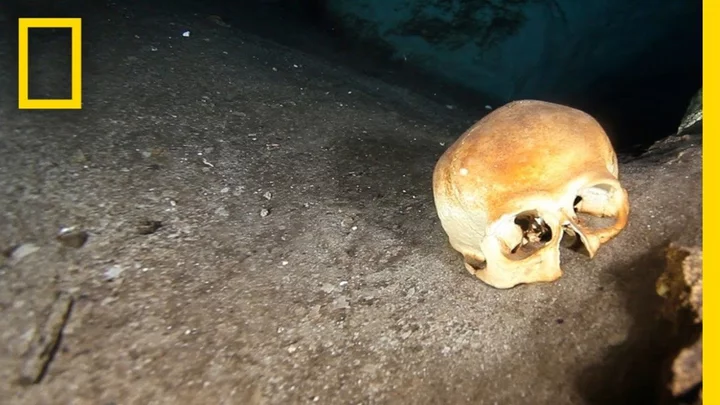

Disturbing cache of elongated human skulls discovered in flooded Mexican sinkhole
When archaeologists explored an underwater cavern in southern Mexico in 2014, they were shocked by what they found. The cavern is known as Sac Uayum, and is located in Mexico’s Yucatán peninsula. It is technically a cenote – a natural pit that comes about after limestone bedrock collapses, exposing groundwater beneath. Local villagers were said to be terrified of the spot, because pits like this were sometimes used by the ancient Maya for sacrificial offerings. Archaeologist Bradley Russell, from College of St Rose, and a group of divers scaled down roughly 20 metres into the unknown. Inside the pit were two chambers with human bones and skulls scattered across the floors of each. The skulls were elongated, as part of an ancient practice that is thought to have involved flattening people’s heads during infancy. Archaeologists still don’t know why the ancient culture did this – but it ain't pretty. The cenote sits just outside the ruins of the ancient Maya city of Mayapán, and the researchers think this shows that, like the modern day locals, the ancient Mayans kept their distance too. Local legend says that Sac Uayum is guarded by a feathered, horse-headed serpent. Older residents of the nearby village of Telchaquillo tell stories of people seeing the serpent perching in a tree, leaping up, spinning around three times, and diving into the water. Russell explained to National Geographic that the sinkhole is said to be “evil”. “To this day, people do not get drinking water from that cenote, it is generally considered taboo. “It’s off-limits, people do not let their children plan near there and there’s a lot of beliefs around this cenote having evil forces or malevolent forces associated with it. “Cenotes are important because the main access to the water that you get is through these sinkholes. “They are also believed to be access to the Mayan underworld and the homes of Gods. “Mayapan is a large city, it’s incredibly dense, there’s nothing like it in the classic period, it’s incredibly dense for Maya history, there’s nothing quite like it.” He added that the location of Sac Uayum – south of Mayapan – is a clue as to what was going on. In Maya beliefs, south is the direction associated with the underworld. Alternatively, Russell also suggested they could have been plague victims. "You wouldn't want them near the rest of the population. And you wouldn't want to drink the water either.” How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-30 03:56

4 Big Misconceptions About the Human Body
Considering how familiar we all are with the human body—since we all have one—there is a surprising number of enduring myths about it.
2023-11-30 00:21

