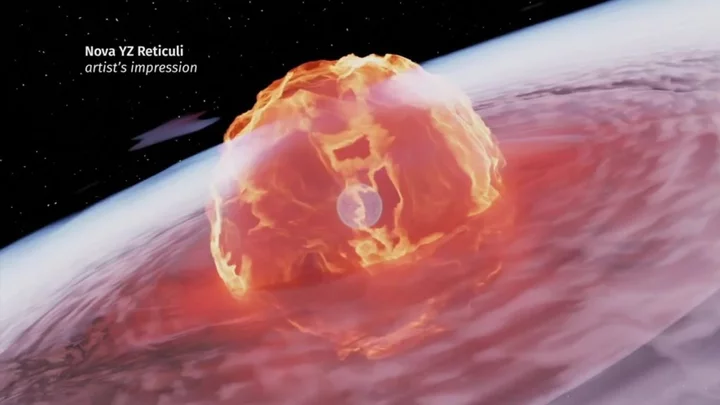

Time-lapse that took 20 years to make shows legendary stellar explosion
Scientists have spent 20 years putting together time-lapse footage offering a stunning window into the past. Two decades of data taken from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory were used by astronomers to create a video of a stellar eruption that actually occurred 180 years ago. Observations from Chandra, taken in 1999, 2003, 2009, 2014 and 2020 were all used, in combination with data from ESA’s XMM-Newton spacecraft. With the combined data, experts were able to capture the stellar explosion, known as Eta Carinae. Eta Carinae is a famous star system containing two large stars, one of which is around 90 times larger than the Sun, while the other is around 30 times as large. The “Great Eruption” from Eta Carinae is believed to be the result of the merging of two stars that were originally part of a three-star system. Eta Carinae Time-Lapse, Chandra X-ray Observatory www.youtube.com It first took place in the mid-19th century and the aftermath is still continuing to be observed today. New footage shows how the explosion has expanded into space with staggering speeds of up to 4.5 million miles per hour. In a statement, NASA officials explained: “During this event, Eta Carinae ejected between 10 and 45 times the mass of the sun. This material became a dense pair of spherical clouds of gas, now called the Homunculus Nebula, on opposite sides of the two stars.” The Homunculus Nebula is the blue cloud visible in the video, while the growing bright orange ring shows how X-ray emissions have grown and expanded over time. “The new movie of Chandra, plus a deep, summed image generated by adding the data together, reveal important hints about Eta Carinae’s volatile history,” the statement read. “This includes the rapid expansion of the ring, and a previously-unknown faint shell of X-rays outside it.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-28 18:53

