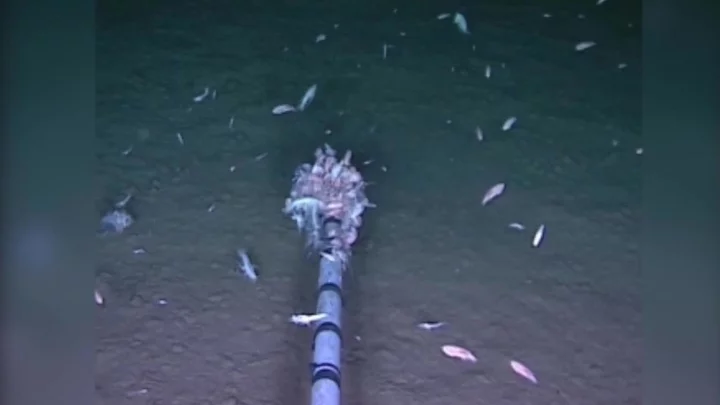

Scientists have found a novel virus at the bottom of the ocean
Scientists have discovered a new virus in the Pacific that is thought to be the deepest ever found in Earth’s oceans. The so-called bacteriophage virus infects and replicates inside bacteria, and was found in the Mariana Trench, which is the Pacific’s deepest point. Bacteriophages are among the world’s most abundant life forms, and are important for regulating population sizes in the oceans and releasing nutrients. This one, the catchily named vB_HmeY_H4907, was picked up at 8,900 metres below sea level. That is still some way off the 11,000 metre floor of the trench. Min Wang, a marine virologist from the Ocean University of China, said: “To our best knowledge, this is the deepest known isolated phage in the global ocean.” “Wherever there’s life, you can bet there are regulators at work. Viruses, in this case.” Scientists think this virus is likely to be distributed widely in the world’s oceans, despite the fact it has only been discovered. It has a similar structure to its host bacteria group halomonas. These are usually found in sediments and geyser-like openings on the seafloor. They also think the virus is lysogenic, which means it infects the host but does not kill it. Dr Wang said the discovery could inform further research about how viruses survive in the world’s harshest environments. “Extreme environments offer optimal prospects for unearthing novel viruses,” he added. The virus was found in the so-called hadal zone, which the study’s authors said is “the planet’s least explored and most mysterious environment, and it is the deepest habitat for life on Earth’s surface”. The area is named after Hades, the Greek god of the underworld. Researchers wrote in the study: “These findings expand our understanding of the phylogenetic diversity and genomic features of hadal lysogenic phages, provide essential information for further studies of phage-host interactions and evolution, and may reveal new insights into the lysogenic lifestyles of viruses inhabiting the hadal ocean.” The findings were published in the journal Microbiology Spectrum. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 20:50
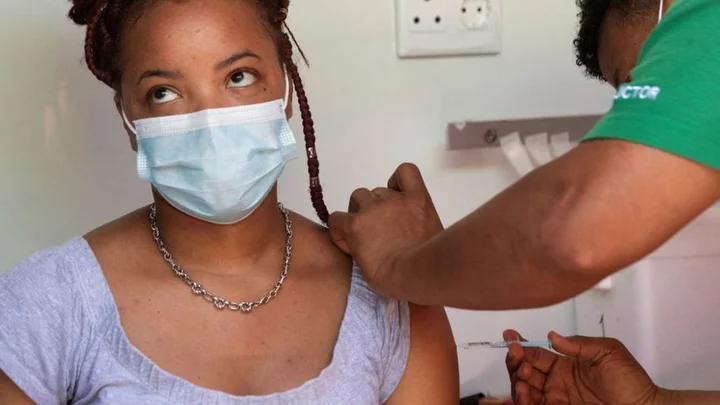
South Africa to clear Covid lockdown criminal records
More than 400,000 people were arrested for breaking some of the world's toughest lockdown restrictions.
2023-09-21 20:29

