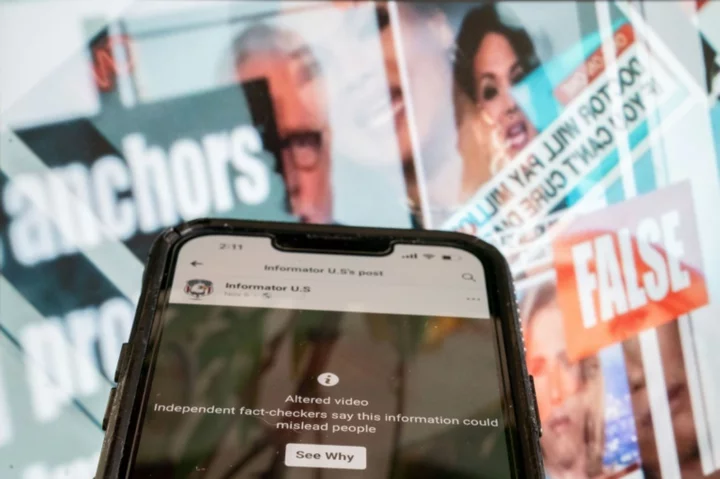
In a Facebook video viewed by thousands, CNN’s Wolf Blitzer appears to hawk a diabetes drug. In another, "CBS Mornings" host Gayle King seems to endorse weight loss products.
But the clips are doctored -- the latest in a rash of deepfakes that hijack images of trusted news personalities in spurious ads, undermining confidence in the news media.
Similar social media posts in recent months have targeted Fox News personality Jesse Watters, CBC host Ian Hanomansing and BBC stars Matthew Amroliwala and Sally Bundock.
In some cases, the journalists have used their own accounts to push back.
"I've never heard of this product or used it! Please don't be fooled by these AI videos," King said on Instagram in October.
After seeing clips of himself supposedly promoting cannabis products, CNN medical correspondent Sanjay Gupta also posted a warning: "These scams have nothing to do with me... my primary concern is for your health, and I do worry you could be harmed if you take these products."
The manipulated videos push everything from unproven treatments to investment schemes -- many promising "guaranteed income" or access to coveted shares. Some also use altered footage of billionaire Elon Musk, founder of Tesla and SpaceX.
Some include links to investment schemes, unapproved products or unrelated e-commerce websites that disappear after several days.
Meta, the parent company of Facebook and Instagram, has banned deepfakes since early 2020, with some exceptions for parody and satire. Other platforms have similar policies.
But such clips -- many of which AFP has fact-checked -- are still spreading online.
- Voice cloning -
"I have seen a rise in these types of videos where a person's voice is cloned from as little as two minutes of their voice, and then any other video of them is modified so that the mouth is consistent with the new audio," Hany Farid, a professor at the University of California-Berkeley specializing in digital forensics, previously told AFP.
Some deepfakes are easy to detect due to their poor quality. However, experts warn the technology is improving -- and TV personalities are easy targets because there is ample footage available to train AI programs.
The trend is worrisome because "people have grown to trust a newscaster like their friend," according to Andrea Hickerson, dean of journalism at the University of Mississippi.
"It's really dangerous because people aren't expecting misinformation and disinformation to come in that way," she said. "It looks like a traditional news outlet."
– 'Crisis of trust' –
AI-manipulated content has become a growing part of investment fraud in particular, which cost Americans some $3.8 billion in 2022, according to the Federal Trade Commission.
Such schemes have reportedly targeted victims in Canada, Australia and other countries. In some cases, they cost individuals tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars.
"The schemes are becoming increasingly complex as criminals fuse traditional tactics with online scams involving cryptocurrencies and artificial intelligence," said attorney Chase Carlson in a blog post earlier this year.
Americans are increasingly worried about the use of AI online -- particularly when it comes to politics.
More than 50 percent expect such falsehoods to affect the outcome of the 2024 election, according to a September poll from Axios and business intelligence firm Morning Consult.
AFP has previously debunked deepfake videos of US President Joe Biden announcing a military draft and former secretary of state Hillary Clinton endorsing Florida Governor Ron DeSantis for president.
Rebekah Tromble, director of the Institute for Data, Democracy and Politics at The George Washington University, said this kind of misinformation "plays into larger concerns about trust in information and trust in institutions."
Only about a third of Americans have a "great deal" or "fair amount" of confidence in the news media, according to an October Gallup poll, matching a low recorded in 2016.
Many of the manipulated clips circulating online are low-quality "cheapfakes," Tromble noted, but they still contribute to "a crisis of trust." She urged news consumers to use caution before sharing such posts on social media.
"There's still a lot of good information out there, and with a healthy dose of skepticism we can snuff out the things that are disinformation," she said.
rl/mgs/df/bgs