People are just learning Google's original name – and thanking god that it was changed
A world without Google would almost be akin to a world without water or air. Indeed, the internet behemoth’s power is so great that it’s even become its own verb. And sure, there are other search engines, but when have you ever heard someone say: “Let me just Bing that”? Yet, it turns out the iconic tech company could have had a very different fate had it stuck to its original name. That’s right, Google hasn’t always been Google. And at its inception back in 1996, it had a somewhat more risqué title. It was called… BackRub. Yep, BackRub. According to Standford University computer scientist David Koller, who wrote about the brand’s genesis back in 2004, founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin came up with the search engine's first name as a nod to its analysis of the web’s “back links”. However, a year after BackRub was born, Page and his officemates – including fellow graduate students Sean Anderson, Tamara Munzner, and Lucas Pereira – discussed a number of possible alternatives to the massage-evoking moniker. According to Koller, the final, fateful brainstorming session occurred one day in September of that year. “Sean and Larry were in their office, using the whiteboard, trying to think up a good name - something that related to the indexing of an immense amount of data,” he recalled. “Sean verbally suggested the word ‘googolplex,’, and Larry responded verbally with the shortened form, ‘googol’ (both words refer to specific large numbers). “ Anderson then searched the Internet domain name registry database to see if the newly suggested name was still available to use. But, since “Sean is not an infallible speller”, “he made the mistake of searching for the name spelt as ‘google.com,’ which he found to be available,” Koller continued. “Larry liked the name, and within hours he took the step of registering the name ‘google.com’ for himself and Sergey.” And the rest, as they say, is history. Sill, 25 years on from that simple domain name registration that would go on to change the world, people have shared their bewilderment that “BackRub” could have become a household name. “I could die without knowing that this was Google's old name,” one X/Twitter user commented. “What were they smoking back in 90s??” asked another. Meanwhile, a third responded with what we’re all now thinking: “Tbh I need a backrub.” At least the tech titans can now give themselves a pat on the back for a job well done with “Google”. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-28 16:51
Sushi could secretly be spreading antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are an increasing area of concern for health experts and scientists are concerned that the popular food sushi could be spreading it. Researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology were interested in looking at the health implications of sushi, which is considered pretty standard fare in the country. Dr. Hyejeong Lee, who recently completed her PhD at the Department of Biotechnology and Food Science at NTNU, investigated different varieties of Aeromonas bacteria in seafood products that aren’t processed in a way that reduces bacteria, such as sashimi (raw fish) and cold-smoked fish. Lee explained: “The goal was to gain more knowledge about Aeromonas in this type of seafood – both the bacteria’s role in the deterioration of the product and in causing disease. Furthermore, we wanted to see if raw seafood can spread antibiotic-resistant bacteria.” While Listeria monocytogenes is the most well-known bacteria that can cause illness from unprocessed seafood, the prevalence of Aeromonas in similar products is an increasing worry for scientists for another reason. This is because Aeromonas bacteria frequently exchange genetic material with other bacteria in the sea, which means they can inherit and spread resistance to antibiotics before ending up in sushi. Lee explained: “Some strains of Aeromonas can also spread antibiotic resistance from one type of bacteria to another. Eating seafood infected by resistant bacteria is a likely way these bacteria can spread from marine animals and environments to humans.” Resistant bacteria are foreseen to be a big problem in the future, with the worst-case scenario being that few or no antibiotics will work at treating them. Experts believe it is important that antibiotic resistance is seen as a broad approach that is seriously considered in all aspects of society. Anita Nordeng Jakobsen, associate professor at NTNU’s Department of Biotechnology and Food Science, explained: “To combat the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, it is important that we adopt a broad approach that looks at animal and human health, food production and the environment together in order to achieve better public health.” Still, Lee was quick to emphasise that the risk of getting sick from Aeromonas is very small, especially for healthy people. But, she stressed: “Aeromonas is often ignored when we talk about food safety. I think my research highlights that the food industry needs to pay more attention to these bacteria." Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-28 15:55

Right again, Einstein! Study shows how antimatter responds to gravity
By Will Dunham In the world of "Star Trek," the starship Enterprise zips through space using a warp
2023-09-27 23:18
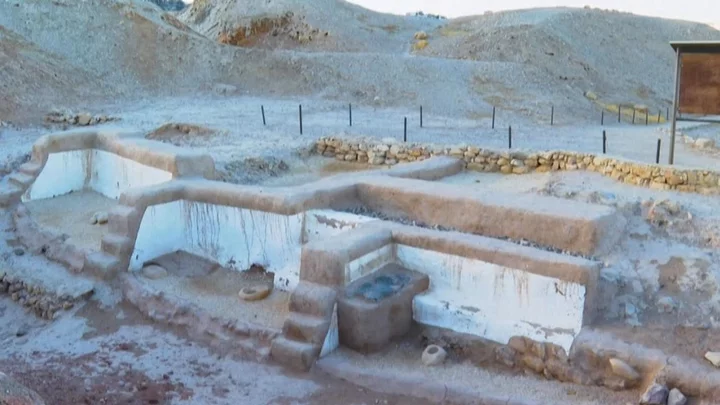