How to see your Spotify Wrapped for 2023?
It's almost that time of year again, when we see how many hours we've shamelessly spent listening to mortifying music and just playing Taylor Swift on loop. Yes, Spotify Wrapped is here again and soon your social media feeds will be full of people either showing you how cool by how much Senegalese lounge Jazz they listen to or embarrassed that they still haven't moved on from The Libertines or The Strokes. Each and every year, even for the most dedicated of music lovers, Spotify Wrapped throws up countless surprises in your top artists and songs leading many to question just how it tallies what you listen to. The past few years Wrapped has arrived earlier and earlier, as reported by the Radio Times, so it's not surprise that its arrived on November 29th. Here are the dates it arrived on the previous years. 2017: 6th December 2018: 6th December 2019: 5th December 2020: 2nd December 2021: 1st December 2022: 30th November Finding your Wrapped couldn't be easier you just need to go to your Spotify app on the day it drops and it'll be there waiting for you at the top of the app alongside your saved songs and albums. Alternatively, if you just use Spotify on a laptop or desktop you can visit spotify.com/wrapped and use it from there. Spotify have never officially said how they compile their data for Wrapped but a Reddit user in 2021 revealed how they believed it works. In the post Hudsonlovestech pointed out six key takeaways that they discovered after downloading their data from the music platform. They were: This year the data was logged from January 1st 00:00 to November 15th 23:59. You have to listen to a song for more than 30 seconds for it to count in your song rankings. Your top songs are calculated by play count rather than total time listened. In your top 100 playlist only the first 10 songs are sorted by play count, the rest are close but sorted by artist. Your total time listening includes podcasts. Your top artists are calculated by total play counts rather than total time listening. If you apply this date to your own listening history then there is a chance you might discover what your Wrapped will look like this year although there is no guarantee. Meanwhile, many users on X/Twitter are posting memes, imagining what their Wrapped will look like this year. To be honest, we're just dreading seeing how much we listened to Ryan Gosling sing 'I'm Just Ken' from the Barbie soundtrack. Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-29 21:51

Putin’s Daughter Pursues Digital Plan in Push to Embrace Africa
Russia is stepping up its pursuit of closer ties with Africa by offering digital expertise in a strategy
2023-11-29 19:50

How to predict your 2023 Spotify Wrapped
It's almost that time of year again, when we see how many hours we've shamelessly spent listening to mortifying music and just playing Taylor Swift on loop. Yes, Spotify Wrapped is almost here again and soon you social media feeds will be full of people either showing you how cool by how much Senegalese lounge Jazz they listen to or embarrassed that they still haven't moved on from The Libertines or The Strokes. Each and every year, even for the most dedicated of music lovers, Spotify Wrapped throws up countless surprises in your top artists and songs leading many to question just how it tallies what you listen to. With the big day somewhere on the horizon (it arrived on November 30 in 2022 and December 1 in 2021) music nerds are curious to know what their Wrapped will look like for 2023. Spotify have never officially said how they compile their data for Wrapped but a Reddit user in 2021 revealed how they believed it works. In the post Hudsonlovestech pointed out six key takeaways that they discovered after downloading their data from the music platform. They were: This year the data was logged from January 1st 00:00 to November 15th 23:59. You have to listen to a song for more than 30 seconds for it to count in your song rankings. Your top songs are calculated by play count rather than total time listened. In your top 100 playlist only the first 10 songs are sorted by play count, the rest are close but sorted by artist. Your total time listening includes podcasts. Your top artists are calculated by total play counts rather than total time listening. If you apply this date to your own listening history then there is a chance you might discover what your Wrapped will look like this year although there is no guarantee. Meanwhile, many users on X/Twitter are posting memes, imagining what their Wrapped will look like this year. To be honest, we're just dreading seeing how much we listened to Ryan Gosling sing 'I'm Just Ken' from the Barbie soundtrack. Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-29 03:26
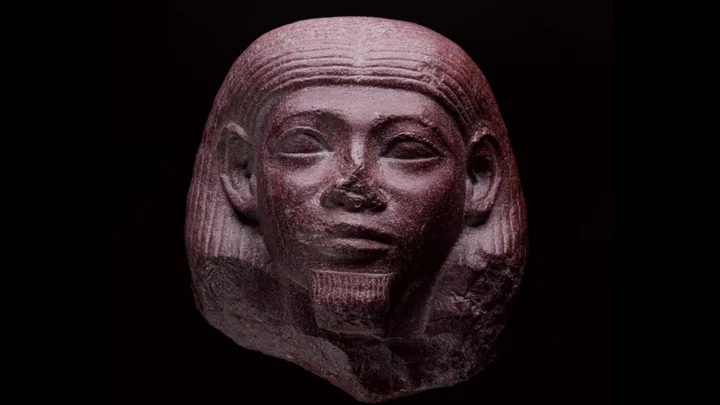

