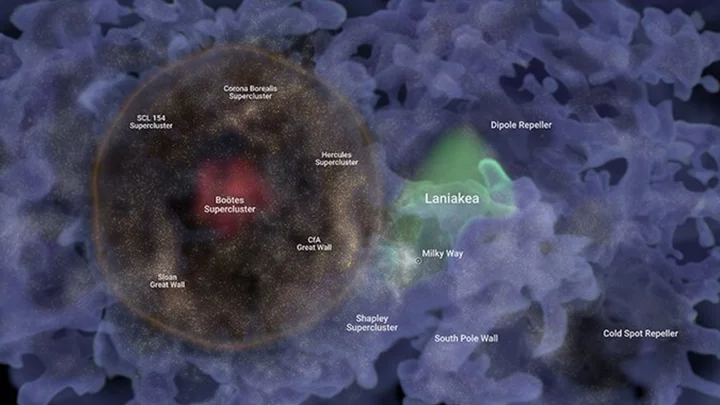
Massive bubble of galaxies could be ‘fossil of the Big Bang’, say scientists
A huge bubble of galaxies that is one billion lightyears across could be a remnant of the ripples caused by the Big Bang, according to astronomers who have mapped the structure. The structure, named Hoʻoleilana by University of Hawaii scientists, is thought to have been caused by so-called Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAOs). These were ripples in the particles of the early Universe in the period following the Big Bang, when planets, solar systems and galaxies were not yet fully formed. As the ripples went outward, they created areas of density in the particles, causing bubble-like structures in which galaxies eventually coalesced. Until now, the BAOs were just a prediction – part of the wider Big Bang theory. No specific structures in the Universe had been found which mimicked their patterns. But Hoʻoleilana fits the description of these huge cosmic bubbles perfectly, according to Brent Tully, who led the study at the University of Hawaii’s Institute for Astronomy. “We were not looking for it. It is so huge that it spills to the edges of the sector of the sky that we were analyzing,” he said. “As an enhancement in the density of galaxies it is a much stronger feature than expected. The very large diameter of 1bn light years is beyond theoretical expectations. “If its formation and evolution are in accordance with theory, this BAO is closer than anticipated, implying a high value for the expansion rate of the universe.” The bubble is absolutely huge. It is made up of several superclusters, structures which themselves are thought to be among the Universe’s largest arrangements of matter. This includes the Hercules Supercluster, the Corona Borealis Supercluster and the Sloan Great Wall. All of these structures contain thousands of galaxies. In the middle of Hoʻoleilana sits the Bootes Supercluster and the Bootes Void, an immense space of nothingness which is an incredible 330m lightyears across. Daniel Pomarede, from the CEA Paris-Saclay University, who contributed to the research, said: “It was an amazing process to construct this map and see how the giant shell structure of Ho’oleilana is composed of elements that were identified in the past as being themselves some of the largest structures of the universe.” The research was published on 5 September in The Astrophysical Journal. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-07 19:45
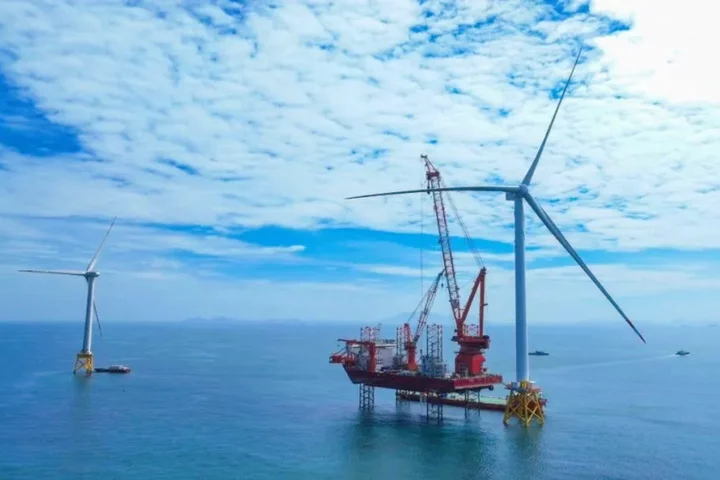

