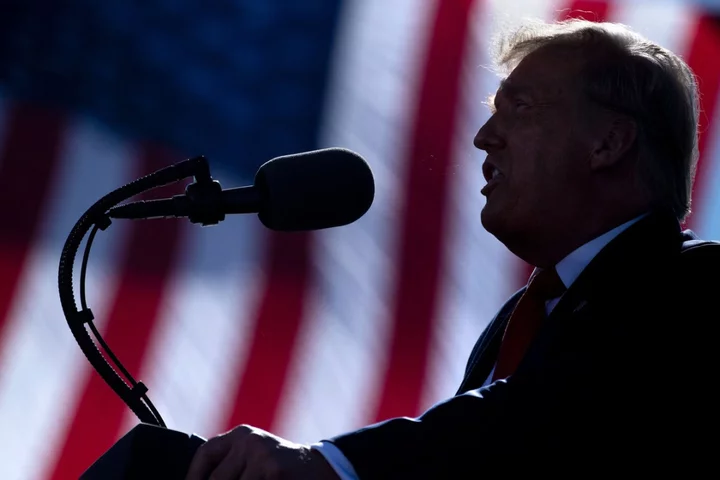
Donald Trump is expected to face seven counts in a federal indictment stemming from the US Department of Justice investigation into his possession of classified documents at his Mar-a-Lago property. Federal prosecutors are expected to charge him with the willful retention of national defense secrets in violation of the Espionage Act, making false statements, obstruction and witness tampering. Mr Trump will surrender, face arrest, and be formally charged in US District Court in Miami, as soon as next week, after a federal grand jury believed there was enough evidence to bring charges against him. A potential sentence, if convicted, could include decades in prison. The exact charges against Mr Trump have not been announced, and it is unclear whether an indictment against him will remain sealed until it is formally presented in federal court. Mr Trump said he was due in federal court in Miami at 3pm ET on Tuesday 13 June. He has repeatedly denied any wrongdoing and declared the investigations against him a “witch hunt”. An investigation from special counsel Jack Smith, who was appointed to lead the Justice Department’s probe into the former president’s alleged mishandling of documents after leaving the White House, reportedly is looking into whether his lawyers falsely certified that he returned classified records to the government, or whether he concealed them, illegally, and lied to his legal team. Federal prosecutors are expected to present compelling evidence that the former president knowingly and deliberately misled his attorneys about his retention of sensitive documents after leaving the White House in January 2021 after losing his re-election bid. Unauthorised retention of national security documents The frontrunner for the 2024 Republican presidential nomination will face charges under the Espionage Act, which the Justice Department invoked against now-former National Security Agency translator Reality Winner while Mr Trump was president in 2018. Julian Assange and Daniel Hale also were charged under the Espionage Act in 2019. Mr Trump is now expected to face that same charge, according to his lawyer James Trusty. One of the six sections under the Espionage Act, Section 793, prohibits “gathering, transmitting or losing” any “information respecting the national defence”. The use of Section 793, which does not make reference to classified information, is understood to be a strategic decision by prosecutors that has been made to short-circuit the former president’s ability to claim that he used his authority as president to declassify documents he removed from the White House and kept at his Florida property long after his term expired on 20 January 2021. That section of US criminal law is written in a way that could encompass Mr Trump’s conduct even if he was authorised to possess the information as president. It states that anyone who “lawfully having possession of, access to, control over, or being entrusted with any document … relating to the national defence” and “willfully” transmits such information in any way can face a prison sentence of up to 10 years. Obstruction A charge of obstruction in this case likely involves the “destruction, alteration, or falsification of records in federal investigations.” In a case before a jury, federal prosecutors must prove whether Mr Trump knowingly retained documents under the National Archives and Records Administration’s custody, and willfully defied the Justice Department’s subpoena for classified documents in his possession. A conviction includes a penalty of up to 20 years in prison. An additional charge of conspiracy, which would need to include another person in order to commit a crime, could carry a sentence of five years. Making false statements Mr Trump could face additional charges for making false statements, or allowing his legal team to make false statements, if prosecutors determine that he lied to law enforcement about the documents in his possession at the subject of the subpoenas against him. That could include an additional five-year sentence, if convicted. Witness tampering Section 1512 under Title 18 includes a broad prohibition against tampering with a witness, victim or informant involved in a federal investigation. It applies to matters before Congress as well as federal agencies and civil and criminal judicial proceedings, including grand jury proceedings. A conviction includes a maximum sentence of 20 years in prison. A federal indictment against Mr Trump arrives days after a last-ditch attempt by his legal team to convince Justice Department officials against charging him. Investigators launched a probe early last year after officials with the National Archives and Records Administration discovered more than 100 documents bearing classification markings while reviewing 15 boxes retrieved from Mr Trump’s Mar-a-Lago home. US Attorney General Merrick Garland appointed Mr Smith, a former war crimes prosecutor at The Hague, as special counsel to lead the probe. An indictment serves as a formal accusation, among a prosecutor’s first steps before a case can be brought to trial. Grand jurors heard evidence and testimony brought forward from prosecutors and witnesses they chose to present. In a trial, a jury will hear from defence attorneys. Following Mr Trump’s formal indictment, prosecutors will share evidence with his legal team and likely begin motions to dismiss the case. Andrew Feinberg contributed reporting Read More Trump indictment - live: Trump says he’s ‘an innocent man’ as he faces seven charges in documents case Read Trump’s furious reaction to federal indictment in classified documents case Trump has been indicted again: Here are all of the major lawsuits and investigations he is facing
Donald Trump is expected to face seven counts in a federal indictment stemming from the US Department of Justice investigation into his possession of classified documents at his Mar-a-Lago property.