Archaeologists have discovered a new language in the ruins of an ancient empire
Ancient clay tablets unearthed from ancient ruins in Turkey by archaeologists have revealed a language lost to the passages of time. The new language was discovered in the ancient capital of the Hittite Empire at Hattusa (known as Boğazköy-Hattusha). The well-preserved tablets are among many incredible artworks found at the site - a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Over the past four decades, researchers have dusted off nearly 30,000 unique tablets - with most written in Hittite. New research, however, shows that some of the tablet haul shows that they are written in a language previously unknown to modern man. Of course, the meaning and words of this language have not been deciphered, but it appears from early inspection to branch off from languages used within the Hittite Empire - and is being referred to as Kalašma. archaeologist Interestingly though, researchers from the Istanbul Department of the German Archaeological Institute have noted that the new language is found within a recitation in a 'cultic ritual text'. While that's usually the basis of a middling horror movie, we're certain that there's nothing to worry about - it stems from an ancient Hittite practice. Professor Daniel Schwemer explains that the discovery wasn't unexpected. "The Hittites were uniquely interested in recording rituals in foreign languages," he said. These ritual texts provide insight into little-known languages, and thanks to this discovery, one more has been added to the list. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-27 20:26
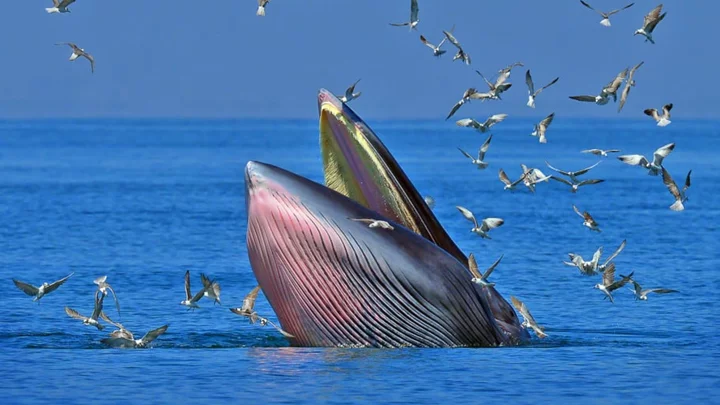

Watch Rare Drone Footage of Bryde’s Whales Feeding
Scientists in New Zealand used a custom-built drone to record this rare moment.
2023-09-27 02:27

New study suggests blue light from phones may drastically alter puberty
Blue light emitted from the screens of phones, tablets and televisions could induce puberty early, a study has found. In the modern day, children are raised with devices all around them, with many having a phone or tablet to keep them entertained from a young age. But, researchers in Turkey have discovered that it exposure to the blue light such devices give off could speed up the onset of puberty. Teams from the Gazi University and Bilkent City Hospital in Ankara revealed how they saw the effect in male rats, which could suggest a link between device screens and early childhood development. Their findings were presented at the 61st Annual European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology Meeting in The Hague and published in the Frontiers in Endocrinology journal. The study emulates the same findings that were observed in female rats, where early puberty was seen. Lead researcher Dr. Aylin Kılınç Uğurlu, of Bikent City Hospital, said: “For the first time, we found a direct relationship between blue light exposure and early puberty in male rats.” They continued: “Our findings align with our previous work on female rats, which also showed similar effects, thereby providing a more comprehensive view of how blue light may influence puberty in both male and female rats.” As part of the study, 18 male rats, all 21 days old, were split into three groups. Two of the groups were assigned either six or 12 hours of blue light exposure per day. The last group was a control and was not exposed to any blue light from screens. Results showed that the rats with exposure to blue light experienced signs of puberty “significantly earlier” compared with the control group. Uğurlu noted in a news report: “I want to emphasise that this is a rat study and direct results cannot be interpreted for humans. “However, we provide an experimental foundation to further investigate the health consequences of ever-increasing screen time in modern society.” Researchers hope to continue their study on the effects of blue light on rats to “understand its long-term effects on reproductive organ damage and fertility”. Uğurlu continued: “Ultimately, this research could lead to preventative measures and contribute to the ongoing discourse on how modern lifestyles affect physiological development and long-term health.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-26 23:59
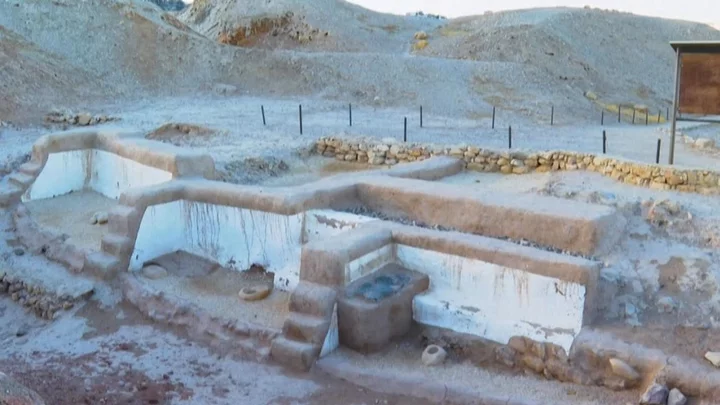

