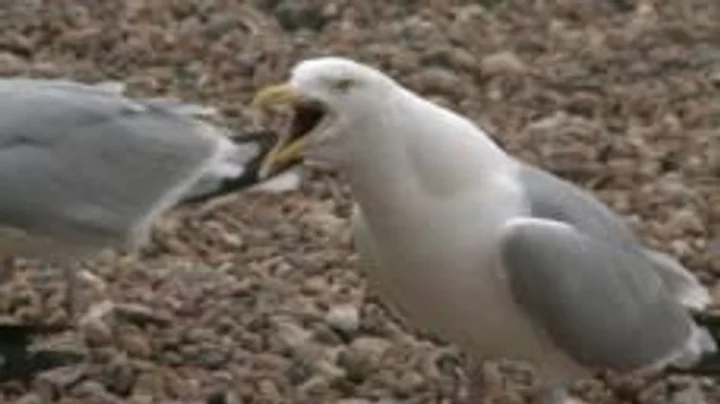

Scientists discover why gulls always prey on people's food
Anyone who has braved a stroll along England's coastline will be aware of seagulls' tyrannical regime. They prey on people eating chips, they swoop down on unsuspecting holidaymakers licking an ice cream, and they can be quite aggressive indeed. And now, terrifying research has revealed that they are more calculating than you may have previously thought. A University of Sussex study on herring gulls at Brighton beach found that the birds choose what to eat by watching what humans are enjoying. Scientists taped green (salt and vinegar) and blue (cheese and onion) packets of Walkers crisps to tiles and placed them a few metres from gulls on Brighton beach and filmed the birds’ behaviour from a distance. In some cases, the researchers ate from one of the bags of crisps. When the scientists didn't eat, less than a fifth of gulls approached the crisp packets placed nearby. But when the researchers were snacking on crisps, 48 per cent of the birds came to check out the packets. Nearly 40 per cent of such approaches ended with gulls pecking at the crisp packets, and of these, 95 per cent were directed at the same colour packet as the scientist was eating from. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter “We’ve shown that adult gulls are able to pay attention to the behaviour of humans and apply that to their own foraging choices,” said Franziska Feist, a biologist and first author on the study. “Given that the urbanisation of gulls is very recent, this ability must come from the gulls’ general smartness and behavioural flexibility.” “It is likely that simply deterring the public from directly feeding gulls may not be enough,” Feist said. “They are still able to observe what we eat and that would inform their ability to target waste, litter and so on.” Dr Madeleine Goumas, an expert on herring gulls at Exeter University who was not involved in the study, said: “We already know from previous research that gulls use information from people when they’re searching for food. “This study shows that we aren’t only drawing gulls’ attention to where food is, but they also learn about the type of food we’re eating. Knowing this may have implications for how we reduce negative interactions between humans and gulls, as we seem to be inadvertently teaching gulls to exploit new food items.” Meanwhile, past alarming research revealed that gulls prefer food that has been touched by people. Overall, it's giving Alfred Hitchcock's The Birds. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-24 22:20
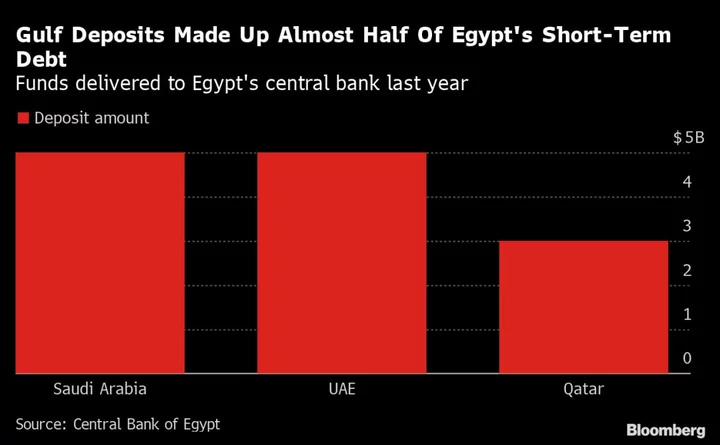
Qatar Says Investments in Egypt Are Coming, But No More Deposits
Qatar said it’s committed to following through on the billions of dollars in investments pledged to cash-strapped Egypt,
2023-05-24 21:55

Chipmaker Analog Devices' weak forecast sparks share selloff
(Reuters) -Analog Devices Inc said on Wednesday that a turbulent economy would weigh on its third-quarter results, sending the chipmaker's
2023-05-24 21:51

EU, U.S. to seek stopgap standards for AI - EU tech chief
By Philip Blenkinsop BRUSSELS The European Union and the United States are set to step up cooperation on
2023-05-24 21:24

Facebook owner Meta starts final round of layoffs
By Katie Paul NEW YORK (Reuters) -Meta Platforms Inc started carrying out the last batch of a three-part round of
2023-05-24 20:27
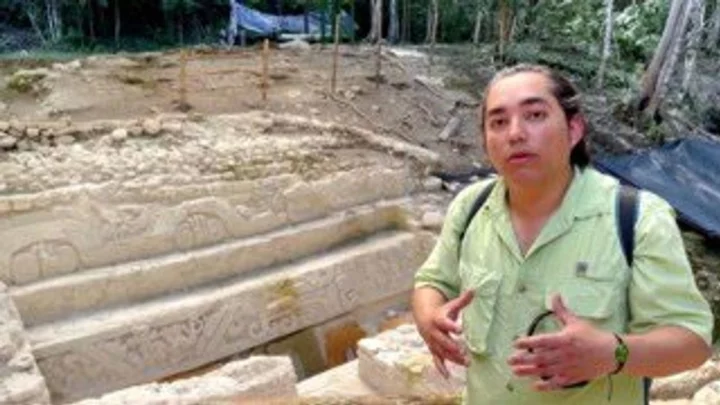

