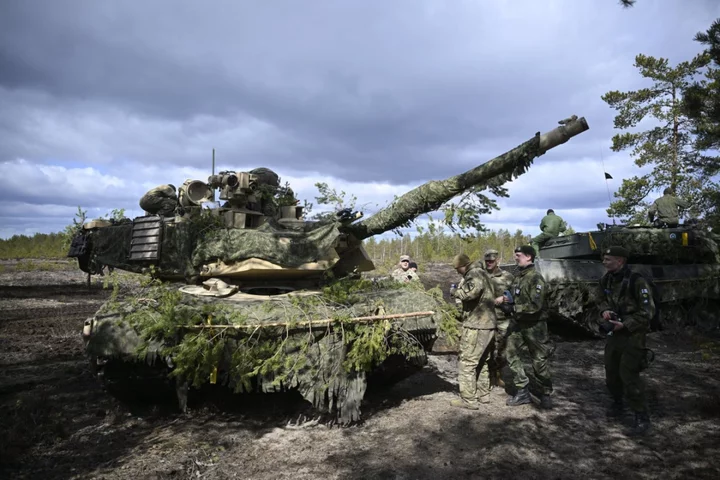

What are depleted uranium shells? The controversial armour-piercing muntions being used in Ukraine
The depleted uranium anti-tank rounds soon to be in Ukraine’s military stockpiles have kicked up a debate over its use in the continuing Russian invasion. Announced by the Pentagon in the latest military tranche on Wednesday, the controversial rounds have spread alarm among Vladimir Putin’s ministers who have warned against the escalation yet again. Britain has already promised armour-piercing rounds containing depleted uranium to Ukraine in March. Prime minister Rishi Sunak had backed drawing out the rounds from the UK military’s stockpiles ultimately “to degrade and deter – primarily – Russian aggression”. But what are these depleted uranium munitions? The 120mm anti-tank shells made of depleted uranium are self-sharpening and flammable penetrator in munitions. They are made of naturally occurring Uranium which has been stripped of mostly – not all – of its radioactive matter. So while it is not a nuclear weapon in itself, it acts as a fuel and also as a great explosive that can be used in tank armour, pressed between sheets of steel armour plate. They can be paired with top-tier tanks Western nations have already provided to Ukraine, and are particularly expected to boost the performance of 31 M1A1 Abram tanks set to be sent to the war-hit nation this fall. These rounds first emerged in the 1970s when the US army started making the armour-piercing rounds and has since used it along with tank armour to multiply the firing effect. Incredibly dense, more than lead, depleted uranium is considered a top-tier choice for projectiles. When fired, it becomes “essentially an exotic metal dart fired at an extraordinarily high speed”, RAND senior defence analyst Scott Boston said. “It’s so dense and it’s got so much momentum that it just keeps going through the armour – and it heats it up so much that it catches on fire,” Edward Geist, a nuclear expert at research organisation RAND said. The depleted uranium has also been added to the US ammunition fired by the Air Force’s A-10 close air support attack plane, known as the tank killer. Depleted uranium munitions, as well as depleted uranium-enhanced armour, have been previously used by US tanks in the 1991 Gulf War against Iraq’s T-72 tanks and again in the invasion of Iraq in 2003, as well as in Serbia and in Kosovo. Is the risk alarming? The UN nuclear watchdog has warned of the emissions of low levels of radiation from depleted uranium when handling and also warned of possible dangers of explosion. This is a bug, not a feature of the munition, says Mr Geist. Categorically, depleted uranium is not marked as a nuclear weapon. It is mainly a toxic chemical, as opposed to a radiation hazard. Particles in aerosols can be inhaled or ingested, and while most would be excreted again, some can enter the bloodstream and cause kidney damage. “High concentrations in the kidney can cause damage and, in extreme cases, renal failure,” the International Atomic Energy Agency has said. The US troops have questioned whether some of the ailments they now face were caused by inhaling or being exposed to fragments after a munition was fired or their tanks were struck, damaging uranium-enhanced armour. Experts have said that if the US military could find another material with the same density but without the radioactivity, it would likely switch. The IAEA has warned that handling of depleted uranium “should be kept to a minimum and protective apparel (gloves) should be worn” and “a public information campaign may, therefore, be required to ensure that people avoid handling the projectiles”. Initial signs of radioactivity from the Ukraine war have started trickling in. Russian foreign ministry spokesperson Maria Zakharova had recently claimed that the use of these munitions has already led to radioactive contamination. How has Russia reacted? In March, Russia was fuming after the Rishi Sunak administration announced it will give depleted uranium rounds to Ukraine, prompting them to issue nuclear threats. This time, after the US joined Britain in sending the depleted uranium shells, Moscow snapped and called the latest