
Salesforce lifts annual forecast as business software demand stays strong
(Reuters) -Salesforce raised its annual revenue forecast on Wednesday and projected quarterly sales above estimates as it benefits from a
2023-08-31 04:54

British officials say AI chatbots could carry cyber risks
By Raphael Satter and Martin Coulter (Reuters) -British officials are warning organisations about integrating artificial intelligence-driven chatbots into their businesses,
2023-08-31 04:47

Gannett to pause AI experiment after botched high school sports articles
Newspaper chain Gannett has paused the use of an artificial intelligence tool to write high school sports dispatches after the technology made several major flubs in articles in at least one of its papers.
2023-08-31 02:57

iPhone event: Everything Apple is expect to reveal at major ‘wonderlust’ launch
Apple is about to hold its biggest event of the year: the iPhone launch. This year, however, it will bring a whole host of new products, including Watches and AirPods too. And those products could be notable as much for their ports as much as any new features they will bring, as Apple is widely expected to finally make a long-rumoured change away from the classic Lightning connector. Here is everything Apple is expected to show at the event on 12 September, which it has called “Wonderlust”. iPhone 15 – four of them It is a long time since just one iPhone was introduced during the iPhone event, and these days Apple seems to have settled on a fairly reliable line-up of four. This year that means there should be an iPhone 15, an iPhone 15 Plus, an iPhone 15 Pro and an iPhone 15 Pro Max. The two larger phones generally are the same as their smaller counterparts, beyond the obvious difference in size, and those sizes should be the same 6.1 inches and 6.7 inches as the iPhone 14 line-up. This year however there will be a small distinction between the Pro and Pro Max. The iPhone 15 and 15 Plus will have much more modest upgrades, which mostly bring it in line with the existing iPhone 14 Pro. It will get the Dynamic Island and a faster chip, rumours suggest. The iPhone 15 Pro and Pro Max will get the more meaningful upgrades. They will include a new chip in the form of the A17, an action button instead of a mute switch, and camera improvements. The camera on the iPhone 15 Pro Max will get its own addition: a periscope camera. That technology has already come to some competitors and means that a long lens can be folded into a small space, allowing for extra zoom capabilities, though it will not fold so small that it will fit in the smaller-sized phone. And all of those iPhones will switch to USB-C rather than the Lightning port that has been on the phone for more than a decade. It remains to be seen whether that will add new capabilities straight away, and last time Apple switched connector it caused quite a stir given the requirement to buy new cables and peripherals. Apple Watch Series 9 The Apple Watch Series 9 is also expected to be a fairly small upgrade. It will get a new processor that will make it faster, but on the outside it will stay the same, in the same design. That upgrade could be the first substantial upgrade to the inside of the iPhone in years. As well as making the Watch run faster, it could also improve its battery life. Apple Watch Ultra The Apple Watch Ultra – first introduced last year – is also set to get its own upgrade. Those too are likely to be limited. It will get all the upgrades from the normal version of the Apple Watch, such as its improved processor. Rumours also suggest that it could be lighter and come in a new, darker colour. AirPods In recent days, rumours have suggested that Apple could be launching new AirPods Pro too. It’s unclear whether that’s just a change of ports to match the iPhone’s, or something more significant. It also remains to be seen whether Apple will offer that case on its own, or require people to buy a whole new set of AirPods to get it. The AirPods Pro case does have wireless charging, so even those stuck with the old version can theoretically power up their iPhone and earphones with the same charger. Other accessories The switch away from the Lightning port doesn’t only affect the iPhone and the AirPods. There are plenty of other devices that still use that port: the AirPods Max, Apple’s Mac peripherals like its keyboards and trackpads, and one of the iPads. Apple could use the event to announce that all of those will be making the switch too. Or it might wait until more relevant events: iPad launches for the tablet, for instance, and Mac launches for the keyboard and other accessories. Headset The headset was revealed in June at Apple’s last big event, its Worldwide Developers Conference. Since then Apple has been largely quiet about it – and the developers that have been using it since have been sworn to secrecy. The headset isn’t due until early next year. But Apple will almost certainly use the event to remind people that it’s coming, and perhaps give some updates. (A potential surprise for the iPhone would be if it can capture the three-dimensional images and videos that can be viewed in the headset, and were a key part of Apple’s demonstration of it. It certainly makes sense that it would be coming to some iPhone in the future.) Surprises? Apple is well-known for introducing surprises at the end of its events. But in fact, they are actually quite rare – especially these days, and especially at iPhone events where Apple wants to ensure the focus is on its biggest products. So there is of course some chance of a big surprise. But it seems unlikely, given how action packed the event already seems to be. Read More Apple announces major event to reveal new phone Apple says its new product is making people ‘audibly gasp’ The powerful technology hidden in every iPhone – and all around you iPhone 15 could bring two major changes to fix battery life iPhone owners to receive payouts from Apple iPhone 15: Global smartphone demand collapses as Apple aims to take top spot
2023-08-31 00:58