How a Scottish boy digging for potatoes found an ancient Egyptian 'masterpiece'
For decades, archaeologists have been trying to work out how a trove of ancient Egyptian artefacts were buried in the grounds of a school in Scotland. In 1952, a schoolboy was sent to dig up potatoes as a punishment – how times have changed – when he found a statue. It turned out to be a masterpiece made some 4,000 years ago. Fourteen years later, more treasure was discovered by a boy during a PE class, before, in 1984, a group found another item with a metal detector. It turned out to be part of a set of 18 antiquities dug up over the next 30 years at Melville House, a historic building in Fife, Scotland. But nobody had any idea how they got there. Now, researchers think they might have unearthed what was going on. Alexander Lesie-Melville was a young heir to Melville House when he travelled to Egypt in 1856. A year later, he had returned to Scotland and died. Leslie-Melville might have picked up the collection on his travels – it certainly beats the Duty Free section at Heathrow – as antique dealers routinely sold ancient artefacts to rich foreigners during that period. After Leslie-Melville died, family members are thought to have moved the objects to an outbuilding, where they were promptly forgotten about. The outbuilding was then demolished. Margaret Maitland, principal curator of the Ancient Mediterranean at National Museums Scotland where most of the objects are housed, said: “The discovery of ancient Egyptian artifacts that had been buried in Scotland for over a hundred years is evidence of the scale of 19th century antiquities collecting and its complex history.” “It was an exciting challenge to research and identify such a diverse range of artefacts.” Dr Elizabeth Goring, who has since investigated the site, said: “Excavating and researching these finds at Melville House has been the most unusual project in my archaeological career, and I’m delighted to now be telling the story in full." The full story will be published in an upcoming article in the journal Proceedings of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-29 02:21
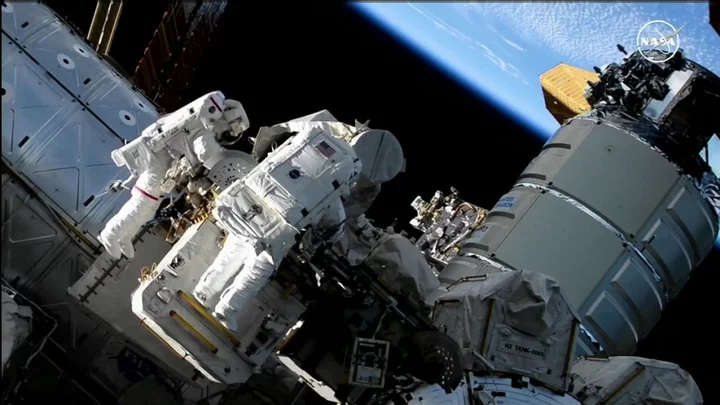

A terrifying thing happens to astronauts' fingernails on a spacewalk
Going on a spacewalk might sound like a lot of fun – but in reality it’s no walk in the park. From their muscles getting less dense all the way to erectile dysfunction, astronauts have to put up with all sorts of things going wrong with their body. And none more gross than what happens to their fingernails. Turns out they just fall right off. The technical term for this is onycholysis, and it has to do with how much – or how little – atmospheric pressure there is in space. Because there is so little ambient pressure in space, astronaut’s space suits need to be pressurised to keep the human body intact. But that’s not good for the hands, it turns out. “Injuries to the hands are common among astronauts who train for extravehicular activity (EVA),” says a 2015 conference paper by space specialists Wyle Laboratories. “When the gloves are pressurized, they restrict movement and create pressure points during tasks, sometimes resulting in pain, muscle fatigue, abrasions, and occasionally more severe injuries such as onycholysis. “Glove injuries, both anecdotal and recorded, have been reported during EVA training and flight persistently through NASA's history regardless of mission or glove model." A 2010 study looked at 232 hand injuries sustained by astronauts, and found that the wider your knuckle joints, the more likely you are to suffer in a space suit. The study suggested that because space suit gloves limit the mobility of these knuckles, the fingers then get put under more pressure. This, in turn, means less blood gets to the fingers, and risks onycholysis. Ouch. Work has been done to try to improve the design of space suit gloves, of course. One team found that the more tailored they were to each astronaut’s finger length the less likely they were to lose their fingernails. That’s no mean feat, however. These gloves are made of at least four layers: one which touches the skin, one which helps create the pressurised environment, another one which makes the pressure layer less stiff, and an outer layer which protects the astronaut from everything on the outside. Mercifully for NASA astronauts at least, they usually have their gloves fitted to each wearer, and with new space suit design moving forward each day, the number of injuries is decreasing. Nonetheless, it sounds like a trip to space is no time for a manicure. How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-28 21:46