military aid of depleted uranium a “criminal act” beyond just escalation. “It is a reflection of Washington’s outrageous disregard for the environmental consequences of using this kind of ammunition in a combat zone. This is, in fact, a criminal act, I cannot give any other assessment,” Russian deputy foreign minister Sergei Ryabkov said. He also reiterated previous warnings by Russia about the risk of a nuclear war, because of what he called Western “pressure” on Moscow. “Now this pressure is dangerously balancing on the brink of direct armed conflict between nuclear powers,” he said. In March, Vladimir Putin had warned that Moscow would "respond accordingly, given that the collective West is starting to use weapons with a ‘nuclear component.’” Several days later, Putin said Russia’s response will see Moscow stationing tactical nuclear weapons in neighbouring Belarus, action to which effect was announced in July as Putin and the Belarusian president said they had already shipped some of the weapons. Read More The Body in the Woods | An Independent TV Original Documentary The harrowing discovery at centre of The Independent’s new documentary US sends Ukraine controversial depleted uranium weapons that can pierce tank armour UN nuclear watchdog report seen by AP says Iran slows its enrichment of near-weapons-grade uranium Kyiv drones explode near Moscow and military HQ as Russia on defensive – live
2023-09-07 22:52
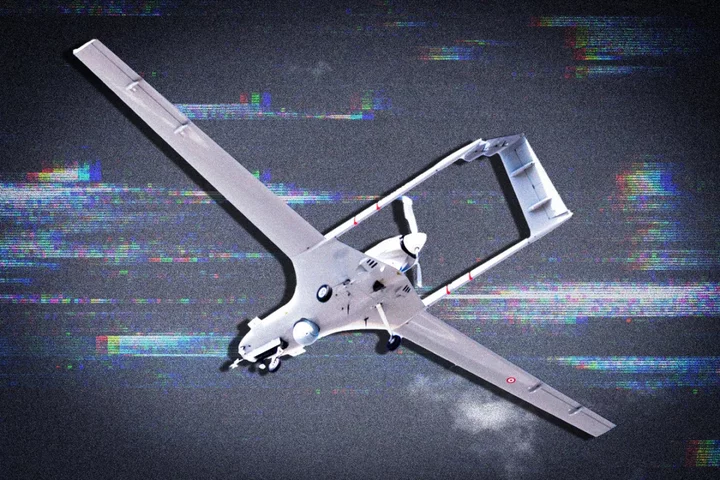

Ukraine drone strike map reveals key places where Kyiv is taking the war to Russia
As drone strikes continue to rain down on Russian soil, Vladimir Putin’s bloody war has reached his own doorstep. The strikes are now daily and on Tuesday the Russian defence ministry said its air defence systems destroyed two drones over the Kaluga and Tver regions, which border the Moscow region, as well as one closer to the capital, over the Istra district. Moscow Mayor Sergei Sobyanin said that the drones “were trying to carry out an attack on Moscow“ and that a consumer services facility was damaged in the Istra district, which is located some 65 km (40 miles) northwest of the Kremlin. Attacks on Russia have increased sharply, with the largest such strikes hitting six regions on one night last week. That assault included two Russian military transport planes being destroyed – and two more damaged – at an airbase in the city of Pskov. Ukraine’s military intelligence chief, Kyrylo Budanov, said that the drones were launched from inside Russia. However, in speaking to the War Zone website, Mr Budanov did not say whether the attack – about 400 miles (700km) from the Ukraine border – was carried out by Ukrainian or Russian operatives. “We are working from the territory of Russia,” he said. Officials confirmed attacks on six targets in the Pskov, Bryansk, Kaluga, Orlov, Ryazan and Moscow regions. Meanwhile, Moscow has continued to carry out drone attacks on Ukrainian targets including port infrastructure. On Monday, 32 Russian kamikaze drones struck the Ukrainian port city of Odesa, damaging civilian and industrial buildings. The assault on the military airfield in Pskov that damaged aircraft has been deemed the most significant attack, situated more than 600km (400 miles) from Ukraine, it was where a number of elite paratroopers are stationed. The state-run Tass news agency reported at least four giant Il-76 transport planes were damaged in the four-hour wave of drones, two of which had “burst into flames”. Moscow retaliated on Wednesday by launching a “massive combined attack” on the Ukrainian capital using drones and missiles, that killed two people and injured another. Kyiv officials normally neither claim nor deny responsibility for attacks on Russian soil, though they sometimes refer obliquely to them. The apparent Ukrainian drones reaching deep into Russia and cross-border sabotage missions are part of Kyiv’s efforts to heap domestic pressure on the Kremlin, militarily and politically. Meantime, a Ukrainian counteroffensive launched in June is chipping away at some parts of the front line, Kyiv officials claim. Read More The Body in the Woods | An Independent TV Original Documentary The harrowing discovery at centre of The Independent’s new documentary Ukraine war – live: Putin accused of trafficking Cubans to fight for Russia in his invasion The three reasons Putin will be terrified of Ukraine’s counteroffensive win Kim Jong-un to hold weapons talks with Putin after ‘travelling to Russia in armoured train’