3 Vikings who need to be benched or fired before Week 3
The Vikings clearly want to compete this season. At 0-2, they need to make some aggressive personnel moves to do so.
2023-09-21 20:22
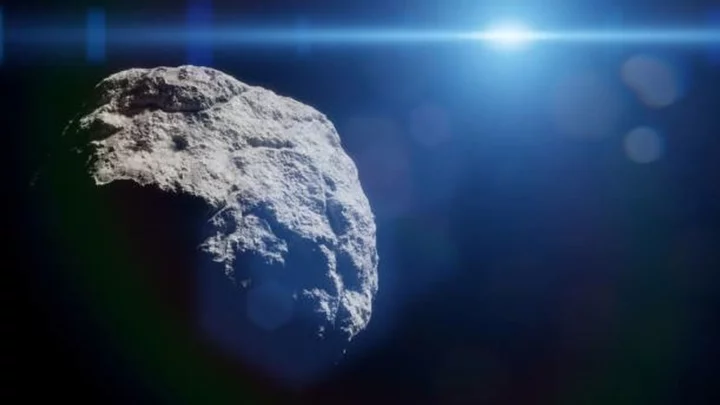

Scientists issue warning about asteroid heading to Earth with force of 24 atomic bombs
Scientists are on alert after NASA confirmed there is a chance an asteroid the size of the Empire State Building could come smashing into Earth. The asteroid is named Bennu after the ancient Egyptian bird god and has been on the space agency’s radar for a long time as they try to prevent it from coming crashing into our planet. Bennu has been categorised as one of the two “most hazardous known asteroids” and, despite the chance of impact standing at 1-in-2,700, it could strike the Earth with the force of 24 times that of the largest nuclear bomb – 1,200 megatons of energy. The carbon-based asteroid is approximately 510 metres wide and experts predict that it will come closest to hitting Earth on September 24, 2182. While the asteroid is quite sizeable, it is not quite as sizeable as the six-mile-wide asteroid which almost completely wiped out the dinosaurs. But, NASA warns that Bennu “could cause continental devastation if it became an Earth impactor”. A space mission launched using NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft has successfully taken a sample from Bennu in order for scientists to better understand the potentially dangerous asteroid. On Sunday (24 September) a capsule of the material will be dropped by OSIRIS-REx and returned to Earth where it will be retrieved and the matter inside studied. Davide Farnocchia of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory told the Science Journal: “We improved our knowledge of Bennu's trajectory by a factor of 20.” As scientists work to investigate how much of a risk it could cause, Farnocchia added: “In 2135, we'll know for sure.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 20:20
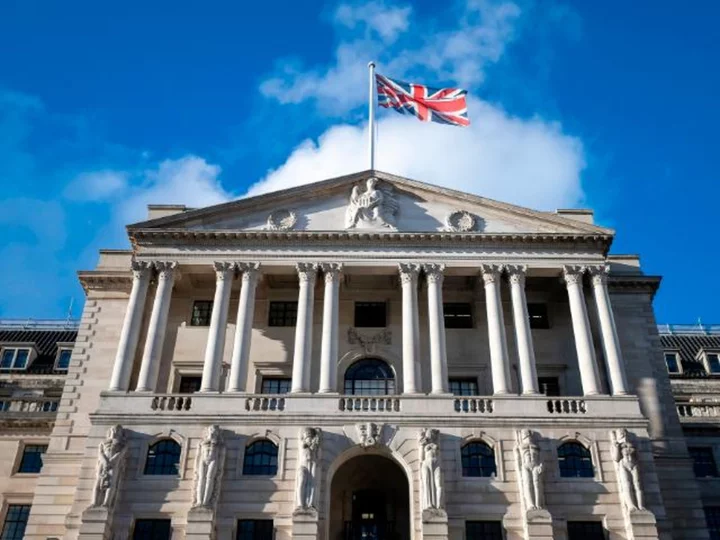

Bank of England pauses after 14 interest rate hikes
The Bank of England paused its historic rate hiking campaign for the first time in nearly two years Thursday after inflation fell unexpectedly in August.
2023-09-21 19:24
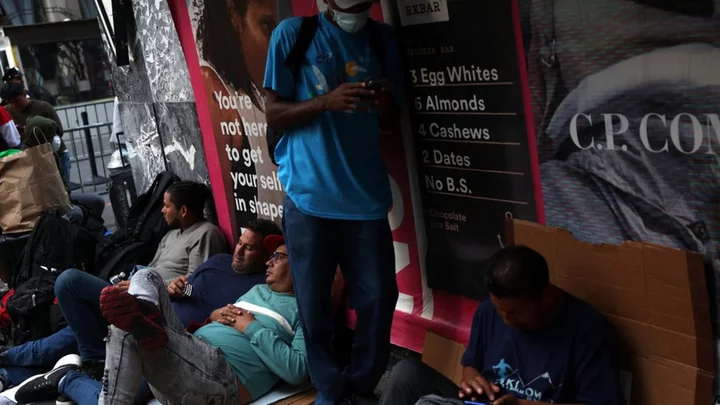