Archaeologists unearth never-before-seen language in ancient ruins
Ancient clay tablets unearthed from ancient ruins in Turkey by archaeologists have revealed a language lost to the passages of time. The new language was discovered in the ancient capital of the Hittite Empire at Hattusa (known as Boğazköy-Hattusha). The well-preserved tablets are among many incredible artworks found at the site - a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Over the past four decades, researchers have dusted off nearly 30,000 unique tablets - with most written in Hittite. New research, however, shows that some of the tablet haul shows that they are written in a language previously unknown to modern man. Of course, the meaning and words of this language have not been deciphered, but it appears from early inspection to branch off from languages used within the Hittite Empire - and is being referred to as Kalašma. archaeologist Interestingly though, researchers from the Istanbul Department of the German Archaeological Institute have noted that the new language is found within a recitation in a 'cultic ritual text'. While that's usually the basis of a middling horror movie, we're certain that there's nothing to worry about - it stems from an ancient Hittite practice. Professor Daniel Schwemer explains that the discovery wasn't unexpected. "The Hittites were uniquely interested in recording rituals in foreign languages," he said. These ritual texts provide insight into little-known languages, and thanks to this discovery, one more has been added to the list. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-26 23:22
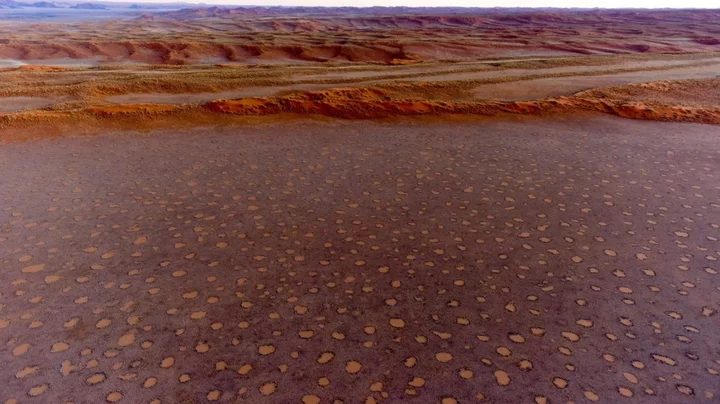