2023-09-07 21:27

Nato boss give verdict on Ukraine’s chances of breakthrough by winter
Ukraine’s offensive against Russian forces is making slow progress, and there may not be a major breakthrough of Russian lines in the next two months as had previously been envisaged, according to Western officials. However, “focusing on such tactical issues” is counterproductive and there is a need to look at the bigger picture, the officials said, adding that this shows that Vladimir Putin is losing the war, as Ukraine has retaken a sizeable amount of territory overall since Russia’s invasion began. Nato’s secretary general Jens Stoltenberg confirmed that Ukraine is making progress in its efforts to regain territory that began in June, contradicting Mr Putin’s claims this week that the counteroffensive “has failed, not stalled”. “The Ukrainians are gradually gaining ground... They have been able to breach the defensive lines of the Russian forces, and they are moving forward,” Mr Stoltenberg said in an update to MEPs at the European Parliament on Thursday. “The Ukrainian offensive is slower than we anticipated a couple of months ago,” one Western official said. “That is an acknowledgement of Russian defences. And it’s also an acknowledgement of how Ukraine is having to pull together a force that is a mixed fleet of both old equipment and donated equipment ... and a civilian population that has been thrown to the fore and doing some of the toughest things in land warfare, which is getting through a minefield.” Mines form a layer of Russia’s defences. “Russia has lost either killed or wounded over 270,000 people and [destroyed] over a couple of thousand tanks, and if you add that to armoured fighting vehicles [then it is] over 4,000 fighting vehicles,” the official added. “There has been an enormous drain on Russia, and particularly its army and its combat effectiveness,” the official said. “And then in the broadest base, you’re seeing Russia under economic pressure and under diplomatic pressure.” Armour supplied by the West, including German Leopard tanks, has been damaged or destroyed in the prolonged battles continuing in the east and south across the last three months. The first of 14 Challenger II tanks provided by Britain was put out of action near Zaporizhzhia this week. According to defence sources, it was immobilised by a mine and then targeted by a Russian Lancet loitering drone. There are no plans, sources say, to replace it at present from within the 145 Challenger IIs currently available for deployment. The Western officials said that arms supplies to Kyiv will continue, and denied that “war fatigue” will begin to spread unless Volodymyr Zelensky’s government can show significant success in the near future. That is something that has been suggested by a number of European politicians. It has also been argued that the Kremlin is banking on American support for Ukraine starting to fray as the US presidential campaign gets under way next year. The possibility of Donald Trump – who was accused of being the “Muscovian candidate” when he was previously in the White House – winning the election greatly adds to this concern. “Russia thinks time is on its side; we think time is on our side,” another official said. “It has been put that if you’re Putin, you’re gambling that Donald Trump wins the next [US] election. But that is quite a long way away.” Read More The Body in the Woods | An Independent TV Original Documentary The harrowing discovery at centre of The Independent’s new documentary
2023-09-07 21:21

What Nelson Mandela and John Madden taught this NFL coach about leadership
Ahead of the start of the NFL season, Washington Commanders coach Ron Rivera sat down with CNN This Morning for a wide-ranging interview on leadership and other topics. Since he took the position in 2020, Rivera has coached the Commanders through a name change, a personal cancer diagnosis and a cultural reckoning for the organization.
