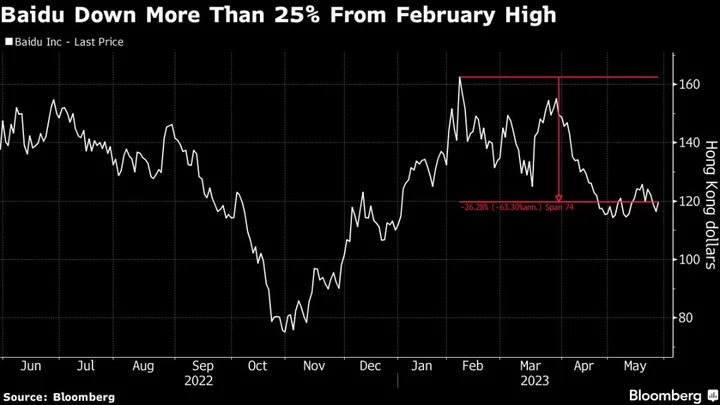
Baidu Shares Jump as Ernie Bot Progress Rekindles AI Bets
Baidu Inc. shares jumped in Hong Kong following reports that it will soon launch a large-language model to
2023-05-29 13:22
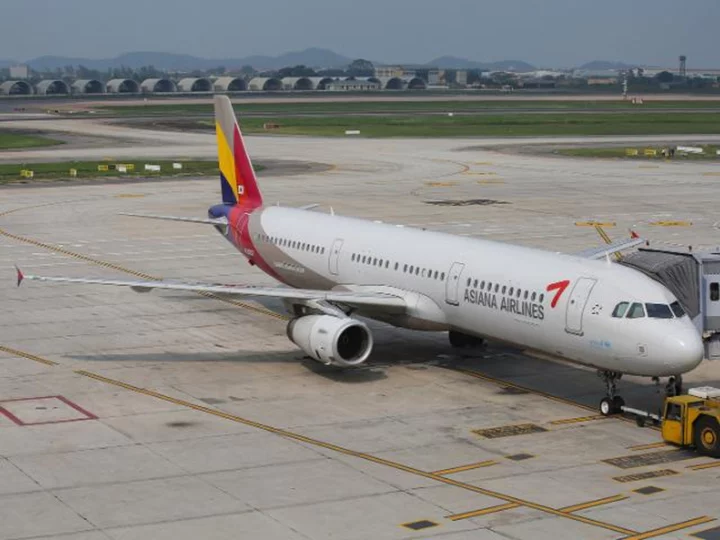

Asiana Airlines to stop selling seats near emergency exit on Airbus A321s
Asiana Airlines will no longer sell tickets for certain emergency exit seats of its Airbus A321-200 aircraft, the airline said Sunday, following a recent incident in which a man allegedly opened a jetliner door during a flight.
2023-05-29 13:21
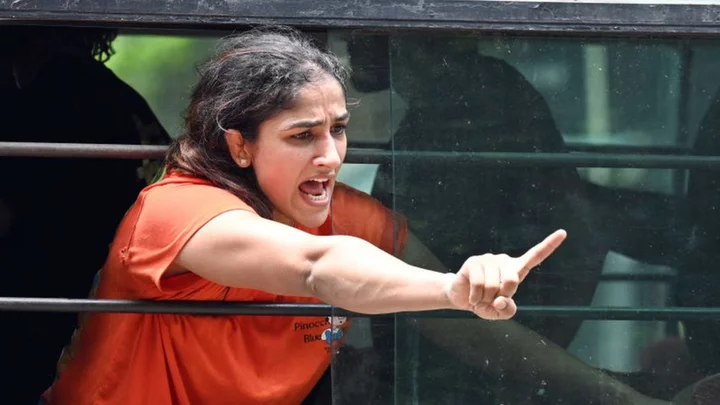

Wrestlers' protest: Delhi police file rioting case after detention
The athletes, including Olympic medallists, were detained by police as they tried to march to parliament.