Intel to invest $1.2 billion in Costa Rica over next two years
SAN JOSE Intel will invest $1.2 billion in Costa Rica over the next two years, the company said
2023-08-31 00:47
Geologists have figured out how to locate diamond ‘explosions’
A group of geologists has recently achieved a breakthrough in identifying potential sites for the formation of diamonds. Diamonds, the hardest naturally occurring material we have found, originate under the extreme conditions of immense pressure and high temperatures deep within the Earth's interior. These precious gems are occasionally pushed to the surface in molten rock formations known as kimberlite. However, there are currently two competing theories regarding what is responsible for this rush of kimberlite which brings diamonds to the surface. In a recent study, these theories were closely examined by a research team. In a piece for The Conversation study author and Associate Professor in Earth Science at the University of Southampton, Thomas Gernon explained: “one proposes that kimberlite magmas exploit the ‘wounds’ created when the Earth’s crust is stretched or when the slabs of solid rock covering the Earth - known as tectonic plates - split up.” “The other theory involves mantle plumes, colossal upwellings of molten rock from the core-mantle boundary, located about 2,900km [1,802] beneath the Earth’s surface.” However, neither of these theories adequately explains how magma manages to find its way through the Earth's crust, or the specific composition of the resulting kimberlite. By employing statistical analysis and machine learning, the team analysed the breakup of continents and its correlation with kimberlite formation. Their findings indicated that the majority of kimberlite volcanoes erupt 20 to 30 million years after tectonic breakup. “It also added a major clue,” Gernon explained. “Kimberlite eruptions tend to gradually migrate from the continental edges to the interiors over time at a rate that is uniform across the continents.” Delving deeper into their investigation through computer-generated models, the team ultimately concluded that diamond eruptions stem from a "domino effect." As continents gradually drift apart from each other, they generate rifts of thinned crust. As this happens, regions of thick, cold rock descend into the hot magma beneath, inducing an upsurge of the mantle, which in turn triggers a similar flow in nearby continents. Gernon elaborated on the team's findings, saying, "Various other results from our computer models then advance to show that this process can bring together the necessary ingredients in the right amounts to trigger just enough melting to generate gas-rich kimberlites,” Gernon explained. “Once formed, and with great buoyancy provided by carbon dioxide and water, the magma can rise rapidly to the surface carrying its precious cargo.” Moreover, the same methodology could potentially be employed to locate diamonds and other rare elements. “The processes triggering the eruptions that bring diamonds to the surface appear to be highly systematic,” Gernon siad. “They start on the edges of continents and migrate towards the interior at a relatively uniform rate.” The study is published in the journal Nature. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 00:25

Analysis-Grayscale victory big boost for decade-long spot bitcoin ETF push
By Hannah Lang and Chris Prentice WASHINGTON A court ruling siding with Grayscale Investments is a big boost
2023-08-31 00:23

Google launches watermarks for AI-generated images
In an effort to help prevent the spread of misinformation, Google on Tuesday unveiled an invisible, permanent watermark on images that will identify them as computer-generated.
2023-08-31 00:17
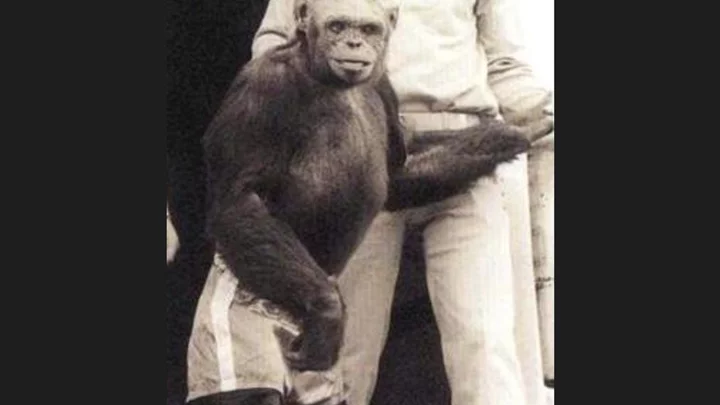