2023-09-07 19:50

‘That ‘70s Show’ actor Danny Masterson faces 30 years to life at sentencing for rapes
“That ’70s Show” star Danny Masterson could get as much as 30 years to life in prison at his sentencing Thursday for the rapes of two women two decades ago. Los Angeles Superior Court Judge Charlaine F. Olmedo is set to sentence the 47-year-old actor after ruling on a defense motion for a new trial that she’s very likely to reject, and after hearing impact statements from the victims. A jury of seven women and five men found Masterson guilty of two counts on May 31 after seven days of deliberations. Both attacks took place in Masterson’s Hollywood-area home in 2003, when he was at the height of his fame on the Fox network sitcom “That ’70s Show.” The jury could not reach a unanimous verdict on a third count, an allegation that Masterson also raped a longtime girlfriend. The verdict came in a second trial after a jury failed to reach verdicts on three counts of forcible rape in December and a mistrial was declared. Prosecutors alleged that Masterson used his prominence in the Church of Scientology — where all three women were also members at the time — to avoid consequences for decades after the attacks. The women blamed the church for their hesitancy in going to police about Masterson. They testified that when they reported him to Scientology officials, they were told they were not raped, were put through ethics programs themselves, and were warned against going to law enforcement to report a member of such high standing. “They were raped, they were punished for it, and they were retaliated against,” Deputy District Attorney Reinhold Mueller told jurors at the trial. “Scientology told them there’s no justice for them.” The church said in a statement after the verdict that the “testimony and descriptions of Scientology beliefs” during the trial were “uniformly false.” “The Church has no policy prohibiting or discouraging members from reporting criminal conduct of anyone — Scientologists or not — to law enforcement,” the statement said. Masterson did not testify, and his lawyers called no witnesses. The defense argued that the acts were consensual, and attempted to discredit the women’s stories by highlighting changes and inconsistencies over time, which they said showed signs of coordination between them. The women whose testimony led to Masterson’s conviction said that in 2003, he gave them drinks and that they then became woozy or passed out before he violently raped them. Olmedo allowed prosecutors and accusers to say directly in the second trial that Masterson drugged the women, while only allowing the women to describe their condition in the first. Masterson was not charged with any counts of drugging, and there was no toxicology evidence to back up the assertion. The issue could be a factor in a planned appeal from the defense of Masterson’s conviction. The Associated Press does not typically name people who say they’ve been sexually abused. Masterson starred with Ashton Kutcher, Mila Kunis and Topher Grace in “That ’70s Show” from 1998 until 2006. He had reunited with Kutcher on the 2016 Netflix comedy “The Ranch,” but was written off the show when an LAPD investigation was revealed the following year. While that investigation began before a wave of women shook Hollywood with stories about Harvey Weinstein in October 2017, the conviction and sentencing of Masterson still represents a major #MeToo era success for Los Angeles prosecutors, along with the conviction of Weinstein himself last year.