2023-05-29 13:19

Takeaways on debt ceiling: McCarthy's balancing act, Biden's choice and the challenges ahead
It’s a deal no one in Washington claims to really like. But after weeks of negotiations, President Joe Biden and House Speaker Kevin McCarthy have struck an agreement to raise the debt ceiling and avert a potentially devastating government default. The stakes are high for both men — and now each will have to persuade lawmakers in their parties to vote for it. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen said last week that the United States could run out of cash to pay the bills and default on its obligations if the debt ceiling is not raised by June 5. The ultimate agreement, hammered out by Biden, McCarthy and a small group of their deputies, is a two-year budget deal that would essentially hold spending flat for 2024, while boosting it for defense and veterans, and capping increases at 1% for 2025. It would suspend the debt limit until January 2025, after the next presidential election. Republicans had insisted on reducing spending and had passed their own bill with much larger cuts last month. The package would also make policy tweaks, including by adding work requirements for some food aid recipients and streamlining an environmental law that Republicans say has made it harder to build energy projects. Takeaways from the deal, and from the negotiations that led up to it: McCARTHY’S DELICATE BALANCING ACT Ever since McCarthy won the House speakership on the 15th ballot in January, it was clear that the debt ceiling negotiations would be his first and perhaps biggest test. Known more for strategy than policy, McCarthy has had a challenge that seemed almost insurmountable, with a narrow majority and a sizable group of hard-right conservatives certain to oppose anything he negotiated with Biden. And he could still find himself in the middle of a crisis if too many in his caucus revolt when the House votes on the package this week. Through it all, the Californian has exhibited his typical laid-back vibe, projecting confidence about the bill and its success. He said Sunday that he will win a majority of Republicans on the bill and some Democrats. In a conference call on Saturday night, McCarthy said, more than 95 percent of the members in his conference “were overwhelmingly excited about what they see.” But some House Republicans were publicly slamming the deal, arguing it did too little to cut the deficit. Rep. Dan Bishop of North Carolina tweeted a vomit emoji, complaining that some Republicans on the call were praising the speaker for getting what he said is “almost zippo in exchange” for the debt-ceiling hike. BIDEN’S RELUCTANT COMPROMISE For months, Biden and his aides had a mantra: There would be no negotiation on the debt limit. But then he negotiated anyway. It’s not where Biden, a veteran of the nasty 2011 debt-limit battle that saw the nation’s credit rating downgraded for the first time in history, wanted to be. But it was a likely scenario — with a Republican-controlled House that had made it clear from the start that it would not raise the borrowing authority under a Democratic president without extracting spending curbs or other policy concessions. There was no way Biden, who is running for re-election next year, would want a historic default on his watch. Biden has continued to insist that he was negotiating on the budget, not the debt ceiling. But pushed by a reporter Sunday evening who noted that was precisely what Republicans were seeking in exchange for lifting the debt limit, the president seemed to break from his talking point. “Sure, yeah,” Biden said, chuckling slightly. “Can