Federal prosecutors are expected to charge him with the willful retention of national defense secrets in violation of the Espionage Act, making false statements, obstruction and witness tampering.
Mr Trump will surrender, face arrest, and be formally charged in US District Court in Miami, as soon as next week, after a federal grand jury believed there was enough evidence to bring charges against him. A potential sentence, if convicted, could include decades in prison.
The exact charges against Mr Trump have not been announced, and it is unclear whether an indictment against him will remain sealed until it is formally presented in federal court. Mr Trump said he was due in federal court in Miami at 3pm ET on Tuesday 13 June.
He has repeatedly denied any wrongdoing and declared the investigations against him a “witch hunt”.
An investigation from special counsel Jack Smith, who was appointed to lead the Justice Department’s probe into the former president’s alleged mishandling of documents after leaving the White House, reportedly is looking into whether his lawyers falsely certified that he returned classified records to the government, or whether he concealed them, illegally, and lied to his legal team.
Federal prosecutors are expected to present compelling evidence that the former president knowingly and deliberately misled his attorneys about his retention of sensitive documents after leaving the White House in January 2021 after losing his re-election bid.
Unauthorised retention of national security documents
The frontrunner for the 2024 Republican presidential nomination will face charges under the Espionage Act, which the Justice Department invoked against now-former National Security Agency translator Reality Winner while Mr Trump was president in 2018. Julian Assange and Daniel Hale also were charged under the Espionage Act in 2019.
Mr Trump is now expected to face that same charge, according to his lawyer James Trusty.
One of the six sections under the Espionage Act, Section 793, prohibits “gathering, transmitting or losing” any “information respecting the national defence”.
The use of Section 793, which does not make reference to classified information, is understood to be a strategic decision by prosecutors that has been made to short-circuit the former president’s ability to claim that he used his authority as president to declassify documents he removed from the White House and kept at his Florida property long after his term expired on 20 January 2021.
That section of US criminal law is written in a way that could encompass Mr Trump’s conduct even if he was authorised to possess the information as president. It states that anyone who “lawfully having possession of, access to, control over, or being entrusted with any document … relating to the national defence” and “willfully” transmits such information in any way can face a prison sentence of up to 10 years.
Obstruction
A charge of obstruction in this case likely involves the “destruction, alteration, or falsification of records in federal investigations.”
In a case before a jury, federal prosecutors must prove whether Mr Trump knowingly retained documents under the National Archives and Records Administration’s custody, and willfully defied the Justice Department’s subpoena for classified documents in his possession. A conviction includes a penalty of up to 20 years in prison.
An additional charge of conspiracy, which would need to include another person in order to commit a crime, could carry a sentence of five years.
Making false statements
Mr Trump could face additional charges for making false statements, or allowing his legal team to make false statements, if prosecutors determine that he lied to law enforcement about the documents in his possession at the subject of the subpoenas against him. That could include an additional five-year sentence, if convicted.
Witness tampering
Section 1512 under Title 18 includes a broad prohibition against tampering with a witness, victim or informant involved in a federal investigation.
It applies to matters before Congress as well as federal agencies and civil and criminal judicial proceedings, including grand jury proceedings. A conviction includes a maximum sentence of 20 years in prison.
A federal indictment against Mr Trump arrives days after a last-ditch attempt by his legal team to convince Justice Department officials against charging him.
Investigators launched a probe early last year after officials with the National Archives and Records Administration discovered more than 100 documents bearing classification markings while reviewing 15 boxes retrieved from Mr Trump’s Mar-a-Lago home. US Attorney General Merrick Garland appointed Mr Smith, a former war crimes prosecutor at The Hague, as special counsel to lead the probe.
An indictment serves as a formal accusation, among a prosecutor’s first steps before a case can be brought to trial.
Grand jurors heard evidence and testimony brought forward from prosecutors and witnesses they chose to present. In a trial, a jury will hear from defence attorneys.
Following Mr Trump’s formal indictment, prosecutors will share evidence with his legal team and likely begin motions to dismiss the case.
Andrew Feinberg contributed reporting
Read More
Trump indictment - live: Trump says he’s ‘an innocent man’ as he faces seven charges in documents case
Read Trump’s furious reaction to federal indictment in classified documents case
Trump has been indicted again: Here are all of the major lawsuits and investigations he is facing