
Britain says may clear restructured Microsoft-Activision deal
Microsoft's restructured acquisition of Activision Blizzard "opens the door" to the deal being cleared, Britain's antitrust regulator said on Friday.
2023-09-22 14:17

X is shutting down feature to send posts to select people after privacy concern
X is shutting down Circles months after some users flagged glitches with the privacy-focused tool that lets users send posts to a select audience. The Elon Musk-owned company that was earlier called Twitter said on Thursday that Circles will be disabled by 31 October. “After this date, you will not be able to create new posts that are limited to your Circle, nor will you be able to add people to your Circle,” X wrote in a post. “You will, however, be able to remove people from your Circle, by unfollowing them,” the company said. Once unfollowed, users previously part of one’s Circle “can no longer see your past Circle Posts,” it said. The feature – similar to Instagram’s Close Friends stories – was officially launched in August 2022 when the platform was called Twitter, and before the Tesla billionaire took over the company. “Twitter Circle is a way to send Tweets to select people, and share your thoughts with a smaller crowd,” the company had said after the feature’s launch. “You choose who’s in your Twitter Circle, and only the individuals you’ve added can reply to and interact with the Tweets you share in the circle,” it had then said. Then in April, a software glitch exposed the private posts of some users to other followers and strangers not part of their Circle, sparking widespread privacy concern. Users began noticing their private Circle posts began appearing on the algorithmically generated “For You” timeline, meaning these posts were being noticed by people outside the intended audience. In some cases, users noticed their Circle posts were even reaching people who don’t even follow them. In emails sent to affected users, X said a “security incident” was behind the public display of their Circle tweets, adding that the issue was “immediately fixed” so these posts were no longer visible outside of the user’s Circle. “We’ve conducted a thorough investigation to understand how this occurred and have addressed this issue,” the company said. “We understand the risks that an incident like this can introduce and we deeply regret this happened,” it said at the time. The software bug added to the number of issues that plagued Twitter following Mr Musk’s takeover of the company and the multibillionaire laying off nearly two-thirds of its workforce. The glitch was likely due to the platform’s recommendation algorithm likely failing to filter out Circle posts before sharing them with others on the site, former Twitter engineer Theo Browne told TechCrunch at the time. Now, in a new update, X said in a post that it is “deprecating Circles as of Oct 31st, 2023”, without delving into why the company is shutting down the feature. Read More Two dead and dozens injured after bus carrying high school band crashes on I-84 in New York Tourist calls police after being charged £500 for chilli crab in Singapore Scientists discover world’s oldest human-built structure, built by an extinct species ChatGPT can now generate images and create illustrated books Man drives off bridge ‘following Google Maps’ Solar panel breakthrough could supercharge ‘miracle material’ production
2023-09-22 12:50
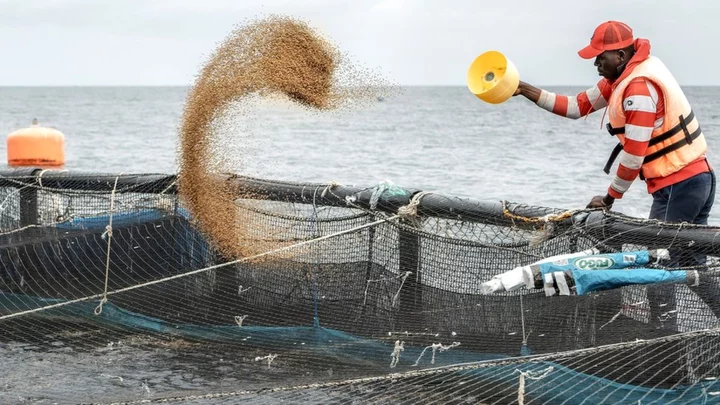

Despite risks fish farms are booming in Africa
Farming fish has seen rapid growth in Africa but it can be an expensive, high-risk operation.
2023-09-22 07:48

YouTube unveils a slew of new AI-powered tools for creators
YouTube on Thursday unveiled a slew of new artificial intelligence-powered tools to help creators produce videos and reach a wider audience on the platform, as companies race to incorporate buzzy generative AI technology directly into their core products.
2023-09-22 05:16

Cisco taps new M&A firm Tidal for $28 billion Splunk deal
By Milana Vinn and Anirban Sen NEW YORK A new mergers and acquisitions advisory firm launched last year
2023-09-22 00:27

