
Google makes preparation for the ‘quantum apocalypse’ with Chrome update
Google is preparing for the “quantum apocalypse”. Experts have warned for years that the development of quantum computers could undermine the encryption that currently secures everything from our private messages to our banking details. Quantum computers are a still largely theoretical technology that proponents claim could dramatically beat the performance of the classical computers we have today. That could be a major positive for applications such as drug research and quantum computing – but could be disastrous for security technology. Much of that security technology depends on mathematical problems that are sufficiently hard for our computers to work out as to keep that data secure. But future quantum computers could overcome those problems in seconds, and break into any data. That is what is referred to by researchers as the “quantum apocalypse”. And an entire subset of computing – post-quantum cryptography – has grown to find ways to secure data even if that future does come about. Now Google has put some of that work into practice, in Chrome. The new technology includes new cryptography that should be resistant to attempts to break it with future quantum computers. It does so by integrating a technology known as X25519Kyber768, a long name for what is actually a hybrid of two cryptographic algorithms. Tying the two together means that data is protected both by an existing secure algorithm and one that is protected against quantum computers. The updates are part of broader work across Google to “prepare the web for the migration to quantum-resistant cryptography”. Devon O’Brien, Google’s technical program manager for Chrome security, who wrote the blog post announcing the changes, noted that quantum computers could be decades away. But remains important to secure data now in part so that it cannot be filed away, ready to break into when the technology arrives. “It’s believed that quantum computers that can break modern classical cryptography won’t arrive for 5, 10, possibly even 50 years from now, so why is it important to start protecting traffic today? The answer is that certain uses of cryptography are vulnerable to a type of attack called Harvest Now, Decrypt Later, in which data is collected and stored today and later decrypted once cryptanalysis improves.” Read More Google is getting ready for the ‘quantum apocalypse’ Vote to empower autonomous ‘robotaxis’ from Cruise and Waymo divides San Francisco ‘Billions’ of computers potentially affect by huge security vulnerability
2023-08-17 13:17

Lenovo Q1 revenue misses, hit by poor PC demand
HONG KONG (Reuters) -China's Lenovo Group on Thursday posted a worse-than-expected 24% fall in revenue for the April-June quarter, hit
2023-08-17 12:55
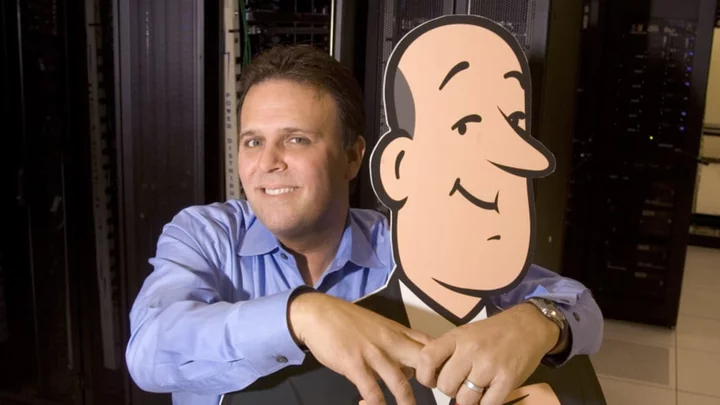

Why Everyone Stopped Asking Jeeves
Ask Jeeves became a casualty of the search engine wars of the early 2000s. Eventually, their mascot was escorted right out the door.
2023-08-17 12:17
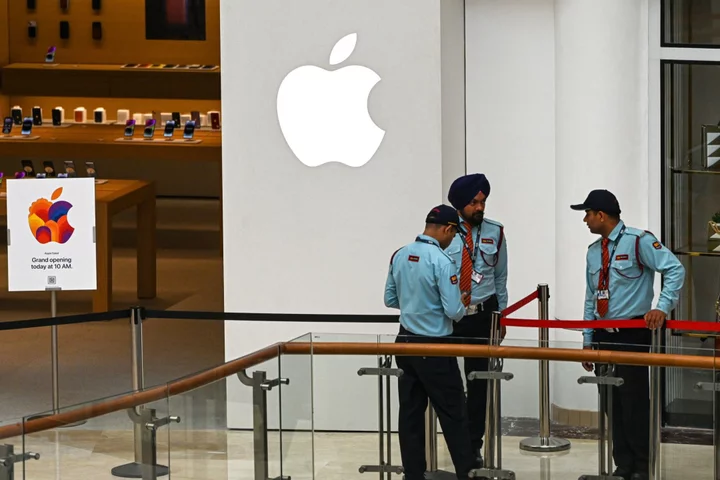

Foxconn Begins iPhone 15 Production in India
Apple Inc.’s next-generation iPhone 15 is beginning production in Tamil Nadu, in an effort to further narrow the
2023-08-17 11:52
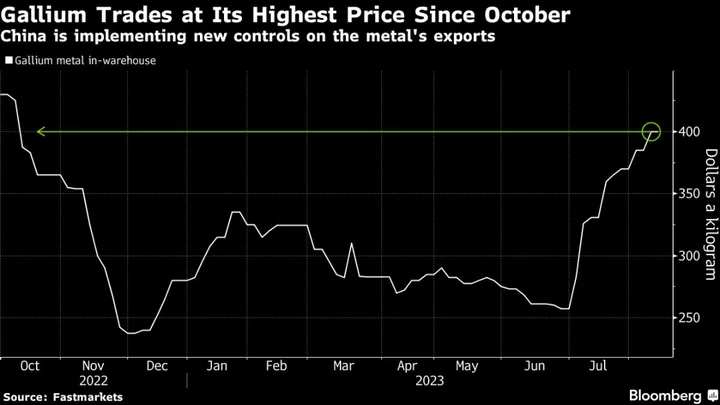
China’s Gallium Exports in Limbo After Start of Curbs
China’s push to control its exports of gallium has sent prices for the metal used in semiconductors to
2023-08-17 11:45

