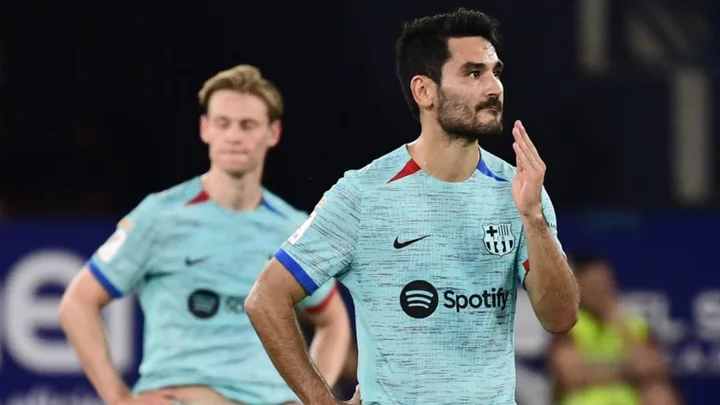

3 ways Barcelona could line up without injured Frenkie de Jong
The options for Xavi to set up his Barcelona midfield without injured starter Frenkie de Jong.
2023-09-26 20:19

How did Young Capone die? Rapper, 35, found dead after going missing
Rapper Young Capone was found dead in Marquette Park after he went missing from Chicago
2023-08-18 11:45

Fans pray for Anna Cardwell as she poses with Eldridge Toney after Mama June revealed daughter's cancer is 'terminal': 'You got this'
Anna Cardwell has lost all her hair after Mama June revealed her cancer is 'terminal'
2023-07-15 13:24

Jets QB Aaron Rodgers announces he had surgery to repair torn Achilles tendon
New York Jets quarterback Aaron Rodgers says on Instagram he had surgery to repair his torn left Achilles tendon on Wednesday
2023-09-15 09:59

'Real-life mermaid': Internet goes gaga over Addison Rae as she shares glimpse of her summer adventures
Social media sensation Addison Rae's Instagram posts during her summer vacation had fans comparing her to a 'real-life mermaid'
2023-09-03 12:56

'The Five' host Tulsi Gabbard warns Michelle Grisham's gun control efforts could harm Democratic Party
'The Five' hosts had discussed Michelle Grisham's gun ban attempts being blocked by the Attorney General and the Sheriff from ABQ
2023-09-18 12:17
Who is FaZe Rain? Grace Van Dien and FaZe Clan co-founder's ongoing feud explained
FaZe Rain took to social media, announcing Grace Van Dien's joining FaZe Clan before the official announcement and the matter blew up
2023-05-30 16:29
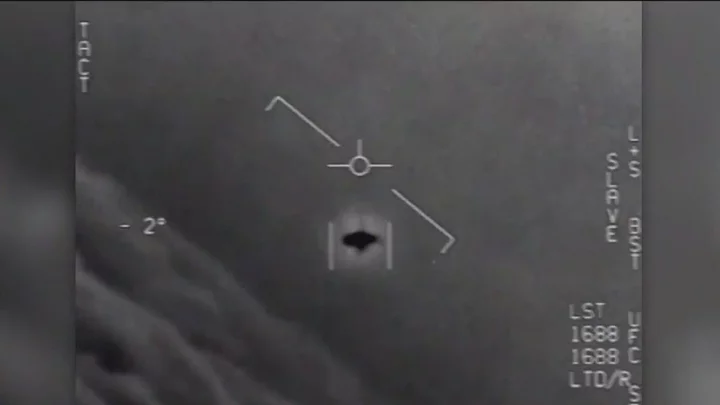

