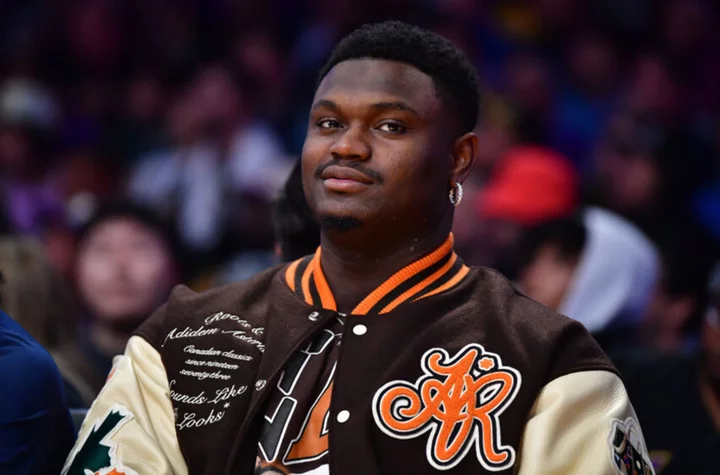

NBA rumors: Dillon Brooks landing spot, Pelicans fire Zion favorite, Paul wants to stay in Phoenix
The offseason doesn't officially open for two weeks but NBA rumors are flying, including about Zion Williamson, Chris Paul and Dillon Brooks.NBA rumors: Pelicans part ways with Zion's favorite assistant coachAccording to Shams Charania, the Pelicans are parting ways with Teresa Weather...
2023-06-16 21:50
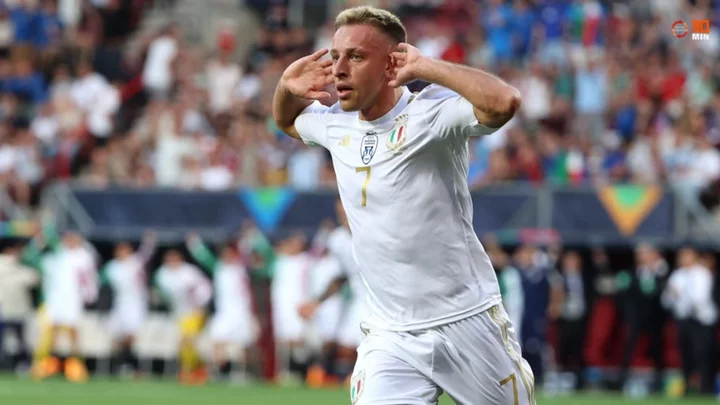

Davide Frattesi snubs Brighton move and is set to join Inter
Brighton made a move to sign Sassuolo midfielder Davide Frattesi, but the player is not ready to leave Italy. Inter are set to beat Milan and Juventus to his signature.
2023-06-16 21:47
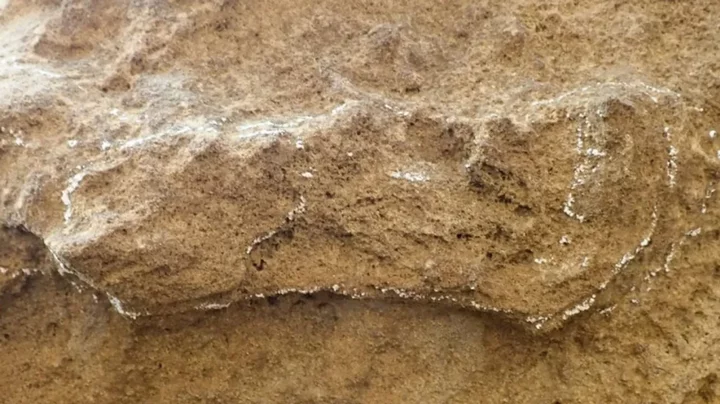

Study of oldest footprint ever may change the entire history of humanity
It’s not often that a single scientific discovery manages to change the way we think about the entire history of humanity. An ancient footprint has been newly uncovered, and it turns out that humans were walking around 30,000 years earlier than we previously thought. Two-legged homo sapiens were living in South Africa, it’s been proven, following the discovery of a 153,000 year old track. It was found in the Garden Route National Park near the coastal town of Knysna on the Cape South Coast. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The footmarks outdate the oldest previous discoveries, with the previous oldest found in nearby areas dated at 124,000 years old. The discoveries were made possible thanks to the optically-stimulated luminescence dating method, which analyses how long it’s been since a grain of sand has been exposed to sunlight. Researchers Charles Helm of Nelson Mandela University and the University of Leicester's Andrew Carr wrote in the Conversation: "In 2023, the situation is very different. It appears that people were not looking hard enough or were not looking in the right places. "Today, the African tally for dated hominin ichnosites (a term that includes both tracks and other traces) older than 50,000 years stands at 14. "Given that relatively few skeletal hominin remains have been found on the Cape coast, the traces left by our human ancestors as they moved about ancient landscapes are a useful way to complement and enhance our understanding of ancient hominins in Africa." The scientists involved believe that the area could be home to many illuminating discoveries given the makeup of the soil. They wrote: "We suspect that further hominin ichnosites are waiting to be discovered on the Cape South Coast and elsewhere on the coast. "The search also needs to be extended to older deposits in the region, ranging in age from 400,000 years to more than 2 million years. "A decade from now, we expect the list of ancient hominin ichnosites to be a lot longer than it is at present – and that scientists will be able to learn a great deal more about our ancient ancestors and the landscapes they occupied." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-16 21:29