China’s Housing Slump Is Much Worse Than Official Data Shows
Judging by China’s official statistics, the nation’s housing market has been remarkably resilient in the face of tepid
2023-08-17 07:57

Two brands suspend advertising on X after their ads appeared next to pro-Nazi content
At least two brands have said they will suspend advertising on X, the platform formerly known as Twitter, after their ads and those of other companies were run on an account promoting fascism. The issue came less than a week after X CEO Linda Yaccarino publicly affirmed the company's commitment to brand safety for advertisers.
2023-08-17 07:45

New York City bans TikTok on government-owned devices over security concerns
By Kanishka Singh WASHINGTON New York City on Wednesday banned TikTok on government-owned devices, citing security concerns, joining
2023-08-17 06:28

Synopsys names insider Ghazi as CEO, forecasts stronger fourth quarter
By Jaspreet Singh and Max A. Cherney Chip design software company Synopsys on Wednesday named 25-year-veteran Sassine Ghazi
2023-08-17 06:25

PayPal to halt UK crypto sales until 2024
By Elizabeth Howcroft LONDON Payments giant PayPal will stop allowing UK customers to buy cryptocurrencies through its platform
2023-08-17 02:57
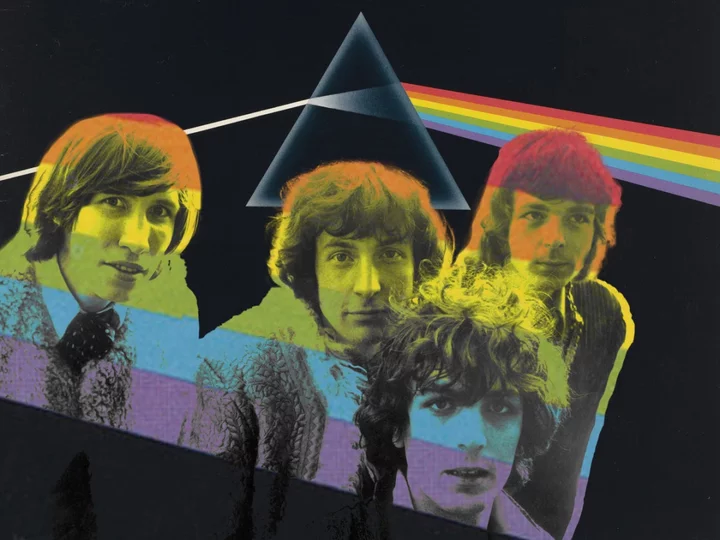

Pink Floyd song reconstructed from person’s brain activity
Neuroscientists have figured out how to reconstruct a song by decoding the brain signals of someone listening to it. A team from the University of California, Berkeley, reproduced Pink Floyd’s song ‘Another Bring in the Wall, Part 1’, after placing electrodes on the brains of patients and playing the music as they underwent epilepsy surgery. Analysis of the brain activity allowed the neuroscientists to create the song’s rhythm, as well as pick out understandable lines like “All in all it’s just another brick in the wall”. Scientists have previously used similar brain-reading techniques in an attempt to decipher speech from thoughts, but this is the first ever time that a recognisable song has been reconstructed from brain recordings. “It’s a wonderful result. One of the things for me about music is it has prosody and emotional content. As this whole field of brain machine interfaces progresses, this gives you a way to add musicality to future brain implants for people who need it, someone who’s got ALS or some other disabling neurological or developmental disorder compromising speech output,” said Robert Knight, a neurologist and UC Berkeley professor of psychology in the Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute who conducted the research. “It gives you an ability to decode not only the linguistic content, but some of the prosodic content of speech, some of the affect. I think that’s what we’ve really begun to crack the code on.” It is a significant development for brain-computer interface technology, which aims to connect humans to machines in order to fix neurological disorders or even add new abilities. Elon Musk claims that future versions of his Neuralink device will allow wearers to stream music directly to their brain, as well as cure depression and addiction by “retraining” certain parts of the brain. The scientists behind the latest research claim that advances in brain recording techniques could soon allow them to make detailed recordings using non-invasive techniques like ultra-sensitive electrodes attached to the scalp. “Non-invasive techniques are just not accurate enough today,” said postdoctoral fellow Ludovic Bellier, who was part of the research team. “Let’s hope, for patients, that in the future we could, from just electrodes placed outside on the skull, read activity from deeper regions of the brain with a good signal quality. But we are far from there.” The research was detailed in a study, titled ‘Music can be reconstructed from human auditory cortex activity using nonlinear decoding models’, published in the scientific journal PLoS Biology. Read More Paralysed man communicates first words in months using brain implant: ‘I want a beer’ Elon Musk’s Twitter slows down access to rival websites Musk’s Twitter takeover sparks mass exodus of climate experts Snapchat experiences ‘temporary outage’ as My AI chatbot posts own Story
2023-08-17 00:57

Visa's pricing of token technology under DOJ probe - Bloomberg News
(Reuters) -Visa is under fresh investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice over allegations it is charging retailers more for
2023-08-16 23:23