World’s largest wind turbine breaks record for power generated in a single day
A wind turbine in China has set a new world record for the most amount of electricity generated in a single day, after operating during typhoon conditions. The Goldwind GWH252-16MW turbine, which was installed at an offshore wind farm in Fujian Province in June, produced 384.1 megawatt hours in a single day – enough to power roughly 170,000 homes. The record was achieved on 1 September, according to state-owned power company China Three Gorges (CTG), surpassing the previous record set by Danish company Vestas in August. The turbine’s rotor has a diameter of 252 metres – more than double the diameter of the London Eye – and at full speed each blade can reach up to 70 per cent of the speed of sound. The record-breaking wind turbine features an innovative design that allows it to adjust its blades in real time when winds reach high speeds. This allowed it to continue operating during Typhoon Haikui last week, during which conventional turbines were forced to shut down. “We are closely monitoring critical components like the main control programme, pitch system and generators to gradually lift power restrictions while ensuring operational safety,” a spokesperson for Goldwind told the South China Morning Post. Figures from the Chinese Wind Energy Association show that China installed more than 11,000 wind turbines last year, 90 per cent of which were at onshore wind farms. Separate figures from the International Energy Agency (IEA) suggest that China added nearly three times as much wind capacity in 2022 compared to the European Union, and accounts for more than a third of all of the world’s installed wind capacity. Projections from the agency indicate that electricity from wind and solar will double over the next five years, providing almost 20 per cent of global power generation by 2027. “China is forecast to install almost half of new global renewable power capacity over 2022-27, as growth accelerates in the next fice years,” a recent IEA report noted. “Very ambitious new renewable energy targets, market reforms and strong provincial government support provide long-term revenue certainty for renewables. In most Chinese provinces, utility-scale renewables are cheaper than regulated coal electricity prices, driving rapid adoption. In the main forecast, China is expected to reach its 2030 target of [renewable] capacity five years in advance.” Read More How tech could turn our homes into renewable energy power stations World’s first solar powered hybrid truck tested on public roads Period and fertility tracking apps scrutinised over data security concerns AI can help generate synthetic viruses and spark pandemics, warns ex-Google executive Google boss says he wants to make people ‘shrug’
2023-09-07 19:24

Period and fertility tracking apps scrutinised over data security concerns
The UK’s data protection regulator is to review period and fertility tracking apps over concerns around the data security of such platforms. The Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) said the review was in response to figures it had obtained from its own research, which found that more than half of women using these apps had concerns over how their data was being used. The data protection watchdog’s research showed a third of women have used apps to track their periods or fertility, and more than half of those who have used an app believed they had noticed an increase in baby or fertility-related adverts since signing up, with 17% said they had found this distressing. The ICO said its poll showed concerns around data use and how secure their data was were named as bigger fears among women than the cost of these apps or ease of use. We want to make sure women can use these services with confidence, so we’re calling for people to share their experiences Emily Keaney, ICO The regulator is now urging users to come forward and report their own experiences using tracking apps as part of a call for evidence. It said it had also contacted companies who provide period and fertility tracking apps to find out how they are processing users’ personal information. The ICO said the focus of its work would be to identify if there was the potential for harm and negative impact on users. “These statistics suggest data security is a significant concern for women when it comes to choosing an app to track their periods or plan or prevent pregnancy,” Emily Keaney, ICO deputy commissioner of regulatory policy, said. “That’s not surprising, given the incredibly sensitive and personal information involved. “We want to make sure women can use these services with confidence, so we’re calling for people to share their experiences. “This will help us understand whether there are areas that need improvement – from how easy it is to navigate privacy policies to whether people have experienced upsetting and unexpected targeted advertising. “We also know some users feel these apps bring many benefits and we’d like to hear about these too. “As with all health apps, we would expect organisations to safeguard their users’ privacy and have transparent policies in place. “This review is intended to establish both the good and bad of how the apps are working currently. “Once we have more information, we will explore next steps, but we will not hesitate to take regulatory action to protect the public if necessary.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Russian cyber-attacks ‘relentless’ as threat of WW3 grows, expert warns Warner Music sign first digital character Noonoouri and release debut single Met should thoroughly investigate cyber security practices, say experts
2023-09-07 19:15

There’s a ‘lost continent’ which holiday makers have been visiting without knowing
Tourists from across the world may have been holidaying on the remains of a 'lost continent' that's been hiding in plain sight. The continent, known as Greater Adria, reportedly broke off from North Africa almost 250 million years ago. Around 120 years later, it started sinking under parts of Southern Europe including the Alps, the Apennines, the Balkans and Greece. Douwe van Hinsbergen, Professor of Global Tectonics and Paleogeography at Utrecht University, said: "Forget Atlantis. Without realising it, vast numbers of tourists spend their holiday each year on the lost continent of Greater Adria." He added: "The only remaining part of this continent is a strip that runs from Turin via the Adriatic Sea to the heel of the boot that forms Italy." This isn't the first time a 'lost' continent has been discovered... Scientists uncovered Zealandia (or Te Riu-a-Māui in the Māori language) that was reportedly 'lost' for 375 years. In the past, there's been speculation as to whether the continent actually exists. It wasn't until 2017 that geologists discovered the continent had been there all along. According to TN News, Zealandia is 1.89 million square miles in size. It was part of a supercontinent called Gondwana, which included most of Western Antarctica and Eastern Australia, over 500 million years ago. It was first said to have first discovered in 1642 by Dutch businessman and sailor Abel Tasman, who was desperate to uncover the "Great Southern Continent". Scientists agreed on the existence of Zealandia, which started to "pull away" from Gondwana for reasons scientists are still trying to understand. Most of the newfound continent is underwater and has been used as an example by geologists at the Zealand Crown Research Institute GNS Science on how something "very obvious" can take a while to uncover. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-07 16:52