Doctor says scientists secretly made a ‘humanzee’ by mixing humans with chimps
Chimpanzees are our closest relatives, so it’s not surprising that they can do many of the things that we can. They’re able to create tools and can even use sign language, plus they share 98.8 per cent of their DNA with humans. It is, therefore, no wonder that the question has often been asked: could humans and chimps ever produce offspring? The answer, according to one evolutionary psychologist, is yes – and it’s already happened. Gordum Gallup made the eyebrow-raising claims in an interview with The Sun Online back in 2018. He told the news site that a human-chimpanzee hybrid – which he dubbed a “humanzee” – was born in a Florida lab 100 years ago. And if you’re wondering how the scientists behind the experiment managed to keep it hushed up for decades, it’s because – according to Gallup – they swiftly killed the infant when they realised the implications of what they’d done. Gallup, a professor at New York’s University at Albany, said his former university teacher told him that the secret birth took place at a research facility in Orange Park, where he used to work. “They inseminated a female chimpanzee with human semen from an undisclosed donor and claimed not only that pregnancy occurred but the pregnancy went full term and resulted in a live birth,” the psychologist told The Sun. “But in a matter of days, or a few weeks, they began to consider the moral and ethical considerations and the infant was euthanised.” Putting Gallup’s unsubstantiated story to one side, it’s unclear whether a human-chimpanzee hybrid is even possible. Some experts believe that our human ancestors and chimpanzees may have been capable of interbreeding as late as 4 million years ago according to IFL Science, which notes that our last common ancestor lived 6-7 million years ago. However, the website also notes that this theory is widely contested. It also points out that other animals with similar genetic differences to that of humans and chimps, such as horses and zebras, have been able to reproduce. And yet, the offspring are often infertile. Nevertheless, back in the 1970s, plenty of people believed that a chimp called Oliver was a human-monkey hybrid thanks to his humanistic walk, intelligence and physical features (he was said to have a smaller, flatter face than his ape peers, according to Historic Mysteries). It wasn't until tests were conducted on Oliver in 1996 that the matter was finally settled: he had 48 chromosomes so was categorically not a humanzee but a regular chimp. Oliver The Humanzee www.youtube.com Still, one certainty is that scientists continue to tread an ethical tightrope when it comes to investigating chimps and their potential to further biomedical research. In 2021, scientists created the first (publicly documented) part-monkey, part-human embryo by growing human stem cells in a macaque monkey. The aim of the work, which was carried out at California’s Salk Institute, was to help create organs for transplants and improve our understanding of human development and disease progression. In 2020, a team of German and Japanese scientists spliced human genes into the brains of marmosets, resulting in the monkey fetuses having larger, more human-like brains, according to the study, which was published in the journal Science. Once the experiment was complete, the team destroyed their creations “in light of potentially unforeseeable consequences with regard to postnatal brain function”. One thing’s for sure, no scientist wants to find themselves the architect of a real-life Planet of the Apes. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 00:16
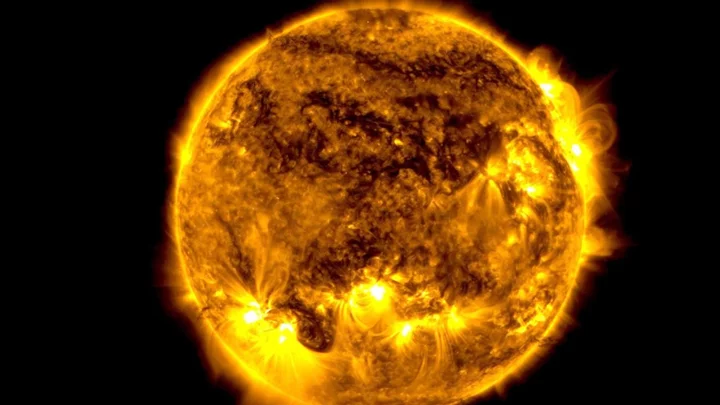