you think of an alternative?” Now he will have to sell it to House Democrats, who must vote for it in big enough numbers to make up for defecting Republicans. Many progressive members in the House have appeared skeptical of the deal, but they remained mostly quiet over the weekend as they waited for more details. But the deal won early praise from another key Democratic group. The New Democrat Coalition, which has roughly 100 members, praised Biden as having negotiated “a viable, bipartisan solution to end this crisis.” LONG-SOUGHT GOP POLICY Republicans were able to win some policy changes they have sought for years, however modest, including on food aid. The bill would raise the age limit for existing work requirements in the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program, also known as food stamps. It would also create a new agency to develop and streamline environmental reviews that Republicans have complained about for decades. The new work requirements for able-bodied SNAP recipients without dependents would phase in by 2025 and expire by 2030. And a provision pushed by Biden would take some vulnerable recipients — like veterans and the homeless — off work requirements entirely. But Republicans made clear that pushing more people to work in exchange for government benefits was a major victory for them, even if mostly symbolic. The bill also would amend the National Environmental Policy Act and designate “a single lead agency” to develop environmental reviews, in hopes of streamlining the process. Republicans had hoped for a much broader permitting package that would make it easier to build and develop energy projects. But Louisiana Rep. Garret Graves, a McCarthy ally who was one of the negotiators, said the bill brings “transformational changes into the permitting and environmental review process” for the first time in four decades. SENATE QUIET, WAITING TO CLOSE McCarthy has said the House will vote on the package Wednesday. If passed, it will then head to the Democratic-led Senate where leaders will have to get agreement from all 100 members to speed up the process and avert a default by next Monday. The White House briefed Democratic senators Sunday and McCarthy briefed Republicans. But most senators remained quiet on the deal as they waited for the full text and to see if McCarthy can navigate it through the House. Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y., and Senate Republican Leader Mitch McConnell of Kentucky cut themselves out of the negotiating process early on, saying it should be a negotiation between the White House and McCarthy. McConnell issued a statement supporting the legislation on Sunday but some in his caucus have criticized it. The two leaders will have to navigate any potential objections over the coming week as they seek to win full support to move quickly on the deal. “With Republicans like these, who needs Democrats?” tweeted Utah Sen. Mike Lee on Saturday, aligning himself with the House Republicans who say the deal is not conservative enough. Read More Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Trump's welcome of Scott into 2024 race shows his calculus: The more GOP rivals, the better for him Stock market today: Asian markets mostly higher after Biden-McCarthy deal on US debt What’s in the cliffhanger deal struck by Biden and McCarthy to raise the debt limit?
2023-05-29 12:52

China, Japan Commerce Ministers Trade Protests at Meeting in US
The trade ministers of China and Japan exchanged protests over chip export controls and the detention of Japanese
2023-05-29 12:50
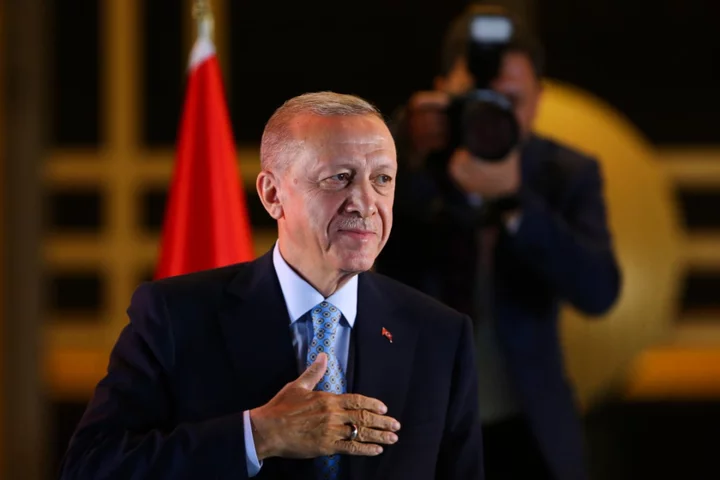

Turkey's Erdogan turns away reform-minded challenger to win another term
Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan turned away a challenger who sought to reverse his authoritarian-leaning changes, securing five more years to oversee the country at the crossroads of Europe and Asia that plays a key role in NATO. Erdogan prevailed by winning more than 52% of the vote in Sunday's presidential runoff, which came two weeks after he fell short of scoring an outright victory in the first round. A majority of Turkish voters in the second round chose him over challenger Kemal Kilicdaroglu, showing their support for a man who they see as a strong, proven leader. Voters were divided between loyalty to Erdogan, who has ruled for two decades, and hopes for the opposition candidate, who promised to return to democratic norms, adopt more conventional economic policies and improve ties with the West. With his immediate political future secure, Erdogan must now confront skyrocketing inflation that has fueled a cost-of-living crisis and rebuild in the aftermath of a devastating earthquake that killed more than 50,000 people. In two speeches — one in Istanbul and one in Ankara — Erdogan thanked the nation for entrusting him with the presidency again. “We hope to be worthy of your trust, as we have been for 21 years,” he told supporters on a campaign bus outside his home in Istanbul. He said the divisions of the election are over, but he continued to rail against his opponent. “The only winner today is Turkey,” Erdogan said outside the presidential palace in Ankara, promising to work hard for Turkey’s second century, which he called the “Turkish century.” The country marks its centennial this year. Supreme challenges lie ahead, starting with the economy that has taken a beating from what critics view as Erdogan’s unorthodox policies. He also must tend to massive rebuilding efforts in 11 provinces hit by the Feb. 6 earthquake that leveled entire cities. Kilicdaroglu said the election was “the most unjust ever,” with all state resources mobilized for Erdogan. “We will continue to be at the forefront of this struggle until real democracy comes to our country,” he said in Ankara. He thanked the more than 25 million people who voted for him and asked them to “remain upright.” The people have shown their will "to change an authoritarian government despite all the pressures,” Kilicdaroglu said. Supporters of Erdogan, a divisive populist and masterful orator, took to the streets to celebrate, waving Turkish or ruling party flags, honking car horns and chanting his name. Celebratory gunfire was heard in several Istanbul neighborhoods. His next term is certain to include more delicate maneuvering with fellow NATO members over the future of the alliance and the war in Ukraine. Leaders across the world sent their congratulations, highlighting Turkey and Erdogan’s enlarged role in global politics. Western politicians said they are ready to continue working with Erdogan despite years of sometimes tense relations. Most imminently, Turkey holds the cards for Sweden’s hopes to join NATO. The bid aims to strengthen the military alliance against Russia and is central to the continuity of a deal to allow Ukrainian grain shipments and avert a global food crisis. “No one can look down on our nation,” Erdogan said in Istanbul. Steven A. Cook, a senior fellow at the Washington-based Council on Foreign Relations, said Turkey was likely to “move the goal post” on Sweden’s membership in NATO as it seeks demands from the United States. He also said Erdogan, who has spoken about introducing a new constitution, was likely to make an even greater push to lock in changes adopted by his conservative