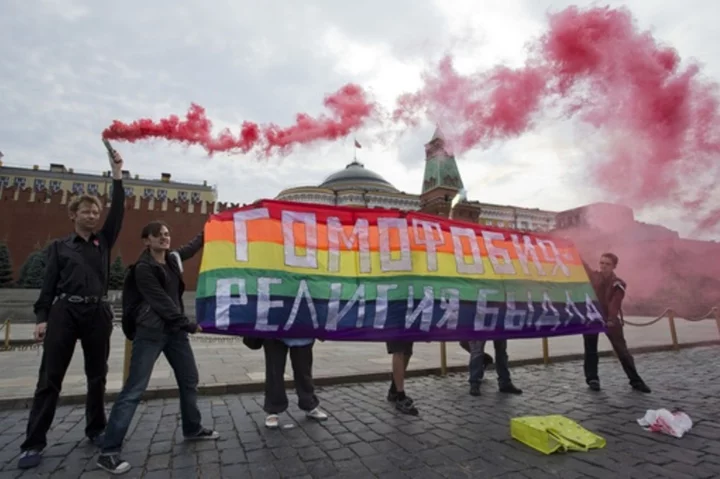TALLINN, Estonia (AP) — Russian lawmakers gave initial approval Wednesday to a bill that would outlaw gender transitioning procedures in yet another blow to the country's beleaguered LGBTQ+ community.
Senior lawmaker Pyotr Tolstoy, who is among the bill’s sponsors, has said it is intended to “protect Russia with its cultural and family values and traditions and to stop the infiltration of the Western anti-family ideology.”
Russia's LGBTQ+ community has been under growing pressure for a decade as President Vladimir Putin and the Russian Orthodox Church embarked on a campaign to preserve what they deem the country’s “traditional values.”
The bill bans any “medical interventions aimed at changing the sex of a person,” as well as changing one’s gender in official documents and public records.
Russian transgender people and LGBTQ+ rights advocates contacted by The Associated Press described the measure as a grim development.
“We knew that they didn’t like us here, but to go absolutely against human rights, against the existing laws even," said Maxim, a 29-year-old transgender activist who spoke on condition of anonymity because of safety concerns.
The only option for those seeking to transition through medical care or changing their gender in documents would be to leave the country, according to human rights lawyer Max Olenichev, who works with the Russian LGBTQ+ community. “Neither medical, nor legal transitioning will be possible without changing the country of residence.”
The bill must receive three readings by Russia’s lower house of parliament, the State Duma, but there is little doubt it will pass because about 400 members of the 450-seat house signed it, including the house speaker and the leaders of all political factions.
The independent Russian news outlet Meduza reported that such a massive show of unity has happened only three times before under Putin, most recently when 385 Duma members signed on to a bill last year to ban “propaganda of nontraditional sexual relations” among adults.
That initiative was quickly rubber-stamped, and by December 2022, any positive or even neutral representation of LGBTQ+ people in movies, literature, or media was outlawed. The bill severely restricting trans rights came just a few months after that.
The crackdown on the LGBTQ+ community started well before last year, however. Maria Sjödin, executive director of the Outright international LGBTQ+ rights group, told AP in an interview that the situation in Russia has been deteriorating “over quite a long period of time, coming up on at least 10 years.”
In 2013, the Kremlin adopted the first legislation restricting LGBTQ+ rights, known as the “gay propaganda” law that banned any public endorsement of “nontraditional sexual relations” among minors. In 2020, Putin pushed through a constitutional reform that outlawed same-sex marriage.
But the Kremlin has ramped up its rhetoric about protecting “traditional values” from what it called the West's “degrading” influence after sending its troops into Ukraine last year, in what rights advocates saw as an attempt to legitimize the war.
“Do we really want to have here, in our country, in Russia, ‘Parent No. 1, No. 2, No. 3’ instead of 'mom' and ‘dad?’" Putin said in September at a ceremony during which four Ukrainian regions were formally annexed by Moscow. "Do we really want perversions that lead to degradation and extinction to be imposed in our schools from the primary grades?”
___
Associated Press religion coverage receives support through the AP’s collaboration with The Conversation US, with funding from Lilly Endowment Inc. The AP is solely responsible for this content.