Part of the sun is broken and scientists are baffled
We don’t want to alarm anyone, but the sun is broken. A section of the sun has left the surface and begun circulating around the top of the star as if it were a huge polar vortex, and it’s not exactly clear why it’s happened. The observation was made possible thanks to the James Webb Space Telescope, and its no surprise that it piqued the interests of scientists everywhere. Tamitha Skov is a space weather physicist who regularly shares updates on social media, and she seemed incredibly excited about the latest developments. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter “Talk about Polar Vortex! Material from a northern prominence just broke away from the main filament & is now circulating in a massive polar vortex around the north pole of our Star,” she wrote. “Implications for understanding the Sun's atmospheric dynamics above 55° here cannot be overstated!” Solar prominences consist of hydrogen and helium, and they extrude from the sun’s service releasing plasma. While there’s confusion around the cause of the phenomenon, it could be related to the reversal of the sun’s magnetic field, as well as the fact that something expected has been known to happen when the sun reaches a 55 degree latitude in every 11-year solar cycle. Solar physicist Scott McIntosh, who is the deputy director at the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colorado told Space.com: "Once every solar cycle, it forms at the 55 degree latitude and it starts to march up to the solar poles. “It's very curious. There is a big 'why' question around it. Why does it only move toward the pole one time and then disappears and then comes back, magically, three or four years later in exactly the same region?" Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-30 22:54

Scientists think there might be life hidden in underground caves on Mars
Scientists have theorised that if we are going to find life on Mars, it will be microbes and they will be living in caves below the surface. The Perseverance rover, NASA’s exploration robot on the Red Planet, is currently searching for signs of ancient life in the Jezero Crater. Scientists already know that there are so-called lava tubes on Mars, which some think could be large enough to shelter the first human astronauts from the cosmic radiation which is bombarding the planet. When these were formed, they thought conditions on Mars were more similar to those on Earth, with flowing water, an atmosphere and a warmer climate. One theory is that as conditions changed on the surface and Mars lost its magnetic field and atmosphere, life could have shifted underground. Daniel Viúdez-Moreiras from Spain’s National Institute for Aerospace Technology calculated that UV radiation levels would be about 2 percent of the radiation levels found at the surface. Fortunately, we have lava tubes here on Earth too, which could tell us what life could look like in similar conditions elsewhere in the Solar System. Hawai’i’s Mauna Loa volcano lava tubes were recently explored by NASA. Within them, life is sheltered from conditions on the surface. On Earth, that is a bad thing: we have sunlight and oxygen. But on Mars, where conditions are much harsher, that is a big advantage. “The microbes we found in Hawaii could be similar to microbes that once lived on Mars,” researcher Chloe Fishman explained to NASA following a trip to collect samples in April, “or even microbes that live there today.” The team brought back samples from the cave so as to sequence the genomes of the microbes they found there. And there are already plans to explore lava tubes on the Moon, too. So maybe, just maybe, they will hold the secret to life on Mars. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-30 19:48

Near-death experience expert says he’s proven there is an afterlife ‘without a doubt’
One of life's unanswered questions that often lies in fear of the unknown is what happens when we die. Now, an American doctor, who has studied over 5,000 near-death experiences, claims there is "without a doubt" life after death. Radiation oncologist Dr Jeffrey Long from Kentucky started his Near-Death Experience Research Foundation back in 1998 and has collected personal recollections from people who have almost faced death. He defined a near-death experience as "someone who is either comatose or clinically dead, without a heartbeat, having a lucid experience where they see, hear, feel emotions, and interact with other beings." After years of "overwhelming" evidence, he has concluded: "There’s certainly an afterlife." Dr Long revealed in an essay for Insider that roughly 45 per cent suggested that "their consciousness separates from their physical body, usually hovering above," during their NDE. One account from a woman who fell unconscious while riding a horse told the doctor that "her consciousness travelled with her horse as he galloped back to the barn." When she woke up, she was able to "describe exactly what happened at the barn." Many others went on to claim that they felt as though they were "transported into another realm," where they saw a bright light and were greeted by deceased loved ones. Even children have described similar experiences. Dr Long candidly said he hasn't found any scientific explanations behind the experiences, adding: "I’ve read brain research and considered every possible explanation for NDEs. The bottom line is that none of them hold water." Previously, in a short film for BBC Ideas, Dr Kathryn Mannix, who specialises in palliative and end-of-life care suggested: "Dying is probably not as bad as you're expecting." She went on to compare death to "a process" and believes society should be open to the conversation about death and change how we speak about it. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-30 18:54