2023-09-07 19:50

Danelo Cavalcante update: New video shows prison escape as Pennsylvania police track more sightings
The manhunt for convicted killer Danelo Cavalcante has now entered its eighth day with details beginning to emerge about how he managed to escape from prison in Pennsylvania. Cavalcante, 34, escaped from Chester County Prison days after he was sentenced to life without parole for stabbing his ex-girlfriend Deborah Brandao, 31, to death in front of her two small children. He is also wanted for a 2017 murder in Brazil. Authorities said during a press conference on Wednesday that he broke out by climbing onto a prison building roof from one of the exercise yards. Newly released surveillance video shows Cavalcante crawling up a wall at the prison before he disappears from the frame. Police said that he later managed to jump down to an area of the prison that had less surveillance. A tower officer tasked with observing the site failed to report the incident and Cavalcante’s escape was only noticed later during a head count. He was last spotted near Chandler Road, Pennsbury Township, on Tuesday evening. Local and federal law enforcement searched the area for hours but did not locate the fugitive. Members of the public are urged to secure their homes from the dangerous killer. Read More Danelo Cavalcante’s escape from Pennsylvania prison captured in newly released video How did Danelo Cavalcante manage to slip past Pennsylvania authorities twice? Father reveals terrifying moment escaped murderer Danelo Cavalcante broke into his home Danelo Cavalcante killed his girlfriend in front of her children. Now he’s on the run after a prison break
2023-09-07 18:48

What are depleted uranium munitions being used in Ukraine and why are they controversial?
The depleted uranium anti-tank rounds soon to be in Ukraine’s military stockpiles have kicked up a debate over its use in the continuing Russian invasion. Announced by the Pentagon in the latest military tranche on Wednesday, the controversial rounds have spread alarm among Vladimir Putin’s ministers who have warned against the escalation yet again. Britain has already promised armour-piercing rounds containing depleted uranium to Ukraine in March. Prime minister Rishi Sunak had backed drawing out the rounds from the UK military’s stockpiles ultimately “to degrade and deter – primarily – Russian aggression”. But what are these depleted uranium munitions? The 120mm anti-tank shells made of depleted uranium are self-sharpening and flammable penetrator in munitions. They are made of naturally occurring Uranium which has been stripped of mostly – not all – of its radioactive matter. So while it is not a nuclear weapon in itself, it acts as a fuel and also as a great explosive that can be used in tank armour, pressed between sheets of steel armour plate. They can be paired with top-tier tanks Western nations have already provided to Ukraine, and are particularly expected to boost the performance of 31 M1A1 Abram tanks set to be sent to the war-hit nation this fall. These rounds first emerged in the 1970s when the US army started making the armour-piercing rounds and has since used it along with tank armour to multiply the firing effect. Incredibly dense, more than lead, depleted uranium is considered a top-tier choice for projectiles. When fired, it becomes “essentially an exotic metal dart fired at an extraordinarily high speed”, RAND senior defence analyst Scott Boston said. “It’s so dense and it’s got so much momentum that it just keeps going through the armour – and it heats it up so much that it catches on fire,” Edward Geist, a nuclear expert at research organisation RAND said. The depleted uranium has also been added to the US ammunition fired by the Air Force’s A-10 close air support attack plane, known as the tank killer. Depleted uranium munitions, as well as depleted uranium-enhanced armour, have been previously used by US tanks in the 1991 Gulf War against Iraq’s T-72 tanks and again in the invasion of Iraq in 2003, as well as in Serbia and in Kosovo. Is the risk alarming? The UN nuclear