Biggest Crypto Stablecoin Tether Was Once Backed by Chinese Securities
Tether Holdings Ltd. once counted securities issued by Chinese companies among the reserves backing its USDT stablecoin, the
2023-06-16 21:27

Odey Asset Management suspends further funds after investor flight- website
LONDON Odey Asset Management has suspended further funds after increased investor redemptions, letters posted on the fund's website
2023-06-16 21:24

No Czech rate hike this year, but outlook for cuts shifts to Q4: Reuters poll
By Jason Hovet PRAGUE The Czech National Bank is likely to opt against hiking interest rates further but
2023-06-16 21:23
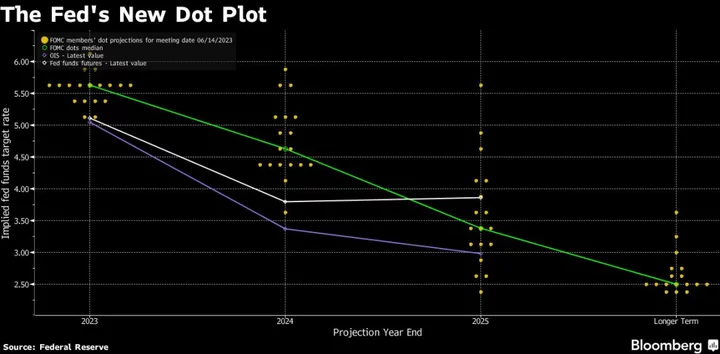
Fed’s Waller Says Fears Over a Few Banks Should Not Alter Policy
Federal Reserve Governor Christopher Waller said it’s not clear that recent banking strains will lead to significantly tighter
2023-06-16 21:22

Help for dads on Father's Day -- and beyond
While Father's Day is an annual tradition celebrated the third Sunday in June, there are several organizations that support dads year-round.
2023-06-16 20:59

Manchester United potential new owners' net worth compared to Newcastle
Here is what Manchester United's potential new owners are worth and how it compares to PIF's involvement with Newcastle.
2023-06-16 20:53

Policy try to identify victims of Canadian road disaster that killed 15
By David Ljunggren OTTAWA Police in the Canadian province of Manitoba on Friday were trying to identify the
2023-06-16 20:51
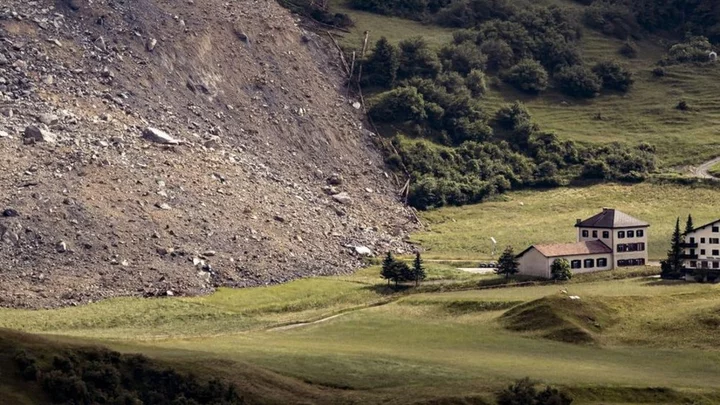

Massive Swiss rockfall stops short of evacuated village of Brienz
Brienz was evacuated last month when geologists warned the rockface above it was due to collapse.
2023-06-16 20:28

Mystery origin of Earth's water has finally been solved
Ever wondered how water first arrived on our planet? Well, it turns out the mystery could finally have been solved. Researchers have undertaken detailed analysis of asteroids and the findings could change the way the scientific community think about origins of water on our planet. Experts at the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory (LPL) have discovered salt crystals on samples recovered from space. As their findings state, these crystals could only have formed with the presence of water. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The research was undertaken on samples of the asteroid Itokawa in 2005 by the Japanese Hayabusa mission. It suggests that S-type asteroids could be home to more water than previously thought. The new findings led some scientists to claim that water is likely to have arrived on asteroids when our planet was first being formed. The senior’s author Tom Zega said: "The grains look exactly like what you would see if you took table salt at home and placed it under an electron microscope. "They're these nice, square crystals. It was funny, too, because we had many spirited group meeting conversations about them, because it was just so unreal. Zega added: "It has long been thought that ordinary chondrites are an unlikely source of water on Earth. Our discovery of sodium chloride tells us this asteroid population could harbour much more water than we thought." Itokawa is a S-type asteroid, and it’s thought that temperatures on their surfaces were too high for water to form. Shaofan Che, who is the lead study author, said: "In other words, the water here on Earth had to be delivered from the outer reaches of the solar nebula, where temperatures were much colder and allowed water to exist, most likely in the form of ice. "The most likely scenario is that comets or another type of asteroid known as C-type asteroids, which resided farther out in the solar nebula, migrated inward and delivered their watery cargo by impacting the young Earth." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-16 20:20
