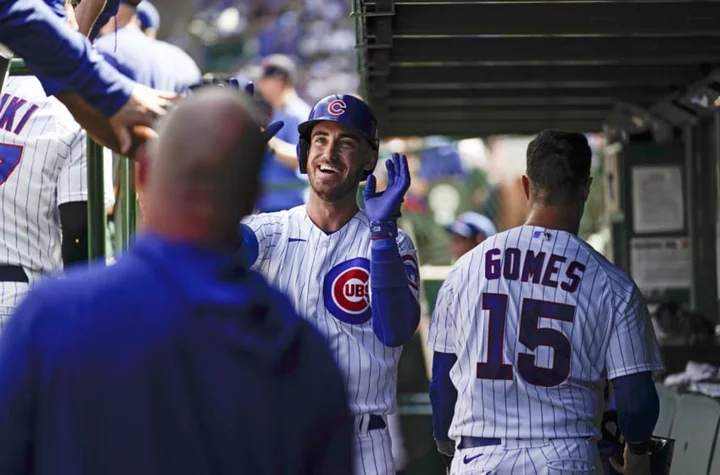

Cubs Rumors: Cody Bellinger buzz, Pete Alonso trade, David Ross hot seat
The Cubs still have high hopes for the rest of 2023, but there's plenty to discuss in regards to their offseason moves.
2023-08-24 01:55

Keith Urban expresses surprise over the unexpected success of Nicole Kidman's AMC Theatres ad
The country star spoke about his wife's 2021 ad for the company and explained why she initially decided to be a part of it
2023-11-26 02:16

A bison gores a woman near lakeside cabins in Yellowstone National Park, seriously injuring her
A bison gored a 47-year-old Arizona woman Monday morning in Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming, leaving her with significant injuries to her chest and abdomen, park officials said.
2023-07-18 06:30

Eni chief executive says plan for pipeline to move gas to Cyprus 'part of our discussion'
The chief executive of the Eni energy company says Cyprus-Israeli plans for a pipeline to move offshore natural gas from those two countries to Cyprus are “part of our discussion” with the Cypriot government
2023-06-28 00:56

Former Wells Fargo exec settles SEC fraud charges, to pay $3 million
By Kanishka Singh WASHINGTON (Reuters) -The former head of Wells Fargo & Co's retail bank agreed to pay a $3
2023-05-31 06:26

Marketmind: Business brakes in June swoon, dollar jumps
A look at the day ahead in U.S. and global markets from Mike Dolan Just as world stock prices raced
2023-06-23 18:26

Goal-scoring defender Souttar hailed as Australia's 'cheat code'
Harry Souttar has been hailed as a "cheat code" after the towering defender scored his 10th goal for Australia in the 1-0 World...
2023-11-22 12:20
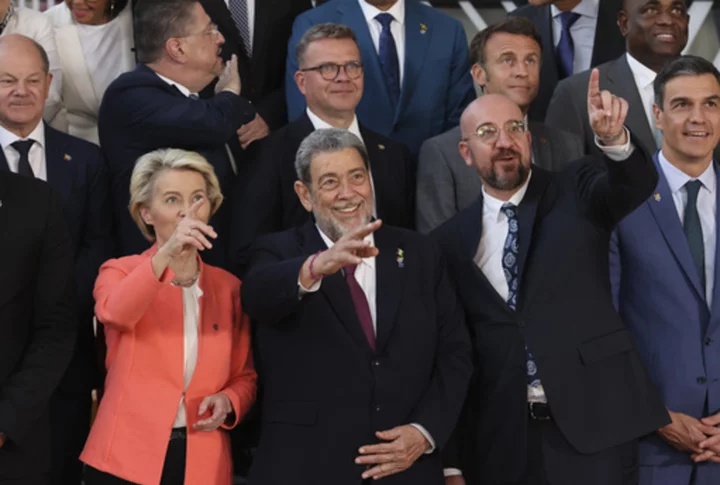

Divisions over the Ukraine war cause a rift at the EU-LatAm summit that was supposed to be a love-in
High anxiety has set in on the closing day of a summit between European Union and Latin American leaders
2023-07-18 16:49
How to unblock UK Netflix from anywhere in the world
TL;DR: ExpressVPN is the best VPN for Netflix. Unblock UK Netflix from anywhere in the
2023-10-28 12:48

‘GMA’ meteorologist Ginger Zee trolled for her coverage of Canadian wildfires
Ginger Zee reported the impact of the fire that engulfed Yellowknife in Canada right after the Maui wildfires in Hawaii
2023-08-19 13:18