Thailand's new PM meets Tesla chief Musk in New York
BANGKOK (Reuters) -Thailand's new Prime Minister Srettha Thavisin said on Thursday he met with Tesla chief Elon Musk in New
2023-09-21 23:55

TikTok was built off of Black creators. Black employees say they faced discrimination
Nnete Matima said she was attracted to work at TikTok because of how the social media platform was "really built upon Black culture" and the work of Black creators.
2023-09-21 23:16

The ten best vacuum cleaners
Chosen by Charlie Minter Click on the image to the right to launch our guide
2023-09-21 21:26
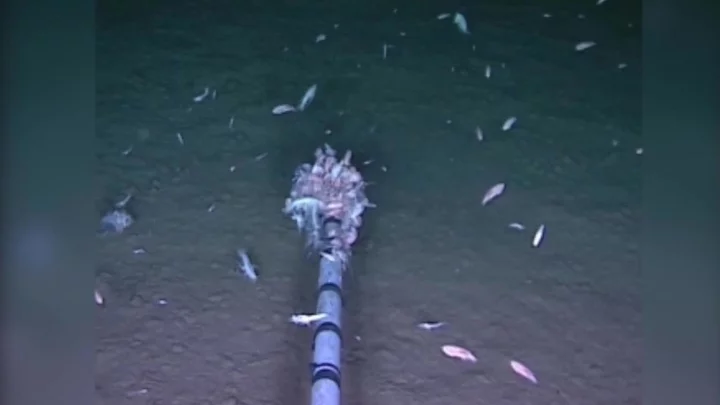

Scientists have found a novel virus at the bottom of the ocean
Scientists have discovered a new virus in the Pacific that is thought to be the deepest ever found in Earth’s oceans. The so-called bacteriophage virus infects and replicates inside bacteria, and was found in the Mariana Trench, which is the Pacific’s deepest point. Bacteriophages are among the world’s most abundant life forms, and are important for regulating population sizes in the oceans and releasing nutrients. This one, the catchily named vB_HmeY_H4907, was picked up at 8,900 metres below sea level. That is still some way off the 11,000 metre floor of the trench. Min Wang, a marine virologist from the Ocean University of China, said: “To our best knowledge, this is the deepest known isolated phage in the global ocean.” “Wherever there’s life, you can bet there are regulators at work. Viruses, in this case.” Scientists think this virus is likely to be distributed widely in the world’s oceans, despite the fact it has only been discovered. It has a similar structure to its host bacteria group halomonas. These are usually found in sediments and geyser-like openings on the seafloor. They also think the virus is lysogenic, which means it infects the host but does not kill it. Dr Wang said the discovery could inform further research about how viruses survive in the world’s harshest environments. “Extreme environments offer optimal prospects for unearthing novel viruses,” he added. The virus was found in the so-called hadal zone, which the study’s authors said is “the planet’s least explored and most mysterious environment, and it is the deepest habitat for life on Earth’s surface”. The area is named after Hades, the Greek god of the underworld. Researchers wrote in the study: “These findings expand our understanding of the phylogenetic diversity and genomic features of hadal lysogenic phages, provide essential information for further studies of phage-host interactions and evolution, and may reveal new insights into the lysogenic lifestyles of viruses inhabiting the hadal ocean.” The findings were published in the journal Microbiology Spectrum. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 20:50

Scientists issue warning about asteroid heading to Earth with force of 24 atomic bombs
Scientists are on alert after NASA confirmed there is a chance an asteroid the size of the Empire State Building could come smashing into Earth. The asteroid is named Bennu after the ancient Egyptian bird god and has been on the space agency’s radar for a long time as they try to prevent it from coming crashing into our planet. Bennu has been categorised as one of the two “most hazardous known asteroids” and, despite the chance of impact standing at 1-in-2,700, it could strike the Earth with the force of 24 times that of the largest nuclear bomb – 1,200 megatons of energy. The carbon-based asteroid is approximately 510 metres wide and experts predict that it will come closest to hitting Earth on September 24, 2182. While the asteroid is quite sizeable, it is not quite as sizeable as the six-mile-wide asteroid which almost completely wiped out the dinosaurs. But, NASA warns that Bennu “could cause continental devastation if it became an Earth impactor”. A space mission launched using NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft has successfully taken a sample from Bennu in order for scientists to better understand the potentially dangerous asteroid. On Sunday (24 September) a capsule of the material will be dropped by OSIRIS-REx and returned to Earth where it will be retrieved and the matter inside studied. Davide Farnocchia of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory told the Science Journal: “We improved our knowledge of Bennu's trajectory by a factor of 20.” As scientists work to investigate how much of a risk it could cause, Farnocchia added: “In 2135, we'll know for sure.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 20:20