New research suggests dinosaurs were wiped out by more than just a meteorite
We’ve all been told the story of what wiped out the dinosaurs – a giant meteor careers down from the sky, crashes into Earth and bang! The rest is history. But what if that wasn’t the whole story? A new study suggests there may have been more to it than just an asteroid – and it involves climate change. A chain of huge volcanic eruptions which eventually cooled the planet an alarming amount may have been partially to blame, according to research. The study, published in Science Advances and co-authored by Don Baker, a professor in McGill University's Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, suggests that this might be the case. The researchers looked into volcanic eruptions at the Deccan Traps, a huge, rugged plateau that formed when molten lava solidified and turned to rock. The plateau dates back to around 66-65m years ago, when magma from deep inside Earth erupted to the surface. That just so happens to be around the time when scientists think the dinosaurs met their demise. Baker’s team suggest that the eruptions produced a staggering 1m cubic kilometres of lava, which then turned into rock, which may have played a key role in cooling the global climate around 65m years ago. The scientists say it’s all to do with how much sulphur and fluorine was pumped into the atmosphere as a result of the eruptions. Incredibly, they found the event could have sparked a drop in temperature all around the world, dubbed a “volcanic winter”. Baker said: “Our research demonstrates that climatic conditions were almost certainly unstable, with repeated volcanic winters that could have lasted decades, prior to the extinction of the dinosaurs. “This instability would have made life difficult for all plants and animals and set the stage for the dinosaur extinction event. “Thus our work helps explain this significant extinction event that led to the rise of mammals and the evolution of our species.” The scientists worked it out using new chemical techniques developed at McGill to measure how much sulphur is in the rock formations which came about at the time, then from that, figuring out how much went into the atmosphere. The paper is titled “Recurring volcanic winters during the latest Cretaceous: Sulfur and fluorine budgets of Deccan Traps lavas.” How to join the indy100's free WhatsApp channel Sign up to our free indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-11-28 21:26

Novartis Raises Annual Sales Growth Forecast After Restructuring
Novartis AG raised its mid-term sales growth forecast as the Swiss drugmaker narrows its focus on innovative medicines
2023-11-28 15:46

North Korea Claims New Spy Satellite Took Photos of White House
North Korea claimed its first spy satellite, which was launched into orbit this month, has taken photos of
2023-11-28 09:00
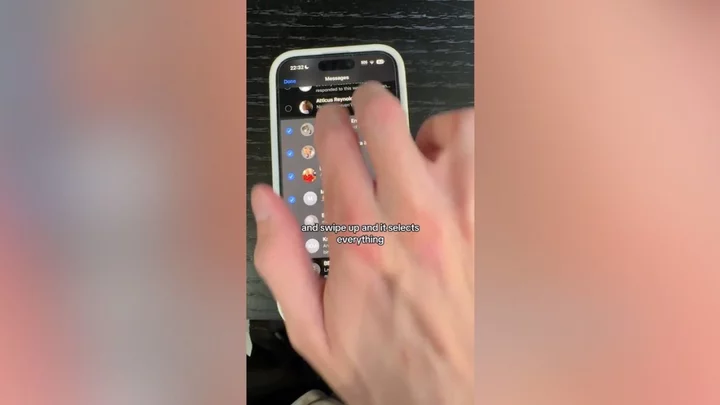
Ex-Apple employee reveals game-changing iPhone hacks everyone should know
A former Apple employee has been sharing some of the handy iPhone hacks he learnt while working at the tech giant - and we can't believe we didn't know them before. From tips as simple as holding your camera button down to record a video instead of swiping, to switching to a 'one-handed keyboard' to save your muscles aching, Tyler Morgan has completely changed the way his followers are using their phones. Arguably one of the most popular he recommended is that you can actually do voiceovers while screen recording, by swiping down to reveal a microphone button. Sign up to our new free Indy100 weekly newsletter
2023-11-28 00:52

North Korea Brings Backs Weapons and Troops to Shut Border Posts
North Korea appears to have deployed soldiers and weapons to guard posts near the border that were shut
2023-11-27 13:48