watchdog has warned of the emissions of low levels of radiation from depleted uranium when handling and also warned of possible dangers of explosion. This is a bug, not a feature of the munition, says Mr Geist. Categorically, depleted uranium is not marked as a nuclear weapon. It is mainly a toxic chemical, as opposed to a radiation hazard. Particles in aerosols can be inhaled or ingested, and while most would be excreted again, some can enter the bloodstream and cause kidney damage. “High concentrations in the kidney can cause damage and, in extreme cases, renal failure,” the International Atomic Energy Agency has said. The US troops have questioned whether some of the ailments they now face were caused by inhaling or being exposed to fragments after a munition was fired or their tanks were struck, damaging uranium-enhanced armour. Experts have said that if the US military could find another material with the same density but without the radioactivity, it would likely switch. The IAEA has warned that handling of depleted uranium “should be kept to a minimum and protective apparel (gloves) should be worn” and “a public information campaign may, therefore, be required to ensure that people avoid handling the projectiles”. Initial signs of radioactivity from the Ukraine war have started trickling in. Russian foreign ministry spokesperson Maria Zakharova had recently claimed that the use of these munitions has already led to radioactive contamination. How has Russia reacted? In March, Russia was fuming after the Rishi Sunak administration announced it will give depleted uranium rounds to Ukraine, prompting them to issue nuclear threats. This time, after the US joined Britain in sending the depleted uranium shells, Moscow snapped and called the latest military aid of depleted uranium a “criminal act” beyond just escalation. “It is a reflection of Washington’s outrageous disregard for the environmental consequences of using this kind of ammunition in a combat zone. This is, in fact, a criminal act, I cannot give any other assessment,” Russian deputy foreign minister Sergei Ryabkov said. He also reiterated previous warnings by Russia about the risk of a nuclear war, because of what he called Western “pressure” on Moscow. “Now this pressure is dangerously balancing on the brink of direct armed conflict between nuclear powers,” he said. In March, Vladimir Putin had warned that Moscow would "respond accordingly, given that the collective West is starting to use weapons with a ‘nuclear component.’” Several days later, Putin said Russia’s response will see Moscow stationing tactical nuclear weapons in neighbouring Belarus, action to which effect was announced in July as Putin and the Belarusian president said they had already shipped some of the weapons. Read More The Body in the Woods | An Independent TV Original Documentary The harrowing discovery at centre of The Independent’s new documentary US sends Ukraine controversial depleted uranium weapons that can pierce tank armour UN nuclear watchdog report seen by AP says Iran slows its enrichment of near-weapons-grade uranium Ukraine Russia war: Izmail port under attack as Kyiv drones downed near Moscow
2023-09-07 18:16

French teenager dies after police car hits scooter near Paris
A 16-year-old boy lost his life after his scooter collided with a police vehicle near Paris. The teenager was taken to Beaujon Hospital in Clichy and was in a serious condition after the accident on Wednesday evening at Elancourt in Yvelines, local media reported. The boy, however, passed away in the evening. The teenager was not named by local media. At the time of the accident, another police car was trailing the teenager, authorities said. The scooter collided with the left side of one of the police vehicles. The Versailles prosecutor’s office confirmed that both police officers operating the vehicles involved were arrested on Wednesday evening. “My colleagues shot in the area, they saw him a second time, at that time he fled again. A little further he hit a second police vehicle on an intersection,” senior police official Tony