Mysterious 'fairy circles' are spreading across the world and scientists don't know why
A natural phenomenon consisting of polka-dot-style formations has been cropping up around the world, and scientists are baffled as to why. The circular-shaped patches of ground have been seen in deserts in Australia and Namibia but now experts believe they are more widespread than originally thought. Known as “fairy circles”, there are now 263 known sites across the globe where they can be found, according to new research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). They have been documented in 15 countries, across three continents, including the Sahel region of Africa, Madagascar, and in Middle-West Asia. And yet, despite the spread of these anomalies, scientists are still none the wiser about how they actually form. A team led by environmental scientist Emilio Guirado, of the University of Alicante in Spain, explained in their paper on the "intriguing" phenomenon: “We conducted a global and systematic assessment of fairy circle-like vegetation patterns and discovered hundreds of [fairy-circle]-like locations on three continents. “Our study provides insights into the ecology and biogeography of these fascinating vegetation patterns and the first atlas of their global distribution.” The mysterious circles appear in desert regions and can be as wide as 12 metres (39 feet) in diameter. They are almost always spaced out and rarely connect or overlap with one another. Several theories have been put forward as to what causes them, including, tiny insects, termites, and plant toxins. But, none have been accompanied by any significant evidence and some have been debunked completely. One significant factor limiting their study is they are often found in places that are difficult to access and are inhospitable. Locating the 263 different sites of “fairy circles” involved analysing high-resolution satellite imagery. Guirado and his team wrote in their paper: “[The sites] include those already identified in Namibia and Western Australia, as well as areas never described before, including the Sahel, Western Sahara, Horn of Africa, Madagascar, Southwest Asia, or Central and Southwest Australia. “By doing so, our study provides a global atlas of areas showing FC-like vegetation patterns and expands the known existence of this vegetation type to new countries and continents.” The team hopes that locating new sites will enable them to find common traits that may point towards their cause. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-26 20:15
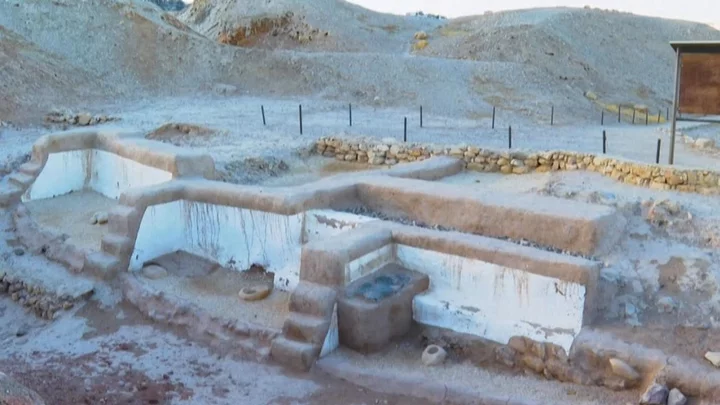

New language discovered in ancient Bronze Age ruins
Ancient clay tablets unearthed from ancient ruins in Turkey by archaeologists have revealed a language lost to the passages of time. The new language was discovered in the ancient capital of the Hittite Empire at Hattusa (known as Boğazköy-Hattusha). The well-preserved tablets are among many incredible artworks found at the site - a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Over the past four decades, researchers have dusted off nearly 30,000 unique tablets - with most written in Hittite. New research, however, shows that some of the tablet haul shows that they are written in a language previously unknown to modern man. Of course, the meaning and words of this language have not been deciphered, but it appears from early inspection to branch off from languages used within the Hittite Empire - and is being referred to as Kalašma. Interestingly though, researchers from the Istanbul Department of the German Archaeological Institute have noted that the new language is found within a recitation in a 'cultic ritual text'. While that's usually the basis of a middling horror movie, we're certain that there's nothing to worry about - it stems from an ancient Hittite practice. Professor Daniel Schwemer explains that the discovery wasn't unexpected. "The Hittites were uniquely interested in recording rituals in foreign languages," he said. These ritual texts provide insight into little-known languages, and thanks to this discovery, one more has been added to the list. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-25 23:28