Cut down on costs and e-waste with a refurbished iPad Air, only $180
TL;DR: As of July 8, get this refurbished iPad Air with 32GB storage and a
2023-07-08 17:28
Geologists have figured out how to locate diamond ‘explosions’
A group of geologists has recently achieved a breakthrough in identifying potential sites for the formation of diamonds. Diamonds, the hardest naturally occurring material we have found, originate under the extreme conditions of immense pressure and high temperatures deep within the Earth's interior. These precious gems are occasionally pushed to the surface in molten rock formations known as kimberlite. However, there are currently two competing theories regarding what is responsible for this rush of kimberlite which brings diamonds to the surface. In a recent study, these theories were closely examined by a research team. In a piece for The Conversation study author and Associate Professor in Earth Science at the University of Southampton, Thomas Gernon explained: “one proposes that kimberlite magmas exploit the ‘wounds’ created when the Earth’s crust is stretched or when the slabs of solid rock covering the Earth - known as tectonic plates - split up.” “The other theory involves mantle plumes, colossal upwellings of molten rock from the core-mantle boundary, located about 2,900km [1,802] beneath the Earth’s surface.” However, neither of these theories adequately explains how magma manages to find its way through the Earth's crust, or the specific composition of the resulting kimberlite. By employing statistical analysis and machine learning, the team analysed the breakup of continents and its correlation with kimberlite formation. Their findings indicated that the majority of kimberlite volcanoes erupt 20 to 30 million years after tectonic breakup. “It also added a major clue,” Gernon explained. “Kimberlite eruptions tend to gradually migrate from the continental edges to the interiors over time at a rate that is uniform across the continents.” Delving deeper into their investigation through computer-generated models, the team ultimately concluded that diamond eruptions stem from a "domino effect." As continents gradually drift apart from each other, they generate rifts of thinned crust. As this happens, regions of thick, cold rock descend into the hot magma beneath, inducing an upsurge of the mantle, which in turn triggers a similar flow in nearby continents. Gernon elaborated on the team's findings, saying, "Various other results from our computer models then advance to show that this process can bring together the necessary ingredients in the right amounts to trigger just enough melting to generate gas-rich kimberlites,” Gernon explained. “Once formed, and with great buoyancy provided by carbon dioxide and water, the magma can rise rapidly to the surface carrying its precious cargo.” Moreover, the same methodology could potentially be employed to locate diamonds and other rare elements. “The processes triggering the eruptions that bring diamonds to the surface appear to be highly systematic,” Gernon siad. “They start on the edges of continents and migrate towards the interior at a relatively uniform rate.” The study is published in the journal Nature. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 00:25
You Might Like...

Dutch government to press ahead with Schiphol flight cap as airlines protest

Taylor Swift news diary: Pop star postpones Rio concert due to extreme weather conditions

Crayola, beloved for its crayons, is now selling flowers

Utah woman accused of killing husband before writing book about grief sued for over $13 million
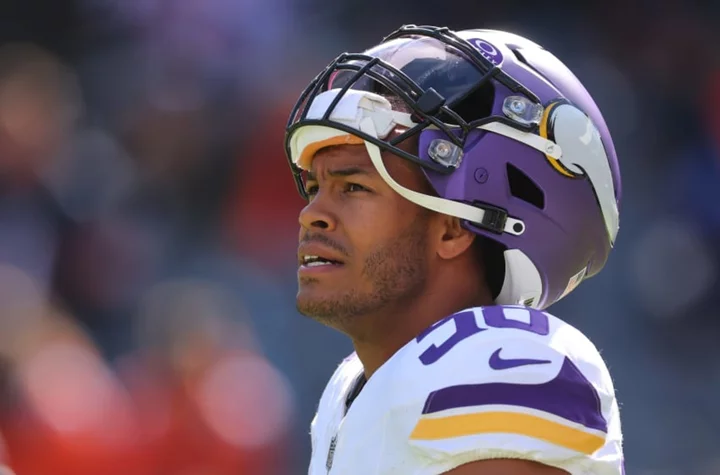

Vikings get long-awaited reunion with former first rounder after Jordan Hicks injury
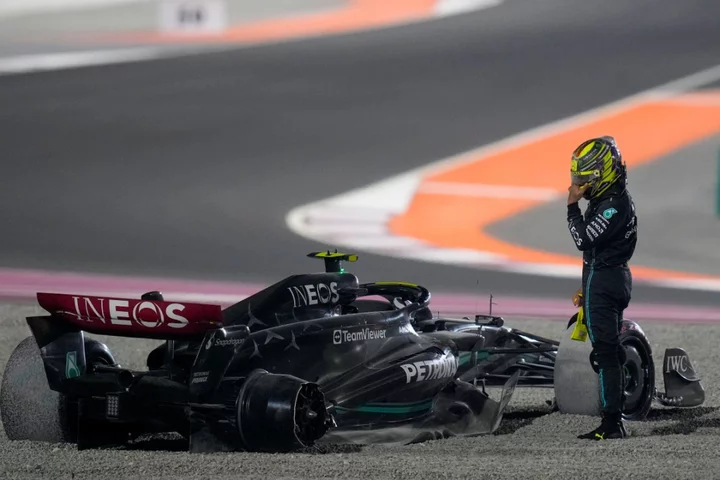

Lewis Hamilton crashes out after first-corner collision with George Russell
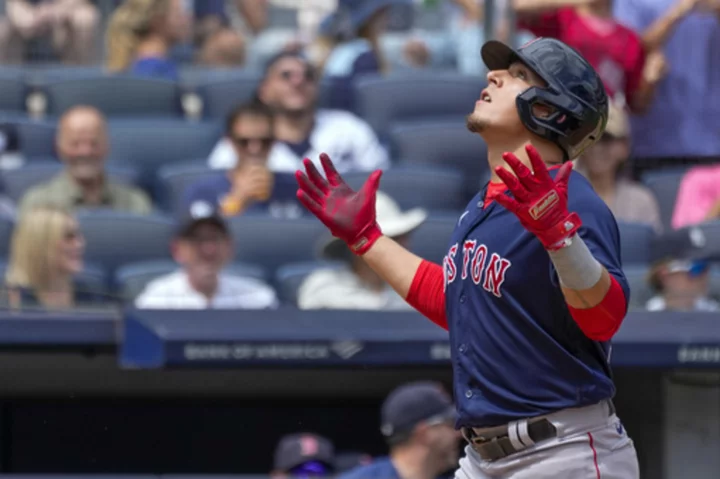

Urias, first Red Sox player to hit grand slams on consecutive pitches, leads Boston over Yankees

German economy to shrink in 2023, govt says