Cisco beefs up cybersecurity play with $28 billion Splunk deal
(Reuters) -Cisco Systems has agreed buy cybersecurity firm Splunk for about $28 billion in its biggest-ever deal to beef up
2023-09-21 20:19
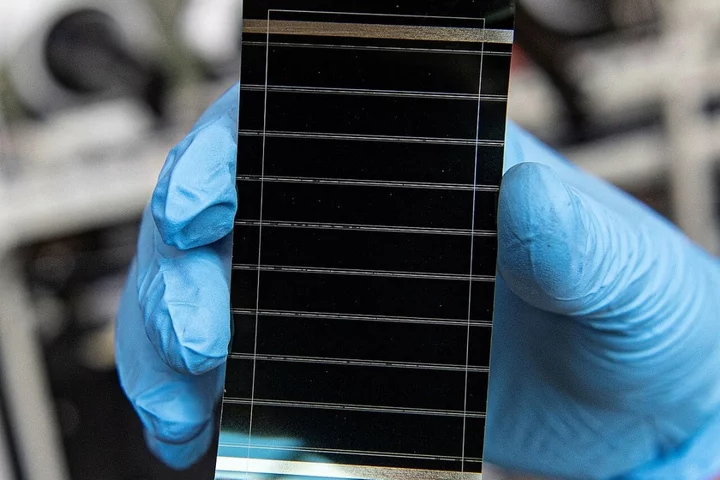
Solar panel breakthrough could supercharge ‘miracle material’ production
Scientists have made a major breakthrough with a new type of solar panel that they claim could supercharge the transition to renewable energy sources. A team from the University of Surrey discovered that a nanoscale “ink” coating could improve stability enough to make next-generation perovskite solar cells suitable for mass production. Perovskite is cheaper and lighter than conventional silicon-based cells, as well as far more efficient, however the emerging technology currently suffers from a drop in efficiency and energy output during the manufacturing process. “Performance limits of traditional solar cells are why researchers are switching to examining perovskite as the next-generation solar technology, especially as applications both terrestrial and in space are rapidly growing,” said Dr Imalka Jayawardena from the University of Surrey’s Advanced Technology Institute (ATI). “Our key development in solar panel technology shows a cost-effective approach to scaling of perovskite solar cells, a development which could help countries around the world to reach their net zero targets faster.” The breakthrough was made when the researchers identified an aluminium oxide that minimises the drop in efficiency during the conditioning of perovskite solar cells. Perovskite has been hailed as a “miracle material” for its potential to transform an array of industries, from ultra high-speed communications to renewable energy. Recent advances have seen it used to create self-healing solar panels that can recover 100 per cent of their efficiency after being damaged by radiation in space, as well as break new efficiency records when combined with silicon to form tandem cells. If the cheap-to-produce perovskite cells can be manufactured at scale while retaining their durability and reliability, then the cost of solar panels would plummet. “Solar and wind energy costs are rapidly decreasing based on technology improvements, to the level where worldwide over 80 per cent of all new additional power generation capacity is based on renewables,” said Ravi Silva, from the ATI, University of Surrey. “The levelized cost of solar electricity is now cheaper than most other power-generating sources. With the maturing of perovskite solar modules, the levelized cost of electricity will significantly decrease further, and that is why this is such an exciting area to work.” The research was detailed in a study, titled ‘Modification of Hydrophobic Self-Assembled Monolayers with Nanoparticles for Improved Wettability and Enhanced Carrier Lifetimes Over Large Areas in Perovskite Solar Cells’, published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Solar PRL. Read More Hundreds of years after it was discovered, one material is about to change the world ‘Miracle material’ smashes solar panel efficiency threshold Scientists invent solar panels that work in a snow blizzard September Supermoon: When is it and how to view it? Amazon Alexa is getting the same brain as ChatGPT
2023-09-21 19:21