US offers almost 500,000 Venezuelans legal status
US cities have been grappling with large numbers of Venezuelans fleeing economic and political turmoil.
2023-09-21 19:19

Roundup: Olivia Wilde Takes Shot at Harry Styles; Vikings Trade For Cam Akers; Lionel Messi Exits Inter Miami Match
Olivia Wilde threw shade at Harry Styles, the Vikings traded for Cam Akers, Lionel Messi left an Inter Miami match with fatigue and more in the Roundup.
2023-09-21 19:18

Former Elon Musk employee speaks out on 'ridiclous' death of Neuralink's monkeys
A new report from Wired has alleged that Elon Musk's Neuralink - a neurotechnology company developing a brain-computer interface - euthanised the company's macaque subjects after they suffered various complications from the implant. The report comes after human-test subjects were recently approved for Neuralink's clinical trial. Elon Musk had claimed earlier this month that "no monkey has died as a result of a Neuralink implant, but public documents obtained by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (PCRM) and seen by Wired, suggest that the primate subjects suffered complications including "bloody diarrhoea, partial paralysis, and cerebral edema." Musk had acknowledged the deaths on September 10 on Twitter/X, denying the deaths were "a result of a Neuralink implant", and that researchers had selected subjects who were already "close to death." However an anonymous former employee called this "ridiculous" if not a "straight fabrication." However, the public records reviewed by Wired suggest a different story. The PCRM, a nonprofit aiming to abolish live animal testing, claim that Musk knew his comments about the primate subjects deaths "to be false". They write that investors deserve to hear the truth about the safety, "and thus the marketability," of Neuralink's product. A December 2019 experiment outlined in one of the documents mentioned a subject known as Animal 15. The documents said that the subject "began to press her head against the floor for no apparent reason" just days after receiving the implant. Her condition only worsened as she "began to lose coordination" and "would shake uncontrollably when she saw lab workers." Staff finally euthanised her months later. Last year, the PCRM filed a complaint with the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) alleging that Neuralink's practices violate the Animal Welfare Act. The US Department of Transportation is also investigating Neuralink over allegations contimanted devices that were removed from monkeys' brains were illegally transported. Indy100 have reached out to Neuralink for comment. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 17:55

A scientist has discovered when Earth's first continent was formed
A researcher has figured out that the Earth’s first continent was formed 3bn years ago, in a new paper that sheds fresh light on the early stages of the planet’s life. Jane Greaves, an astronomy professor in the School of Physics and Astronomy at Cardiff University in Wales, was examining continent formation on distant stars and planets. It is thought that exoplanets with continents that formed in a similar way to Earth’s are more likely to be habitable, and perhaps even contain alien life. In the process, she calculated when several distant planets’ continents were born, as well as those a little closer to home. Continents on Earth sit on top of the planet’s hot, viscous mantle. Heat from the inner core stops the mantle from solidifying. The reason the core is hot is because it contains radioactive elements that came from neutron star collisions billions of years ago such as forms of Uranium, Thorium and Potassium. By analysing how many materials like this are present on Earth and on other planets, we are also able to estimate when the continents formed. On Earth, that was about 9.5 billion years since the beginning of the universe. Meanwhile, in Greaves' sample, the first continents appeared 2bn years before Earth’s on the exoplanets of younger, so-called thin disk stars. Older, thick disk stars analysed in her work produced rocky planets with continents that appeared even earlier: about 4 to 5bn years before Earth’s. “The outlook seems very promising for finding rocky exoplanets with continents, given that nearby Sun-like stars have already produced a few candidate hosts,” she wrote. The study, “When were the First Exocontinents?” is published in Research Notes of the American Astronomical SocietySign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 17:25

Erik ten Hag reveals how Man Utd must respond to Andre Onana howler
Erik ten Hag insists that Manchester United need to "support" Andre Onana after his error for Bayern Munich's first goal in an eventual 4-3 win.
2023-09-21 17:21

Andre Onana takes blame for Bayern Munich loss with honest admission over Man Utd start
Andre Onana takes the blame for Man Utd's 4-3 loss to Bayern Munich & admits his start in England has been poor.
2023-09-21 16:53

Thailand's weakening baht not all bad for economy - PM
BANGKOK Thailand's central bank is monitoring the weak baht, which is not entirely bad for the economy and
2023-09-21 15:25