Generation AI: education reluctantly embraces the bots
By Barbara Lewis and Supantha Mukherjee LONDON/STOCKHOLM At leading Swedish university Lund, teachers decide which students can use
2023-09-07 16:51

UK has not backed down in tech encryption row, minister says
LONDON (Reuters) -Britain will require social media companies to take action to stop child abuse on their platforms, and if
2023-09-07 15:52

AI can help generate synthetic viruses and spark pandemics, warns former Google executive
Synthetic viruses could be generated through the misuse of artificial intelligence and potentially spark pandemics, a former Google executive and AI expert has warned. Google DeepMind co-founder Mustafa Suleyman expressed concern that the use of AI to engineer pathogens to cause more harm may lead to a scenario like a pandemic. “The darkest scenario is that people will experiment with pathogens, engineered synthetic pathogens that might end up accidentally or intentionally being more transmissible or more lethal,” he said in a recent episode of a podcast. Similar to how there are restrictions in place to prevent people from easily accessing pathogenic microbes like anthrax, Mr Suleyman has called for the means to restrict access to advanced AI technology and software that runs such models. “That’s where we need containment. We have to limit access to the tools and the know-how to carry out that kind of experimentation,” he said in The Diary of a CEO podcast. “We can’t let just anyone have access to them. We need to limit who can use the AI software, the cloud systems, and even some of the biological material,” the Google DeepMind co-founder said. “And of course on the biology side it means restricting access to some of the substances,” he said, adding that AI development needs to be approached with a “precautionary principle”. Mr Suleyman’s statements echo concerns raised in a recent study that even undergraduates with no relevant background in biology can detail suggestions for bio-weapons from AI systems. Researchers, including those from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, found chatbots can suggest “four potential pandemic pathogens” within an hour and explain how they can be generated from synthetic DNA. The research found chatbots also “supplied the names of DNA synthesis companies unlikely to screen orders, identified detailed protocols and how to troubleshoot them, and recommended that anyone lacking the skills to perform reverse genetics engage a core facility or contract research organization”. Such large language models (LLMs), like ChatGPT, “will make pandemic-class agents widely accessible as soon as they are credibly identified, even to people with little or no laboratory training,” the study said. The study, whose authors included MIT bio risk expert Kevin Esvelt, called for “non-proliferation measures”. Such measures could include “pre-release evaluations of LLMs by third parties, curating training datasets to remove harmful concepts, and verifiably screening all DNA generated by synthesis providers or used by contract research organizations and robotic ‘cloud laboratories’ to engineer organisms or viruses”. Read More China’s ‘government-approved’ AI chatbot says Taiwan invasion is likely Government urged to address AI ‘risks’ to avoid ‘spooking’ public Scientists give verdict on Harvard professor’s claim of finding materials in sea from outside Solar System Google boss says he wants to make people ‘shrug’ Why is Elon Musk obsessed with the letter X? Elon Musk ‘borrowed $1bn from SpaceX’ at same time as Twitter acquisition
2023-09-07 15:50

China's top chipmaker may be in hot water as US lawmakers call for further sanctions after Huawei 'breakthrough'
Shares in SMIC, China's largest contract chipmaker, plunged on Thursday, after two US congressmen called on the White House to further restrict export sales to the company.
2023-09-07 15:49
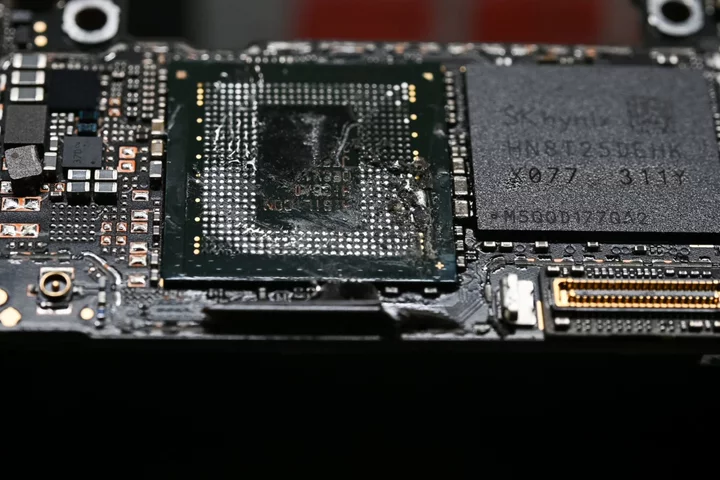

SK Hynix Investigating Use of Its Chips in New Huawei Phone
SK Hynix Inc. has opened an investigation into the use of its chips in the latest phone from
2023-09-07 14:20

China's Tencent says large language AI model 'Hunyuan' available for enterprise use
BEIJING China's Tencent Holdings said its large language artificial intelligence (AI) model "Hunyuan" will be available for enterprise
2023-09-07 09:51

Wall Street Journal: China bans use of iPhones for government officials
China has banned the use of iPhones for central government officials, The Wall Street Journal reported, citing unnamed people familiar with the matter.
2023-09-07 09:24