Vallee was quoted as saying by BFMTV. Two separate investigations have been initiated, with law enforcement authorities saying the tragedy stemmed from the boy’s refusal to comply. An inquiry was initially launched for “involuntary injury”, but has been reclassified as a case of “manslaughter”, local media said. Additionally, a second investigation has been initiated for “refusal to comply” and assigned to the Yvelines departmental security. Several policemen were dispatched to Elancourt later during the day as a precautionary measure in case of potential incidents or disturbances. In late June, the death of 17-year-old Nahel Merzouk during a traffic stop in a Paris suburb ignited five days of riots and looting in the area. The shooting had occurred after the 17-year-old was gunned down in his car for failing to stop. He was then allegedly caught driving through a bus lane at rush hour. Nahel’s family claimed the officer “planned” the attack “in his head”. “They took my baby,” Nahel’s mother had said in a TikTok video. “He was still a child, he needed his mother. This morning he gave me a big kiss and told me he loved me. I told him be careful and I loved him.” Read More Britain’s Olympic success will be judged on athlete happiness – not just medals – at Paris 2024 King Charles set for royal first as state visit to France is rescheduled ‘Adventurous’ 93-year-old goes ‘out in style’ as ashes scattered by drone Cricket, breakdancing, 7 other sports still waiting for word on 2028 Los Angeles Olympic status BBC’s director of sport Barbara Slater to retire after 40 years at the broadcaster Interpol at 100: A mixed legacy of hunting fugitives and merging police data from 195 countries
2023-09-07 17:26
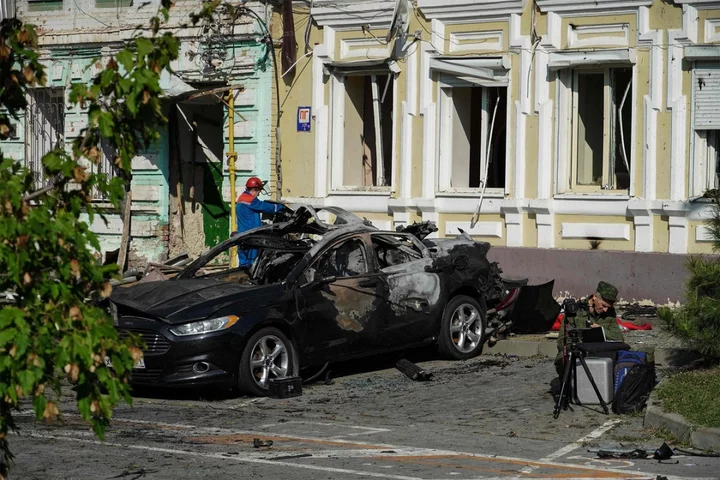

Ukraine-Russia war – live: Izmail port under attack as Kyiv drones downed near Moscow
Russia’s relentless attack on the port city of Izmail entered its fourth day as Ukrainian drones heading to three Russian cities, including Moscow, were shot down overnight. A Ukrainian drone targeted Moscow, but was shot down southeast of the city without causing any damage or injuries, mayor Sergei Sobyanin said. Two more drones were shot down over the southern region of Rostov, which borders Ukraine, as explosions rocked the centre, Rostov-on-Don. At least one person was injured as the attack damaged three buildings and several cars. Two other drones were shot down over the Bryansk region, which also borders Ukraine, governor Alexander Bogomaz reported. Drone debris damaged a railway station and several cars, he said. In recent weeks drones have repeatedly targeted Moscow, with some hitting buildings in the city center, while others being shot down on the outskirts of the city. In Russia’s attack on Izmail, located on the Danube river, at least one person was injured while infrastructure has been damaged, including grain silos. Read More From Challenger to Leopard: How Ukraine’s tanks compare to Russia’s A look at the uranium-based ammo the US is sending to Ukraine NATO member Romania says it has found drone pieces from Russian attacks in Ukraine on its territory Russian commander ‘used two military helicopters to transport his pet cat’
2023-09-07 17:21

US sends Ukraine controversial depleted uranium weapons that can pierce tank armour
Ukraine will be armed with depleted uranium anti-tank rounds that can aid its troops in piercing Russian tanks, said the Pentagon. The controversial 120mm anti-tanks shells will be used to boost the performance of 31 M1A1 Abram tanks the US will give Ukraine in the fall. The US is looking to aid Kyiv in dismantling Russian lines in eastern, northeastern and southern regions amid a simmering counteroffensive by the Ukrainians. The rounds, developed by the US during the Cold War, have previously destroyed Soviet tanks, including the decades old T-72 tanks dispatched by Moscow in the continuing war. The 46th drawdown of military equipment from the Department of Defence includes additional air defence equipment, artillery rounds and anti-tank weapons, and was announced shortly after Secretary