Local baffled by mysterious 'UFO' hovering in the sky
A mysterious spinning ‘UFO’ has been spotted in the night sky by a stunned local. The brightly illuminated object is seen spinning in the air, but it appears to hover above a mountain. The shocked onlooker zooms in on the mysterious aircraft while saying in wonder: “It’s moving.” The hovering UFO was filmed in the village of Honorato Vásquez, Ecuador, on Tuesday (9 Sept) evening. The local authorities have yet to respond to claims that the object was from outer space. One local said: “I believe it.” Manuel wrote: “Those crazy aliens.” Yet Eddy joked: “In that drone there, you wouldn’t even be able to fit two-quarters of a Martian!” It followed an alleged aerial battle between military personnel and several alien spaceships in Argentina this month. Scared locals claimed that the military base was attacked by four black triangular-shaped UFOs. Scores of residents gathered outside the Commander Espora Air Naval Base near Bahía Blanca, Buenos Aires, as thunderous noises sounded from within the perimeter walls. The Commission for the Study of UFO Phenomena of the Argentine Republic, an organisation dedicated to investigating alleged alien sightings, claimed to have information that there were four UFOs seen attacking the military base. The group said the alien spacecrafts were black and triangular in shape and that Argentine troops fired at them with anti-aircraft weapons. Group spokesperson Andrea Pérez Simondini said witnesses saw “four lights entering the territory from across the ocean before taking a strategic position over one of the buildings where ammunition is stored”. However, the military authorities have denied that the base was under attack and claimed that the videos were faked by unscrupulous locals. Navy spokesperson Captain Germán Luis Zarralanga said their Sikorsky SH-3 Sea King helicopter was taking part in a training exercise that night, but was not involved in any kind of altercation with other aircraft. When discussing the social media footage, the spokesperson said: “It’s an edit. I don’t know what their intentions were. “Airport security and airport workers did not report seeing anything, and everyone at the base was sleeping except for the person piloting the helicopter. There was no type of special activity, no tactical manoeuvres, just a normal helicopter training flight, nothing related to ammunition.” One local commented: “Incredible! How many UFOs? I can't believe it! Amazing. An interplanetary war has begun.” Another said: “Are you telling me that it was one of the first-ever confrontations between humans and UFOs and we shot them down?” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-24 18:52
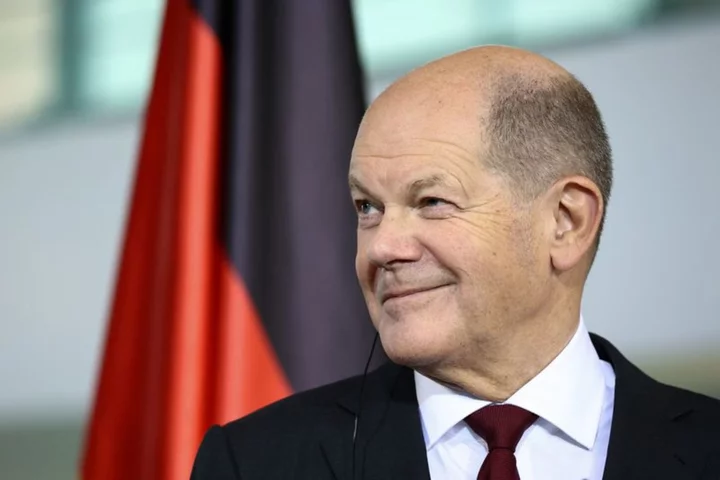

German government, car industry to strategise on goal of 15 million EVs by 2030
BERLIN German Chancellor Olaf Scholz will convene car executives with ministerial leaders, energy executives and unions on Monday
2023-11-24 21:28

Election tribunal rejects Peter Obi's presidential election challenge in Nigeria
One of President Bola Tinubu's opponents failed to prove allegations of rigging, the court rules.
2023-09-07 00:57
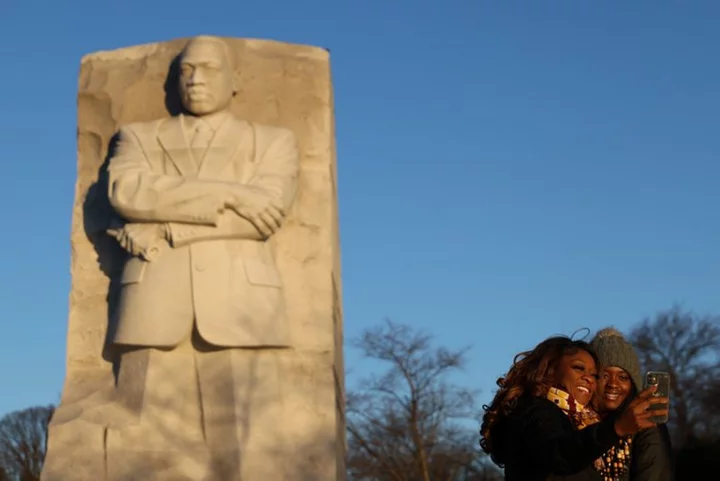

Sixty years after King's 'dream' speech, thousands gather in Washington
By Rachel Nostrant Thousands of Americans will converge on Washington on Saturday to commemorate the 60th anniversary of
2023-08-26 19:18
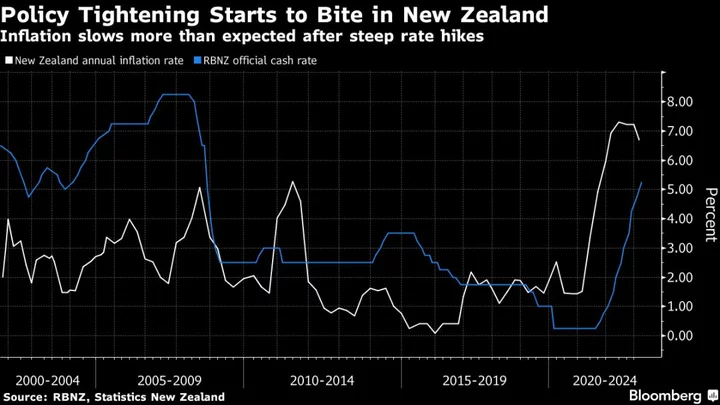
US Inflation Set to Stay Firm in Challenge for the Fed
The latest marker of underlying US price pressures will offer little hope of settling the debate among Federal
2023-05-21 04:23
You Might Like...
Gunfire erupts at prominent Shiite shrine in southern Iran, wounding at least 4 people
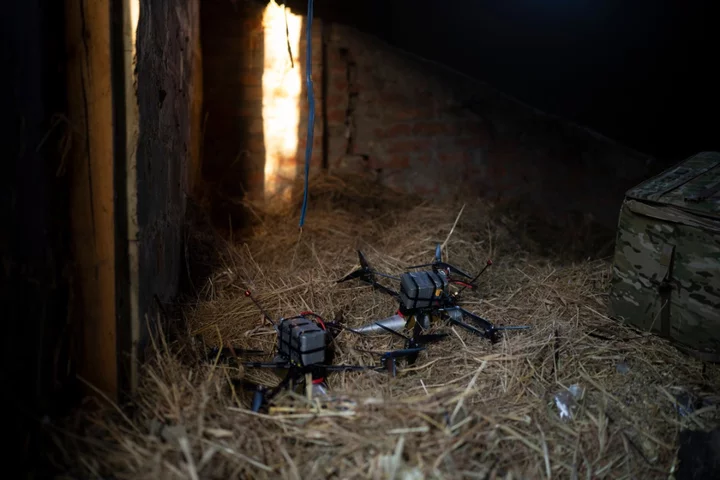