Scientists believe alien life could exist under 'impossible' conditions
Scientists have found that one of the key pillars of theory around how life works – that it depends on carbon – may not be the case on other planets. Here on Earth, life depends on organic compounds which are composed of carbon, and often involve other elements such as sulphur, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and phosphorus. With organic compounds, life is partly sustained by chemical interactions called autocatalysis, which are self-sustaining. That means they produce molecules which then enable the reaction to happen again, and do not need any outside influence to keep going on. In the new study, scientists looked for autocatalysis in non-organic compounds. The theory is that if autocatalysis helps drive a process called abiogenesis – the origin process for life – then this origin process could also come from non-organic matter. Betül Kaçar, an astrobiologist, bacteriologist and evolutionary biologist at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, told news outlet Space.com: “It's important to explore these possibilities so that we have an idea of what all forms of life can look like, not just Earth life.” "One of the major reasons that origin-of-life researchers care about autocatalysis is because reproduction — a key feature of life — is an example of autocatalysis. “Life catalyses the formation of more life. One cell produces two cells, which can become four and so on. “As the number of cells multiply, the number and diversity of possible interactions multiplies accordingly.” The scientists searched in a huge trove of existing scientific documents for examples of autocatalysis, and found 270 different cycles of the reactions. Most of the 270 examples did not feature organic compounds, but rather elements which are rare in life forms such as mercury, or the radioactive metal thorium. “It was thought that these sorts of reactions are very rare,” Kaçar said in a statement. “We are showing that it's actually far from rare. You just need to look in the right place.” Now, it means scientists can test these cycles to get a better understanding of how autocatalysis can work. “The cycles presented here are an array of basic recipes that can be mixed and matched in ways that haven't been tried before on our planet,” said study author Zhen Peng, also an evolutionary biologist at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. “They might lead to the discovery of completely new examples of complex chemistry that work in conditions where carbon- or even silicon-based cycles are too either combusted or frozen out.” The scientists published their findings in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-25 23:16
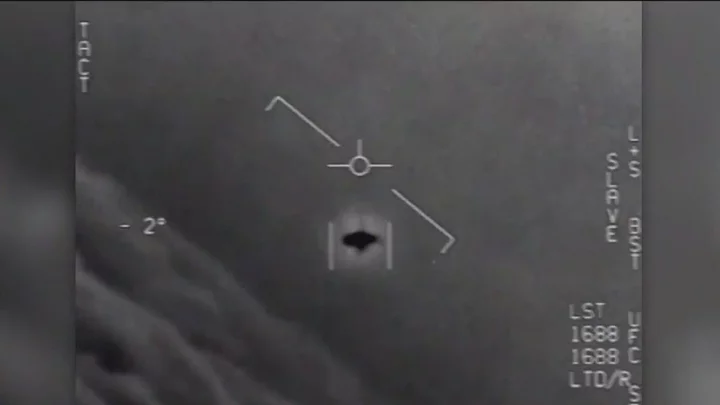

Local baffled by mysterious 'UFO' hovering in the sky
A mysterious spinning ‘UFO’ has been spotted in the night sky by a stunned local. The brightly illuminated object is seen spinning in the air, but it appears to hover above a mountain. The shocked onlooker zooms in on the mysterious aircraft while saying in wonder: “It’s moving.” The hovering UFO was filmed in the village of Honorato Vásquez, Ecuador, on Tuesday (9 Sept) evening. The local authorities have yet to respond to claims that the object was from outer space. One local said: “I believe it.” Manuel wrote: “Those crazy aliens.” Yet Eddy joked: “In that drone there, you wouldn’t even be able to fit two-quarters of a Martian!” It followed an alleged aerial battle between military personnel and several alien spaceships in Argentina this month. Scared locals claimed that the military base was attacked by four black triangular-shaped UFOs. Scores of residents gathered outside the Commander Espora Air Naval Base near Bahía Blanca, Buenos Aires, as thunderous noises sounded from within the perimeter walls. The Commission for the Study of UFO Phenomena of the Argentine Republic, an organisation dedicated to investigating alleged alien sightings, claimed to have information that there were four UFOs seen attacking the military base. The group said the alien spacecrafts were black and triangular in shape and that Argentine troops fired at them with anti-aircraft weapons. Group spokesperson Andrea Pérez Simondini said witnesses saw “four lights entering the territory from across the ocean before taking a strategic position over one of the buildings where ammunition is stored”. However, the military authorities have denied that the base was under attack and claimed that the videos were faked by unscrupulous locals. Navy spokesperson Captain Germán Luis Zarralanga said their Sikorsky SH-3 Sea King helicopter was taking part in a training exercise that night, but was not involved in any kind of altercation with other aircraft. When discussing the social media footage, the spokesperson said: “It’s an edit. I don’t know what their intentions were. “Airport security and airport workers did not report seeing anything, and everyone at the base was sleeping except for the person piloting the helicopter. There was no type of special activity, no tactical manoeuvres, just a normal helicopter training flight, nothing related to ammunition.” One local commented: “Incredible! How many UFOs? I can't believe it! Amazing. An interplanetary war has begun.” Another said: “Are you telling me that it was one of the first-ever confrontations between humans and UFOs and we shot them down?” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-24 18:52
