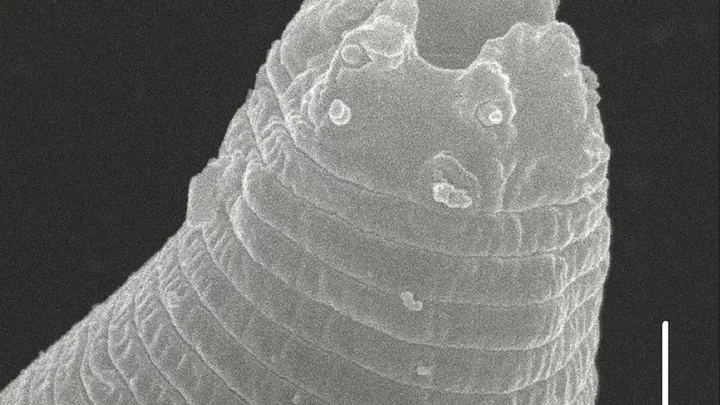

Experts resurrect parasite after 46,000 years in Siberian permafrost
Scientists have resurrected a parasite which has been dormant in the frozen permafrost of Siberia for 46,000 years. The microscopic creatures were first uncovered as part of a remarkable discovery back in 2018. At the time, researchers led by Anastasia Shatilovich found two of the worms in sub-zero temperatures in the soil. At first, it was previously thought that the creatures could stay in their slumber for just 40 years. However, it was later revealed that they could stay inactive for tens of thousands of years. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The creatures tend to shut down their systems when they are in unfavourable conditions. This means they won’t move or reproduce, and their metabolism stops. Carbon analysis has revealed that the worms – also known as nematodes – came from a prehistoric era. The developments could change the way experts approach bringing back other extinct species, too. During an analysis, the research team discovered the worms were Panagrolaimus kolymaensis - a species that was previously thought to be extinct. The scientists wrote in their paper: “Previously, we had shown that nematodes from the Siberian permafrost with morphologies consistent with the genera Panagrolaimus and Plectus could be reanimated thousands of years after they had been frozen. “Several viable nematode individuals were found in two of the more than 300 studied samples of permafrost deposits spanning different ages and genesis.” It’s not the only thing that scientists have recovered from permafrost, either. It was announced earlier this year that scientists are busy working on reviving 'zombie viruses’ that have been lying dormant for tens of thousands of years in Arctic conditions, and while it sounds absolutely terrifying, it could be important when it comes to protecting us all in the future. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-28 19:22

Algeria media guide
An overview of the media in Algeria, as well as links to broadcasters and newspapers.
2023-07-28 19:19

Niger coup: General Tchiani declares himself leader
General Abdourahmane Tchiani is addressing the nation after staging a coup.
2023-07-28 19:19

Enphase Energy slumps as lukewarm US demand weighs on revenue forecast
Shares of Enphase Energy slumped 17% in premarket trading on Friday, after the solar inverter maker's third-quarter revenue
2023-07-28 18:53
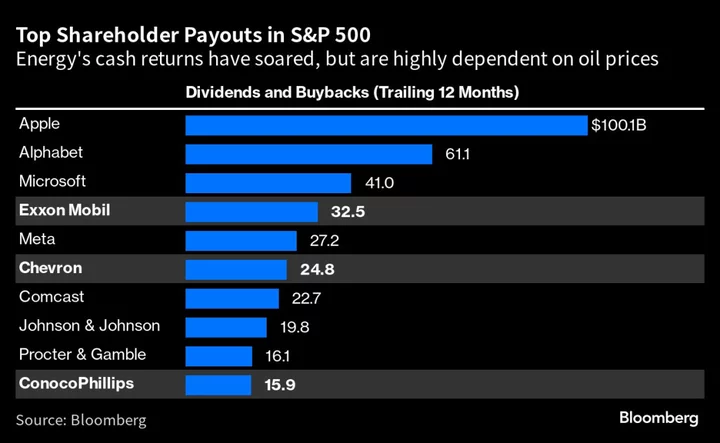
Exxon Profit Misses Estimates as Natural Gas, Refining Falter
Exxon Mobil Corp. fell short of analysts’ expectations with a third straight drop in profit — the longest
2023-07-28 18:50
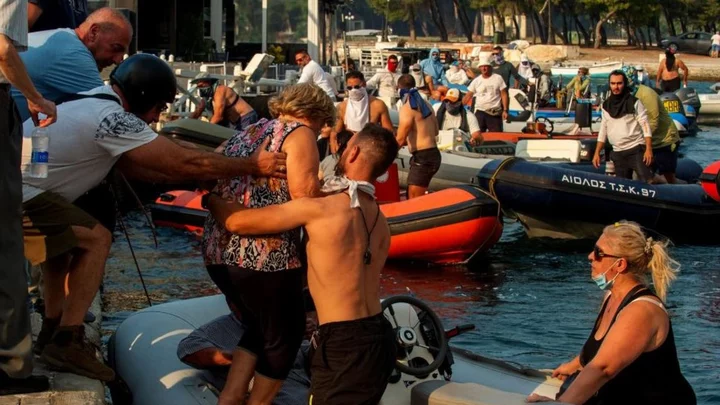