Ukraine ‘hits power substation’ in drone attacks on Russian border regions

Swedish Fund Alecta Faces Prosecutor Probe on Its Property Stake
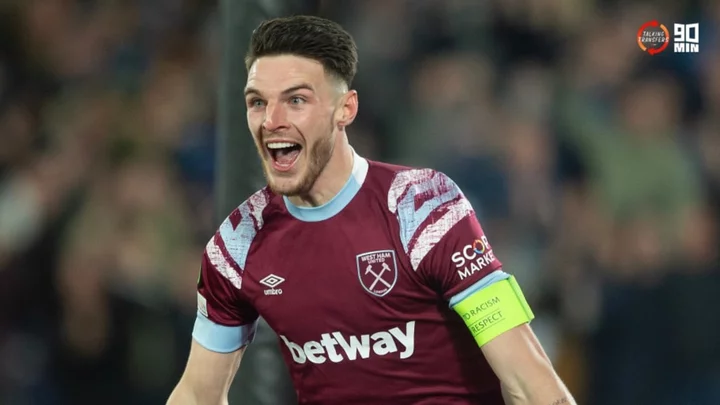

Arsenal make British record bid worth £105m for Declan Rice

Did Matthew Perry have children? Late 'Friends' star once said 'he'd be great' at being a father

‘Vanderpump Rules’ fans slam Ariana Madix as she shades ex Tom Sandoval with 'Single AF Cocktails' book
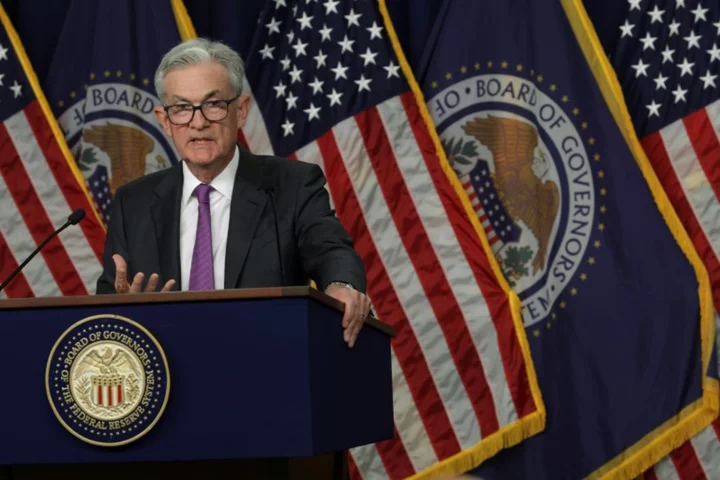

US Fed likely to pause rate hikes and raise growth forecast
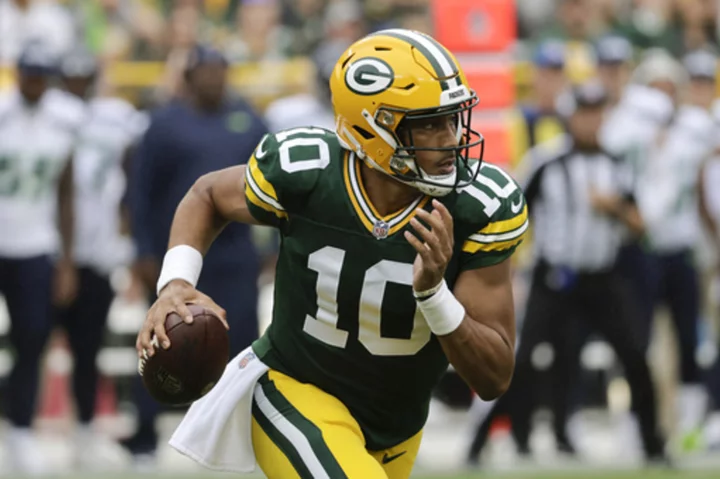

Love connects with Watson on TD pass as Packers close preseason with 19-15 victory over Seahawks