and religious Justice and Development Party, or AKP. In his victory remarks, Erdogan said rebuilding the quake-struck cities would be his priority. He also said a million Syrian refugees would go back to Turkish-controlled “safe zones” in Syria as part of a resettlement project being run with Qatar. Erdogan has retained the backing of conservative voters who remain devoted to him for lifting Islam’s profile in Turkey, which was founded on secular principles, and raising the country’s influence in international politics. Erdogan’s rival was a soft-mannered former civil servant who has led the pro-secular Republican People’s Party, or CHP, since 2010. The opposition took months to unite behind Kilicdaroglu. He and his party have not won any elections in which Erdogan ran. In a frantic outreach effort to nationalist voters in the runoff, Kilicdaroglu vowed to send back refugees and ruled out peace negotiations with Kurdish militants if he was elected. Erdogan and pro-government media portrayed Kilicdaroglu, who received the backing of the country’s pro-Kurdish party, as colluding with “terrorists” and supporting what they described as “deviant” LGBTQ rights. In his victory speech, Erdogan repeated those themes, saying LGBTQ people cannot “infiltrate” his ruling party or its nationalist allies. In Ankara, Erdogan voter Hacer Yalcin said Turkey’s future was bright. “Of course Erdogan is the winner ... Who else? He has made everything for us," Yalcin said. “God blesses us!” Erdogan, a 69-year-old Muslim, is set to remain in power until 2028. He transformed the presidency from a largely ceremonial role to a powerful office through a narrowly won 2017 referendum that scrapped Turkey’s parliamentary system of governance. He was the first directly elected president in 2014 and won the 2018 election that ushered in the executive presidency. The first half of Erdogan’s tenure included reforms allowing the country to begin talks to join the European Union, as well as economic growth that lifted many out of poverty. But he later moved to suppress freedoms and the media and concentrated more power in his own hands, especially after a failed coup attempt that Turkey says was orchestrated by the U.S.-based Islamic cleric Fethullah Gulen. The cleric denies involvement. In the Kurdish-majority city of Diyarbakir, 37-year-old metalworker Ahmet Koyun said: “It is sad on behalf of our people that a government with such corruption, such stains, has come into power again. Mr. Kemal would have been great for our country, at least for a change of scene." But he said everyone must accept the results. ___ Bilginsoy reported from Istanbul. Bela Szandelszky in Ankara, Turkey; Mucahit Ceylan in Diyarbakir, Turkey; and Cinar Kiper in Bodrum, Turkey, contributed to this report. Read More Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Analysis: Only Erdogan knows his plans for Turkey’s future. That is the problem AP News Digest 8:40 a.m. Erdogan declared winner of Turkey presidential run-off – extending his 20-year rule
2023-05-29 12:48
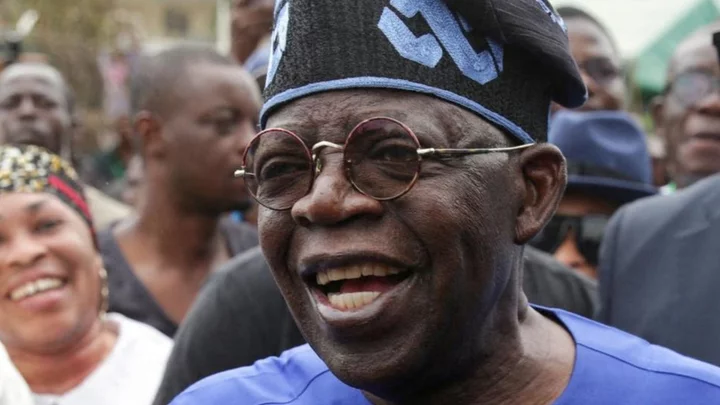

Bola Tinubu inauguration: Nigeria to swear in new president
Bola Tinubu, 71, won February's election with a promise to renew hope and needs to act fast.
2023-05-29 12:29

PwC Australia Puts Nine Partners on Leave as Scandal Deepens
PwC Australia is putting nine senior partners on leave and appointing independent directors to its board as the
2023-05-29 12:29
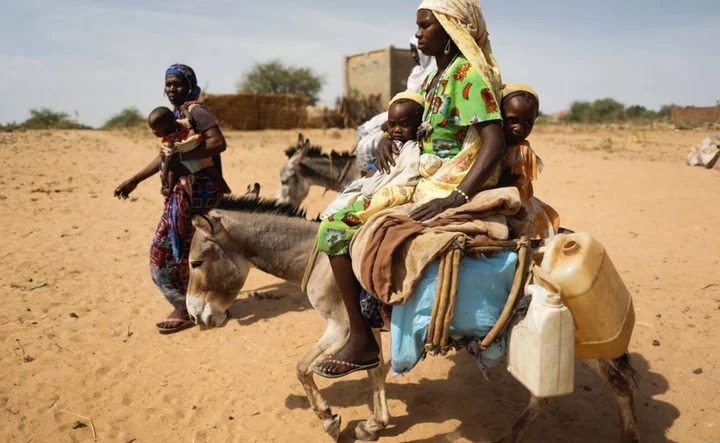

Sudan Darfur crisis: 'Everything civilians can use has been burned or destroyed'
Large-scale destruction caused by Arab militias in western Sudan is now visible from space.