Greek fires at Nea Anchialos prompt blasts forcing F-16s to evacuate base
Residents escape by boat and the air force evacuates fighter planes as an ammunition depot explodes.
2023-07-28 18:47

Chevron expects annual production at low-end of prior forecast
(Reuters) -Chevron Corp said on Friday that its annual production forecast was near the low-end of its previously estimated range.
2023-07-28 18:46
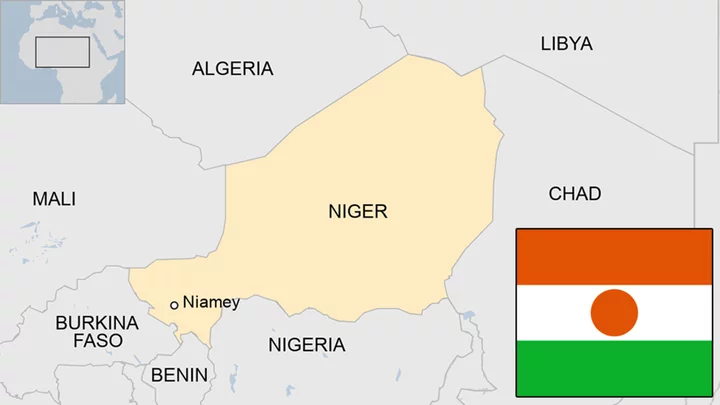
Niger country profile
Provides an overview of Niger, including key dates and facts about this west African country.
2023-07-28 18:45

India Sets Steady Path Toward Local Semiconductor Industry
Applied Materials Inc., a leading producer of chipmaking equipment, is expanding in India because it believes the country’s
2023-07-28 18:28

American families of IS victims sue cement maker Lafarge over Syria payments
ZURICH The families of U.S. aid workers and soldiers killed or injured by Islamic State and Al-Nusra Front
2023-07-28 18:27
Drugmakers go under the skin, skirting early US Medicare price negotiations
By Michael Erman NEW YORK Injectable versions of some widely-used cancer drugs including Johnson & Johnson's blockbuster multiple
2023-07-28 18:25
Hepatitis B and C could cause ‘significantly higher cancer risk’ than smoking daily pack of cigarettes
People living with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) could be just as likely or more likely to develop cancer than someone smoking a pack of cigarettes a day, new research suggests. According to the Center for Disease Analysis (CDA) Foundation, people infected with hepatitis B and C viruses “have a similar or significantly higher risk of developing cancer than someone who actively smokes one pack of cigarettes per day”, and therefore HBC and HBC should be “considered as cancer causing infections and international guidelines should be reconsidered accordingly”. Hepatitis is the term used to describe inflammation of the liver, according to the NHS. Hepatitis B is spread in the blood of an infected person – it can be spread from infected women to their babies, or through unprotected sex and injecting drugs – and hepatitis C is usually spread through blood-to-blood contact with an infected person. The NHS says HCV is most commonly spread in the UK through sharing needles used to inject drugs. The foundation found that HBV and HCV viruses are highly oncogenic. Oncogenes are mutated genes which can lead to cancers in multiple organs and sites. Homie Razavi, managing director at CDA Foundation said: “Hepatitis B and C infections are silent epidemics. These viral infections are cancer causing but since infected individuals don’t show any symptoms until it is too late, most infections go unnoticed. “It is important for all of us to recognise the high risk of cancer associated with hepatitis B and C infections and get patients linked to care. Treatment can reduce the risk of cancer by 85% or more.” As part of a call on World Hepatitis Day 2023 (July 28), the World Hepatitis Alliance (WHA) has launched a campaign called ‘We’re not waiting’ with its global network of 323 members in over 100 countries, in order speed up the fight against the disease, which claims a life every 30 seconds. In a new survey, the WHA found that 42% of people around the world are unaware that viral hepatitis is one of the leading causes of liver cancer. Nearly three-quarters (74%) of those surveyed said knowing that hepatitis causes liver cancer means they are more likely to get tested, whilst 82% would get vaccinated. In total, over 350 million people have been diagnosed with either hepatitis B or C around the world, which results in more than 1.1 million deaths every year. And by 2040, deaths caused by this disease could surpass mortality from malaria, HIV, and tuberculosis combined, according to the WHA. “Every year, more than a million lives are lost to hepatitis,” said Danjuma Adda, president of the WHA. “The theme of World Hepatitis Day 2023 is ‘We’re not waiting’. It’s a call to accelerate elimination efforts of viral hepatitis now and the urgent need for testing and treatment for the real people who need it. “Individuals and communities around the world are making change happen in their own lives and in [the] world around them. We celebrate them, while demanding more action. We’re not waiting for change – we’re fighting to make it happen.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live
2023-07-28 17:57