'Impossible' ancient Mayan city discovered in remote jungle
It feels like every day there’s a science story that comes along ready to blow our tiny minds, and today is no exception. A series of ancient interconnected cities have been discovered in the remote El Mirador jungle Guatemala, and it’s changing our entire understanding of the ancient civilisation. More than 400 settlements have been uncovered with some dating back as far as 1,000 BC. They’re linked by roads too, and it’s led them to be described as “the first freeway system in the world”. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Richard Hansen, a research professor at the University of Idaho, is an expert on the project and he’d called the findings a “game-changer”. It was previously thought that the Mayan peoples were nomadic, but these cities have changed the scientific community’s understanding. Speaking to the Washington Post, Hansen said: "We now know that the Preclassic period was one of extraordinary complexity and architectural sophistication, with some of the largest buildings in world history being constructed during this time.” On top of the 110 miles of interconnected roads, the discoveries also showed evidence of organised agriculture and even hydraulic systems. The findings are the result of work which first began in 2015, which saw lidar technology uncovered signs of ancient structures below the surface. Archaeologist Enrique Hernández, from San Carlos University said about the findings: “Now there are more than 900 [settlements]… We [couldn’t] see that before. It was impossible,” he said. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-05-24 19:17
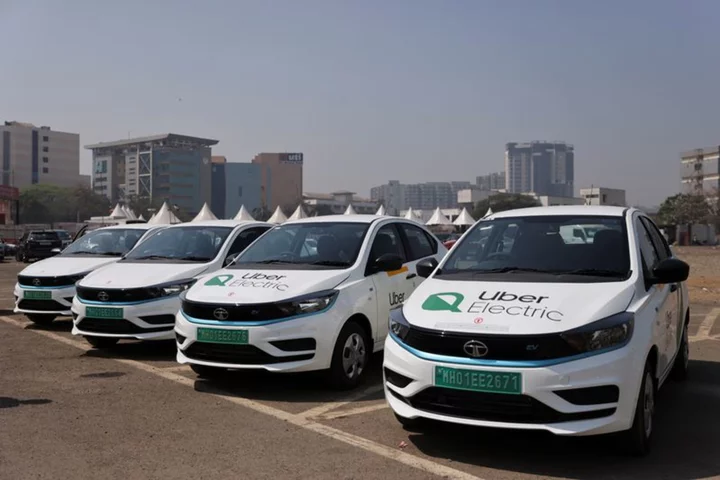

Uber steps up EV push in India with Uber Green
By Aditi Shah and Navamya Ganesh Acharya NEW DELHI/BENGALURU (Reuters) -Ride-hailing platform Uber Technologies is stepping up its efforts to
2023-05-24 18:21

Ericsson Cleared by Nasdaq Stockholm in Iraq Insider Case
Nasdaq Stockholm cleared Ericsson AB of any violations regarding the Swedish telecom company’s disclosure of a probe into
2023-05-24 17:50

Ready for a digital euro? At 25, European Central Bank preps for future of money
Proposals for a digital European currency are taking shape
2023-05-24 17:27

Japan's Rakuten set to raise $2.18 billion through share issue
TOKYO (Reuters) -Japanese e-commerce and fintech conglomerate Rakuten Group Inc will raise up to 294.2 billion yen ($2.18 billion) by
2023-05-24 16:58
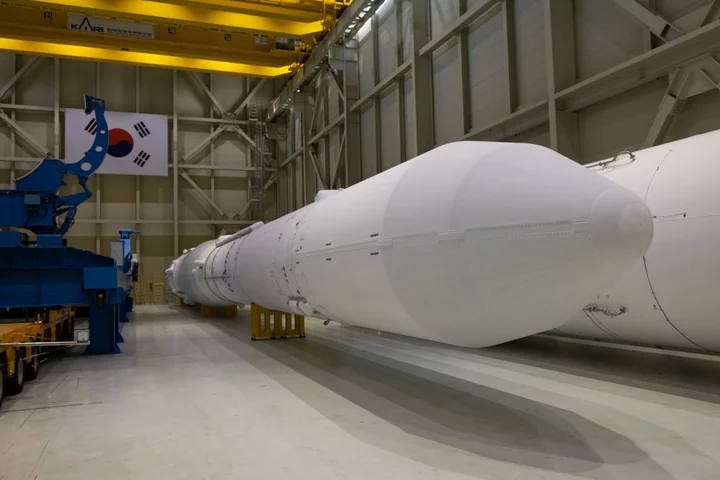

Korea Space Race Heats Up as North and South Plan Launches
The two Koreas are in a space race. The North is upgrading its space center to accommodate the
2023-05-24 15:52

Axa Venture Partners to Raise €1.5 Billion Fund for Tech
Axa Venture Partners announced a new €1.5 billion ($1.6 billion) late-stage fund to invest in European and North
2023-05-24 15:47