of State Antony Blinken met with his Ukrainian counterpart and foreign minister Dmytro Kuleba on Wednesday. “We want to make sure that Ukraine has what it needs not only to succeed in the counteroffensive but has what it needs for the long term to make sure that it has a strong deterrent, strong defence capacity so that, in the future, aggressions like this don’t happen again,” Mr Blinken said in a statement before the two leaders met. The UK had also announced in March that it would give depleted uranium rounds to Ukraine, leaving Russia fuming and falsely claiming they had provided nuclear components. On Thursday, Russia snapped at Washington and called the latest military aid of depleted uranium a “criminal act” beyond just escalation. “It is a reflection of Washington’s outrageous disregard for the environmental consequences of using this kind of ammunition in a combat zone. This is, in fact, a criminal act, I cannot give any other assessment,” said Russian deputy foreign minister Sergei Ryabkov. He also reiterated previous warnings by Russia about the risk of a nuclear war, because of what he called Western “pressure” on Moscow. “Now this pressure is dangerously balancing on the brink of direct armed conflict between nuclear powers,” he said. Russia has deployed hypersonic missiles to thermobaric weapons on civilian targets in its full-scale invasion of Ukraine which has continued for more than 20 months now. Officials in Moscow have never taken responsibility for explaining using ballistic Kinzhal missiles, a barrage of which was fired on Ukraine in March this year. The missile has a range of up to 2,000km (about 1,250 miles) and flies at 10 times the speed of sound, making it hard to intercept. In April this year, the British defence ministry said Russia is likely handing over thermobaric multiple launch rocket systems to its elite airborne forces, suggesting its use in the continuing war. Thermobaric weapons, fired using the multiple launch rocket systems, are considered to be some of the most brutal war weapons in existence. “The highly destructive TOS-1A, which Russia designates as a ‘heavy flamethrower’, is typically operated by Russia’s specialist Chemical, Biological and Radiological Protection Troops in Ukraine, and has not previously been formally associated with the VDV,” the ministry had said. Russia had admitted to using the flamethrower weapon in March last year. Also known as vacuum bombs, they suck in oxygen and generate a powerful explosion that can have a devastating impact on victims – especially in an enclosed space. In another attack, Russia used cluster bombs which killed a child and two adults hiding in a pre-school in northeastern Ukraine. While the depleted uranium rounds retain some radioactive properties, they can’t generate a nuclear reaction like a nuclear weapon would, RAND nuclear expert and policy researcher Edward Geist said. The Pentagon has defended the use of the munitions. The US military “has procured, stored, and used depleted uranium rounds for several decades, since these are a longstanding element of some conventional munitions,” Pentagon spokesman Marine Corps Lt Col Garron Garn said in a statement in March. Read More The Body in the Woods | An Independent TV Original Documentary The harrowing discovery at centre of The Independent’s new documentary UN nuclear watchdog report seen by AP says Iran slows its enrichment of near-weapons-grade uranium Ukraine war: US send depleted uranium to Kyiv after blast near Russia military base Greek shipper pleads guilty to smuggling Iranian crude oil and will pay $2.4 million fine
2023-09-07 16:17
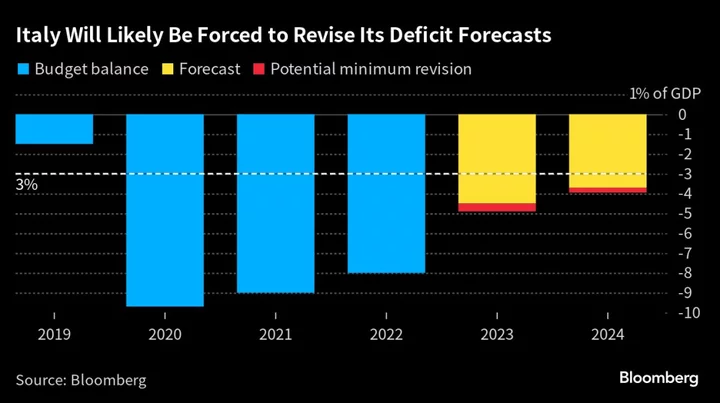
Meloni Faces Worsening Italian Budget Deficit for This Year
Giorgia Meloni’s government is confronting drastically worsening budget figures, adding pressure to her options on how to bolster
2023-09-07 15:22
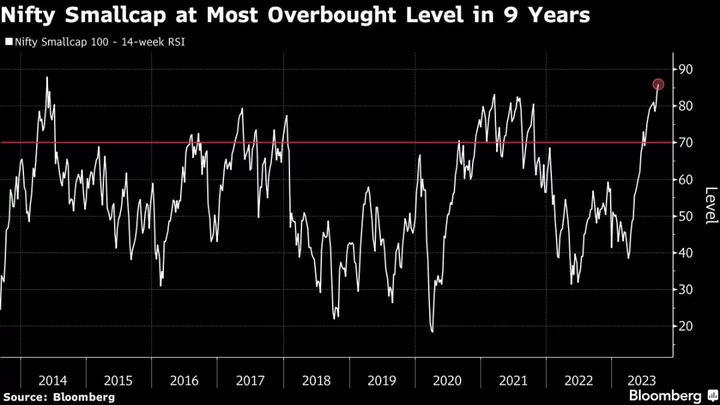
A $775 Billion India Stock Rally at Risk as Small Caps Overheat
The rally in Indian equities that has swelled the market’s total valuation by $775 billion in a little
2023-09-07 15:19