2023-05-29 12:27
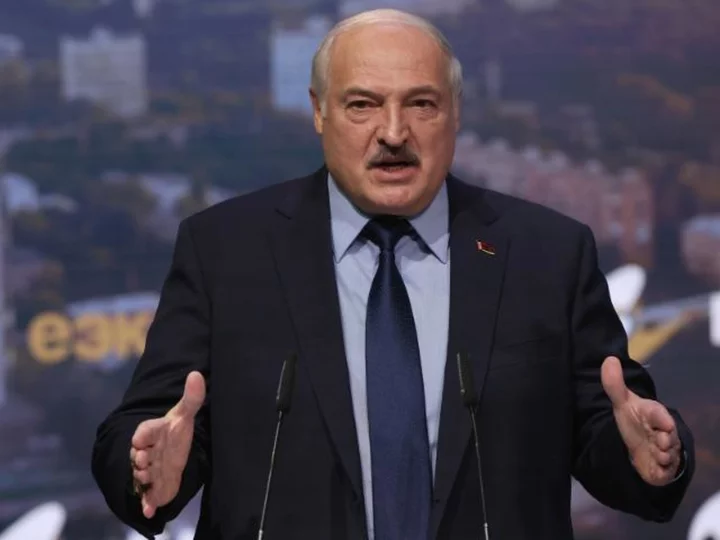

Lukashenko offers nuclear weapons to nations willing 'to join the Union State of Russia and Belarus'
Belarus President Alexander Lukashenko has claimed that nations who are willing "to join the Union State of Russia and Belarus" will be given nuclear weapons, days after confirming the transfer of some tactical nuclear weapons from Moscow to Minsk had begun.
2023-05-29 11:59
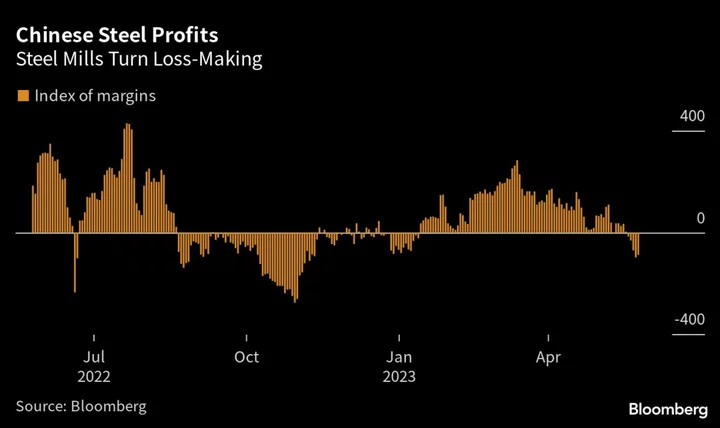
It’s Not a Good Time to Be a Steel Mill or Coal Mine in China
China’s raw materials producers are at the forefront of falling industrial profits as poor demand and price deflation
2023-05-29 11:52
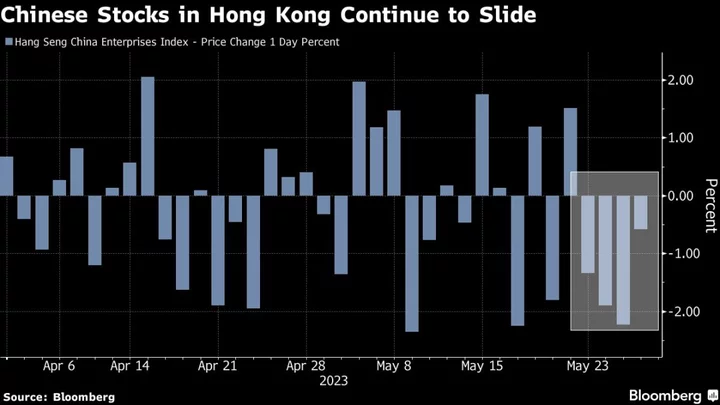
Chinese Stocks in Hong Kong Extend Slump, Approach Bear Market
A gauge of Chinese shares traded in Hong Kong inched closer to bear-market territory as a wobbling economic
2023-05-29 11:49
